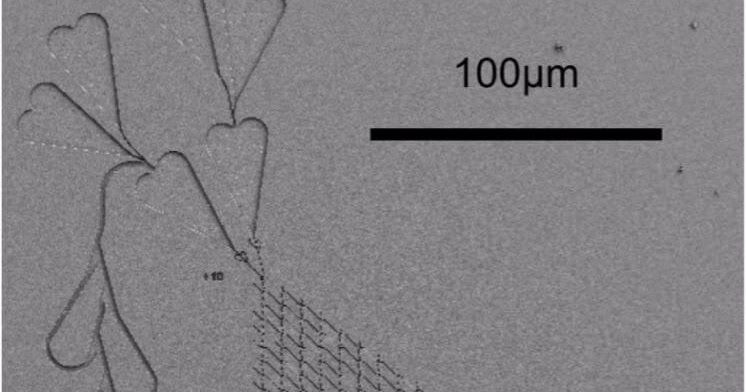
Electronic computers are extremely powerful at performing a high number of operations at very high speeds, sequentially. However, they struggle with combinatorial tasks that can be solved faster if many operations are performed in parallel.
The EU Horizon 2020 has launched Bio4Comp, a five-year €6.1M project to build more powerful and safer biocomputers that could outperform quantum computing.
The Bio4Comp project has the ambitious goal of building a computer with greater processing speed and lower energy consumption than any of the most advanced computers existing today. Ultimately, this could translate into enabling large, error-free security software to be fast enough for practical use, potentially wiping out all current security concerns.
A total of €6.1M have been awarded to an European team of researchers from TU Dresden, Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft, Lund University, Linnaeus University and Bar Ilan University, as well as the British company Molecular Sense.