Researchers have found that graphene-enhanced hard drives can store data at ten times the density of existing HDDs.
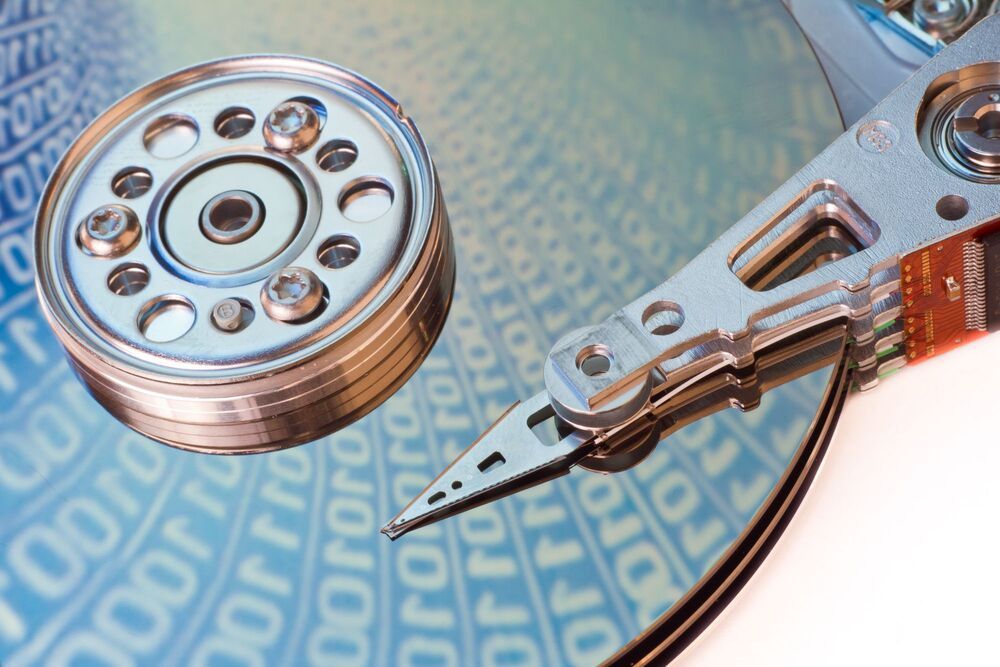
By leveraging the wonder material graphene, a group at the University of Cambridge is claiming an advance in data storage that resembles more of a leap than a step forward. The new design unlocks higher operating temperatures for hard disk drives (HDDs) and with it, unprecedented data density, which the team says represents a ten-fold increase on current technologies.
In a HDD, data is written onto fast-spinning platters by a moving magnetic head. Special layers called carbon-based overcoats (COCs) protect these platters from mechanical damage and corrosion during operation, though these can only perform within a certain temperature range and also take up a lot of space.
The Cambridge researchers were able to replace the COCs used in commercial HDDs with between one and four layers of graphene, a material that is a single layer of carbon atoms with incredible strength and flexibility, among other highly-valued properties. The thinness of the graphene enabled significant space savings but also outperformed current COCs in preventing mechanical wear, reduced corrosion by 2.5 times and also offered a two-fold reduction in friction.