Stable nanomagnets that ultimately improves data storage on the smallest of devices.
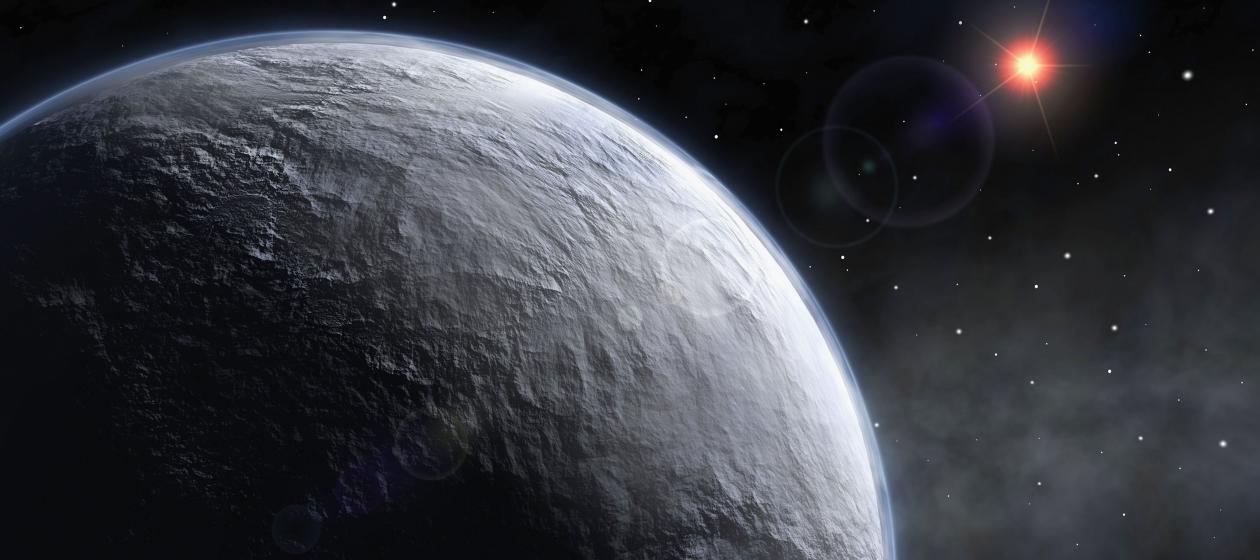
Abstract: So-called “zero-point energy” is a term familiar to some cinema lovers or series fans; in the fictional world of animated films such as “The Incredibles” or the TV series “Stargate Atlantis”, it denotes a powerful and virtually inexhaustible energy source. Whether it could ever be used as such is arguable. Scientists at Jülich have now found out that it plays an important role in the stability of nanomagnets. These are of great technical interest for the magnetic storage of data, but so far have never been sufficiently stable. Researchers are now pointing the way to making it possible to produce nanomagnets with low zero-point energy and thus a higher degree of stability (Nano Letters, DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b01344).
Since the 1970s, the number of components in computer chips has doubled every one to two years, their size diminishing. This development has made the production of small, powerful computers such as smart phones possible for the first time. In the meantime, many components are only about as big as a virus and the miniaturization process has slowed down. This is because below approximately a nanometre, a billionth of a meter in size, quantum effects come into play. They make it harder, for example, to stabilise magnetic moments. Researchers worldwide are looking for suitable materials for magnetically stable nanomagnets so that data can be stored safely in the smallest of spaces.
In this context, stable means that the magnetic moments point consistently in one of two preassigned directions. The direction then codes the bit. However, the magnetic moments of atoms are always in motion. The trigger here is the so-called zero-point energy, the energy that a quantum mechanical system possesses in its ground state at absolute zero temperature. “It makes the magnetic moments of atoms fluctuate even at the lowest of temperatures and thus works against the stability of the magnetic moments”, explains Dr. Julen Ibañez-Azpiroz, from the Helmholtz Young Investigators Group “Functional Nanoscale Structure Probe and Simulation Laboratory” at the Peter Grünberg Institute and at the Institute for Advanced Simulation. When too much energy exists within the system, the magnetic moments turn over and the saved information is lost.