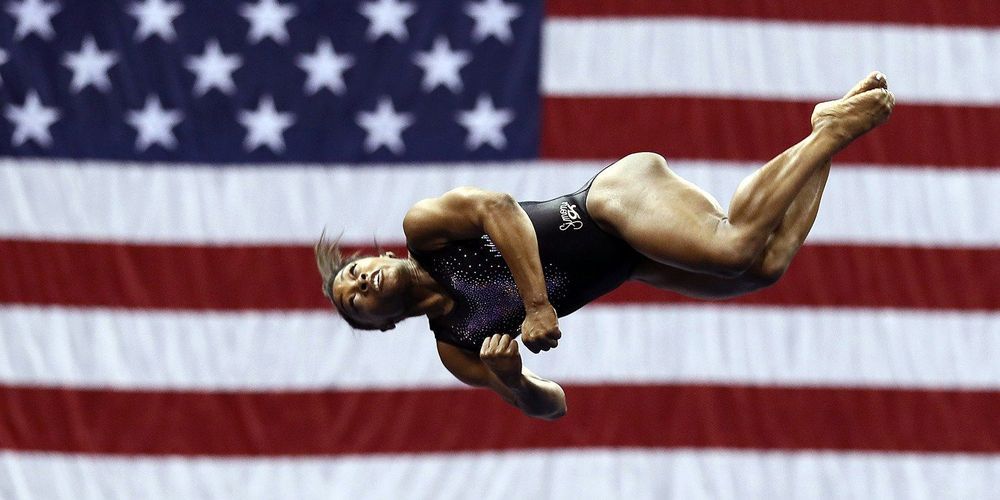
What. The. Heck. Did you see that? Simone Biles appears to defy the laws of physics with this epic tumbling pass from the 2019 US Gymnastics Championships. It’s called a triple-double. That means she rotates around an axis going through her hips twice while at the same time rotating about an axis going from head to toe THREE times. Yes, it’s difficult—but it doesn’t defy physics, it uses physics.
Let’s go over the three key parts of this move. You can follow the physics, but I don’t recommend trying this triple-double in your backyard.