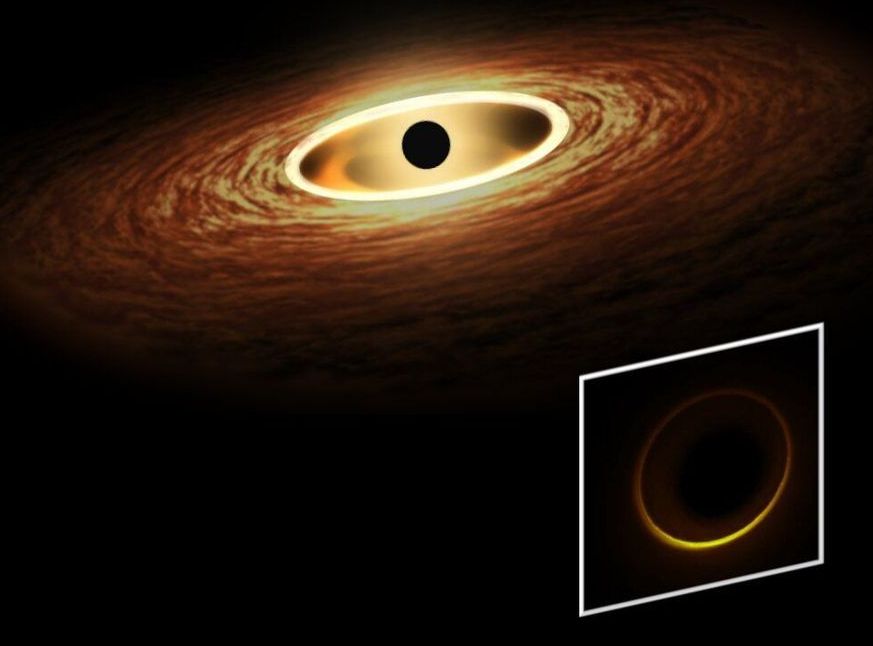
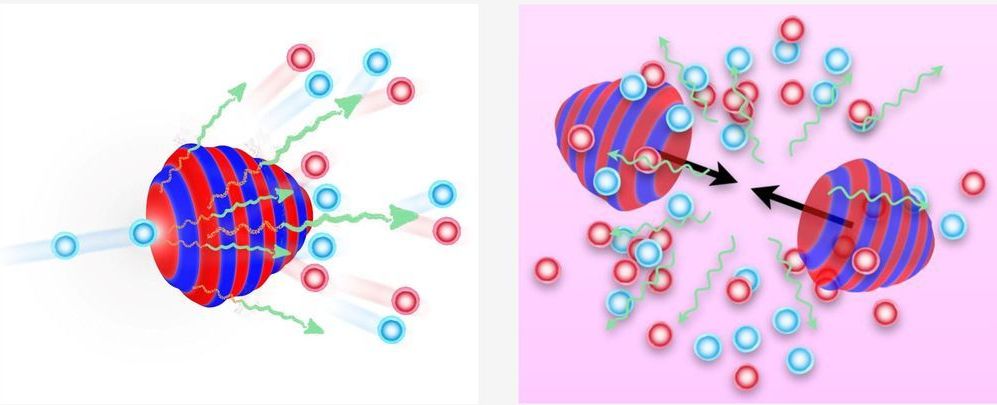
Black holes, regions in space with such an intense gravitational field that no matter or radiation can escape from them, are among the most mysterious and fascinating cosmological phenomena. Over the past five years or so, astrophysicists collected the first observations of the strong gravitational forces around black holes.
The LIGO-Virgo collaboration was able to detect gravitational waves around these celestial objects using some of the most advanced gravitational-wave detectors in the world. Meanwhile, the Event Horizon Telescope research group captured the very first image of a black hole shadow.
While both these observations are highly promising and captivating, neither of them is likely to unveil the event horizon, the boundary defining the specific region in space around a black hole from which nothing can escape. Nonetheless, they should contain a signature pointing to a neighboring region just outside of the event horizon, wherein light is bent so strongly that its path closes over itself and forms circular orbits known as light rings.