If researchers have detected an axion particle forged inside the sun, the potentially “Nobel Prize-winning finding” would defy the laws of physics.
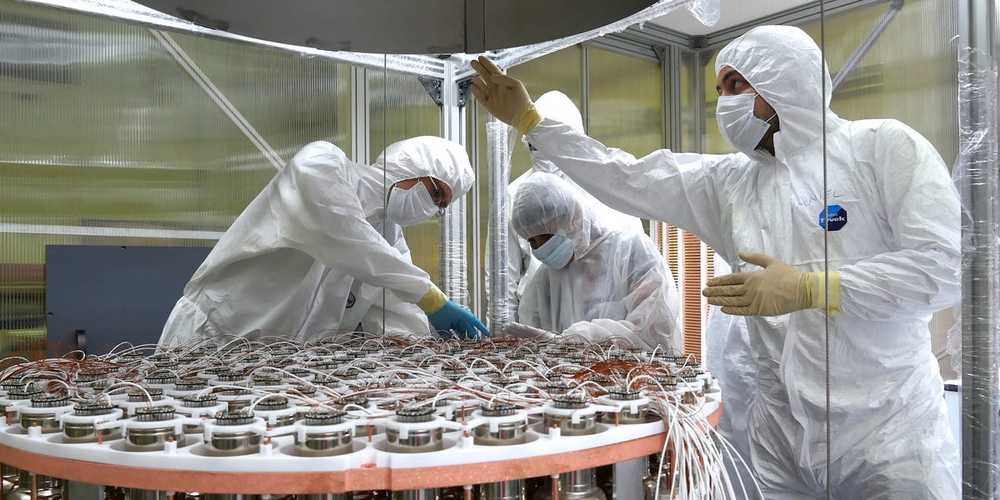


Ultracold atoms trapped in appropriately prepared optical traps can arrange themselves in surprisingly complex, hitherto unobserved structures, according to scientists from the Institute of Nuclear Physics of the Polish Academy of Sciences in Cracow. In line with their most recent predictions, matter in optical lattices should form tensile and inhomogeneous quantum rings in a controlled manner.
An optical lattice is a structure built of light, i.e. electromagnetic waves. Lasers play a key role in the construction of such lattices. Each laser generates an electromagnetic wave with strictly defined, constant parameters which can be almost arbitrary modified. When the laser beams are matched properly, it is possible to create a lattice with well known properties. By overlapping of waves, the minima of potential can be obtained, whose arrangement enables simulation of the systems and models well-known from solid state physics. The advantage of such prepared systems is the relatively simple way to modify positions of these minima, what in practice means the possibility of preparing various type of lattices.
“If we introduce appropriately selected atoms into an area of space that has been prepared in this way, they will congregate in the locations of potential minima. However, there is an important condition: the atoms must be cooled to ultra-low temperatures. Only then will their energy be small enough not to break out of the subtle prepared trap,” explains Dr. Andrzej Ptok from the Institute of Nuclear Physics of the Polish Academy of Sciences (IFJ PAN) in Cracow.
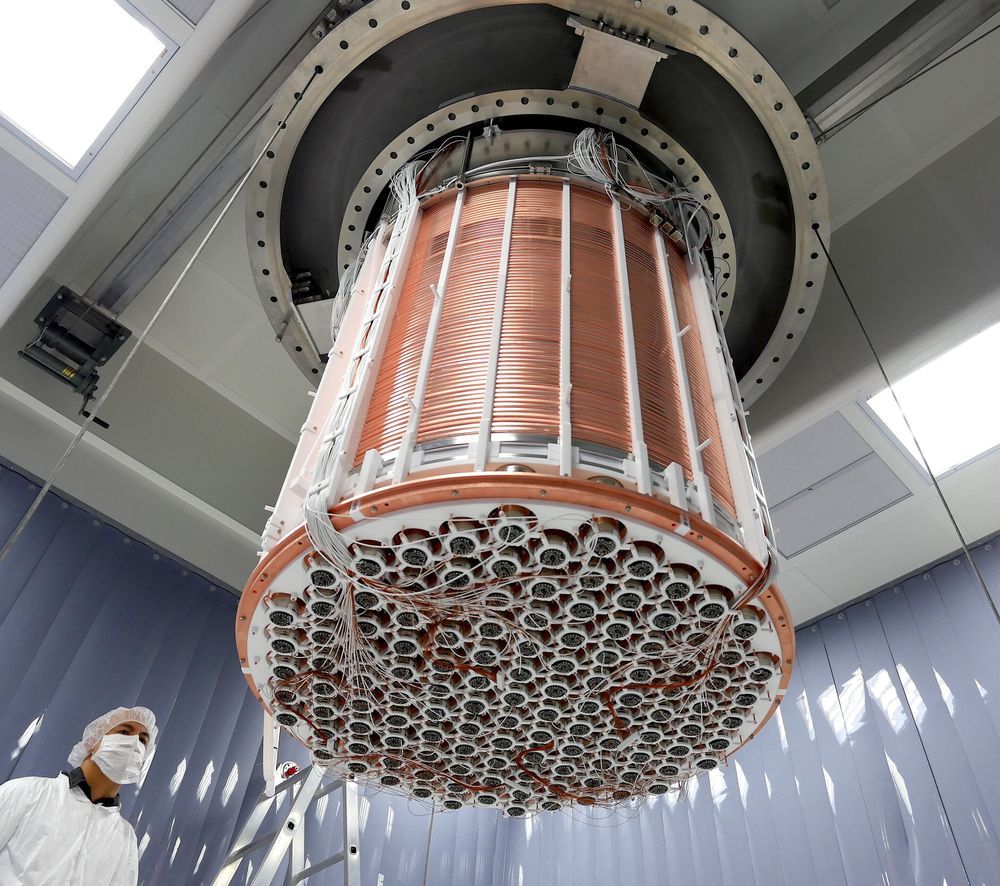

Scientists from the international XENON collaboration, an international experimental group including the Kavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe (Kavli IPMU), University of Tokyo; the Institute for Cosmic Ray Research (ICRR), University of Tokyo; the Institute for Space-Earth Environmental Research (ISEE), Nagoya University; the Kobayashi-Maskawa Institute for the Origin of Particles and the Universe (KMI), Nagoya University; and the Graduate School of Science, Kobe University, announced today that data from their XENON1T, the world’s most sensitive dark matter experiment, show a surprising excess of events. The scientists do not claim to have found dark matter. Instead, they have observed an unexpected rate of events, the source of which is not yet fully understood. The signature of the excess is similar to what might result from a tiny residual amount of tritium (a hydrogen atom with one proton and two neutrons), but could also be a sign of something more exciting—such as the existence of a new particle known as the solar axion or the indication of previously unknown properties of neutrinos.
XENON1T was operated deep underground at the INFN Laboratori Nazionali del Gran Sasso in Italy, from 2016 to 2018. It was primarily designed to detect dark matter, which makes up 85% of the matter in the universe. So far, scientists have only observed indirect evidence of dark matter, and a definitive, direct detection is yet to be made. So-called WIMPs (Weakly Interacting Massive Particles) are among the theoretically preferred candidates, and XENON1T has thus far set the best limit on their interaction probability over a wide range of WIMP masses. In addition to WIMP dark matter, XENON1T was also sensitive to different types of new particles and interactions that could explain other open questions in physics. Last year, using the same detector, these scientists published in Nature the observation of the rarest nuclear decay ever directly measured.
The XENON1T detector was filled with 3.2 tons of ultra-pure liquefied xenon, 2.0 t of which served as a target for particle interactions. When a particle crosses the target, it can generate tiny signals of light and free electrons from a xenon atom. Most of these interactions occur from particles that are known to exist. Scientists therefore carefully estimated the number of background events in XENON1T. When data of XENON1T were compared to known backgrounds, a surprising excess of 53 events over the expected 232 events was observed.
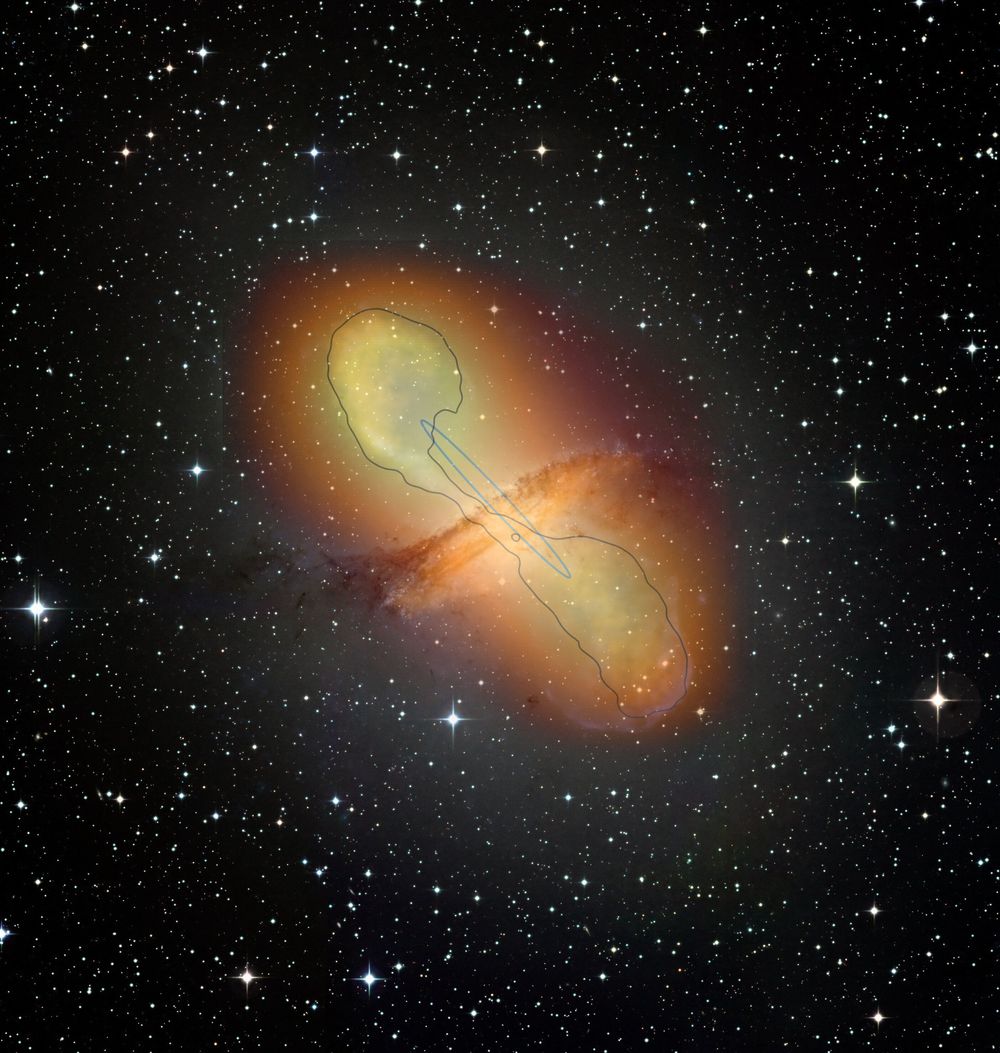

An international collaboration bringing together over 200 scientists from 13 countries has shown that the very high-energy gamma-ray emissions from quasars, galaxies with a highly energetic nucleus, are not concentrated in the region close to their central black hole, but in fact, extend over several thousand light-years along jets of plasma. This discovery shakes up current scenarios for the behavior of such plasma jets. The work, published in the journal Nature on June 18, 2020, was carried out as part of the H.E.S.S collaboration, involving in particular the CNRS and CEA in France, and the Max Planck society and a group of research institutions and universities in Germany.
Over the past few years, scientists have observed the universe using gamma rays, which are very high-energy photons. Gamma rays, among the cosmic rays that constantly bombard the Earth, originate from regions of the universe where particles are accelerated to huge energies unattainable in human-built accelerators. Gamma rays are emitted by a wide range of cosmic objects such as quasars, which are active galaxies with a highly energetic nucleus.
The intensity of the radiation emitted from these systems can vary over very short timescales of up to one minute. Scientists therefore believed that the source of this radiation was very small and located in the vicinity of a supermassive black hole, which can have a mass several billion times that of the sun’s. The black hole is thought to gobble up the matter spiraling down into it and eject a small part of it in the form of large jets of plasma at relativistic speeds, close to the speed of light, thus contributing to the redistribution of matter throughout the universe.



Circa 2014
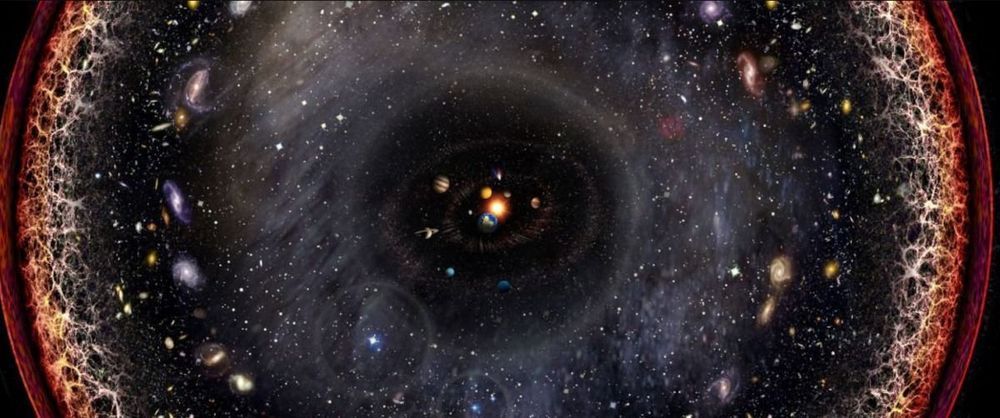
Roughly 13.75 billion years ago, our universe came into existence. Very shortly thereafter, primordial light started shooting across the cosmos and spreading throughout the early universe. At this juncture, the universe itself was also expanding. The inflation of the universe slowed after the first initial burst, but since then, the rate of expansion has been steadily increasing due to the influence of dark energy.
Essentially, since its inception, the cosmos has been growing at an ever increasing rate. Cosmologists estimate that the oldest photons that we can observe have traveled a distance of 45–47 billion light-years since the Big Bang. That means that our observable universe is some 93 billion light-years wide (give or take a few light-years). These 93 some-odd billion light-years contain all of the quarks, quasars, stars, planets, nebulae, black holes…and everything else that we could possibly observe; however, the observable universe only contains the light that has had time to reach us.
How can the universe be 93 billion light-years across if it is only 13.8 billion years old? Light hasn’t had enough time to travel that far…? Ultimately, understanding this facet of physics is the key to understanding what lies beyond the edge of the observable universe and whether we could ever get there.
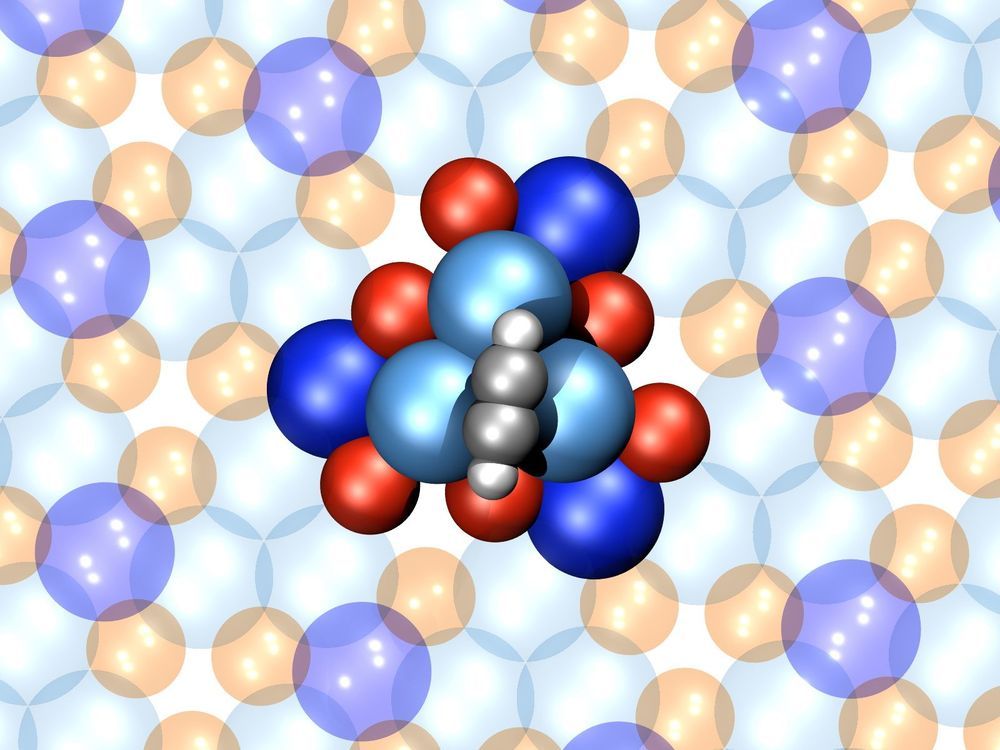
Researchers at Empa and EPFL have created one of the smallest motors ever made. It’s composed of just 16 atoms, and at that tiny size it seems to function right on the boundary between classical physics and the spooky quantum realm.
Like its macroscopic counterparts, this mini motor is made up of a moving part (the rotor) and a fixed part (the stator). The stator in this case is a cluster of six palladium atoms and six gallium atoms arranged in a rough triangular shape. Meanwhile, the rotor is a four-atom acetylene molecule, which rotates on the surface of the stator. The whole machine measures less than a nanometer wide.
The molecular motor can be powered by either thermal or electrical energy, although the latter was found to be much more useful. At room temperature, for example, the rotor was found to rotate back and forth at random. But when an electric current was applied using an electron scanning microscope, the rotor would spin in one direction with a 99-percent stability.

On September 10, 2008, CERN’s Large Hadron Collider (LHC) fired up for the very first time. In the decade since, the world’s largest and most powerful particle accelerator has been responsible for some of the most important breakthroughs in scientific history, most notably the discovery of the Higgs boson in 2013. New Atlas is celebrating the 10-year anniversary with a look back at the LHC’s achievements and, with a massive new upgrade in the works, what physics puzzles it could help piece together in the future.
Not only is the Large Hadron Collider the world’s largest particle accelerator, it’s the world’s largest machine, full-stop. That’s thanks to a 27-km-long (16.7-mi) ring of pipes that house the particle beams, along with thousands of powerful magnets and an advanced cooling system of liquid helium.
The ring is made up of two separate tubes, with high-energy particle beams circling in opposite directions. Superconducting electromagnets accelerate the particles almost to the speed of light, and for those to work they need to be kept extremely cold: −271.3° C (−456.3° F) to be exact, which is colder than outer space. That’s where the liquid helium comes in, chosen because it’s the only known element to remain in a liquid form at such low temperatures.