Check this out!
UChicago hasthis been able for the first time conduct an experiment shows the behavior of quantum materials in curved space. In their own words, “We are beginning to make our photons interact with each other. This opens up many possibilities, such as making crystalline or exotic quantum liquid states of light. We can then see how they respond to spatial curvature.”
Interplay of light, matter is of potential technological interest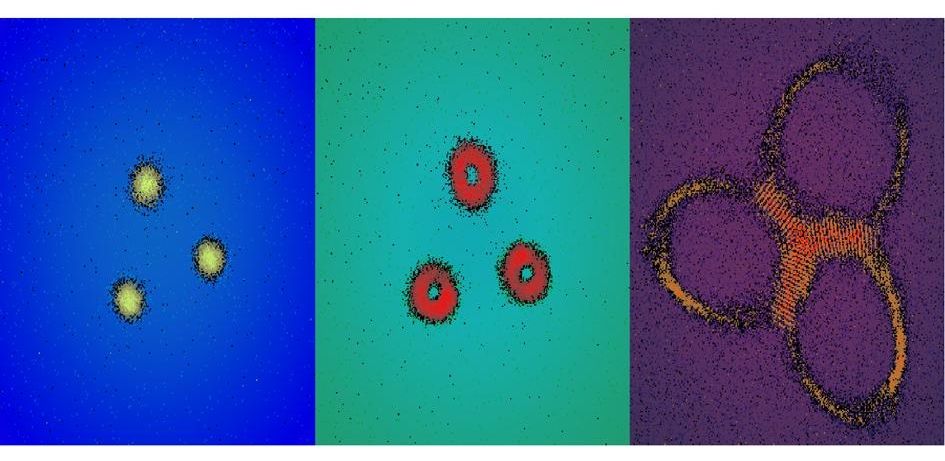
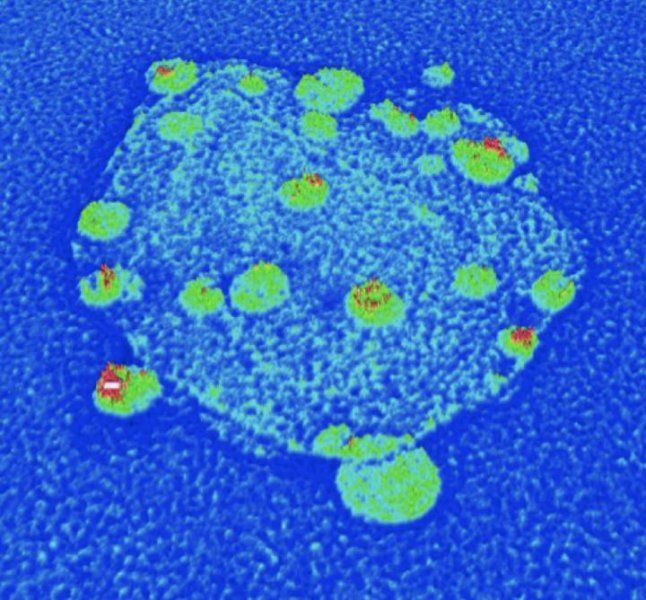
These false-color images represent the quantum Hall state that UChicago physicists created by shining infrared laser light at specially configured mirrors. Achieving this state with light instead of matter was an important step in developing computing and other applications from quantum phenomena. Courtesy of Nathan Schine, Albert Ryou, Andrey Gromov, Ariel Sommer, and Jonathan Simon.
CHICAGO–(ENEWSPF)–June 10, 2016. Light and matter are typically viewed as distinct entities that follow their own, unique rules. Matter has mass and typically exhibits interactions with other matter, while light is massless and does not interact with itself. Yet, wave-particle duality tells us that matter and light both act sometimes like particles, and sometimes like waves.
Harnessing the shared wave nature of light and matter, researchers at the University of Chicago, led by Jonathan Simon, the Neubauer Family Assistant Professor of Physics, have used light to explore some of the most intriguing questions in the quantum mechanics of materials. The topic encompasses complex and non-intuitive phenomena that are often difficult to explain in non-technical language, but which carry important implications to specialists in the field.
Read more