Another approach to QC; the title of the article is misleading because you still are using quantum properties in the approach.
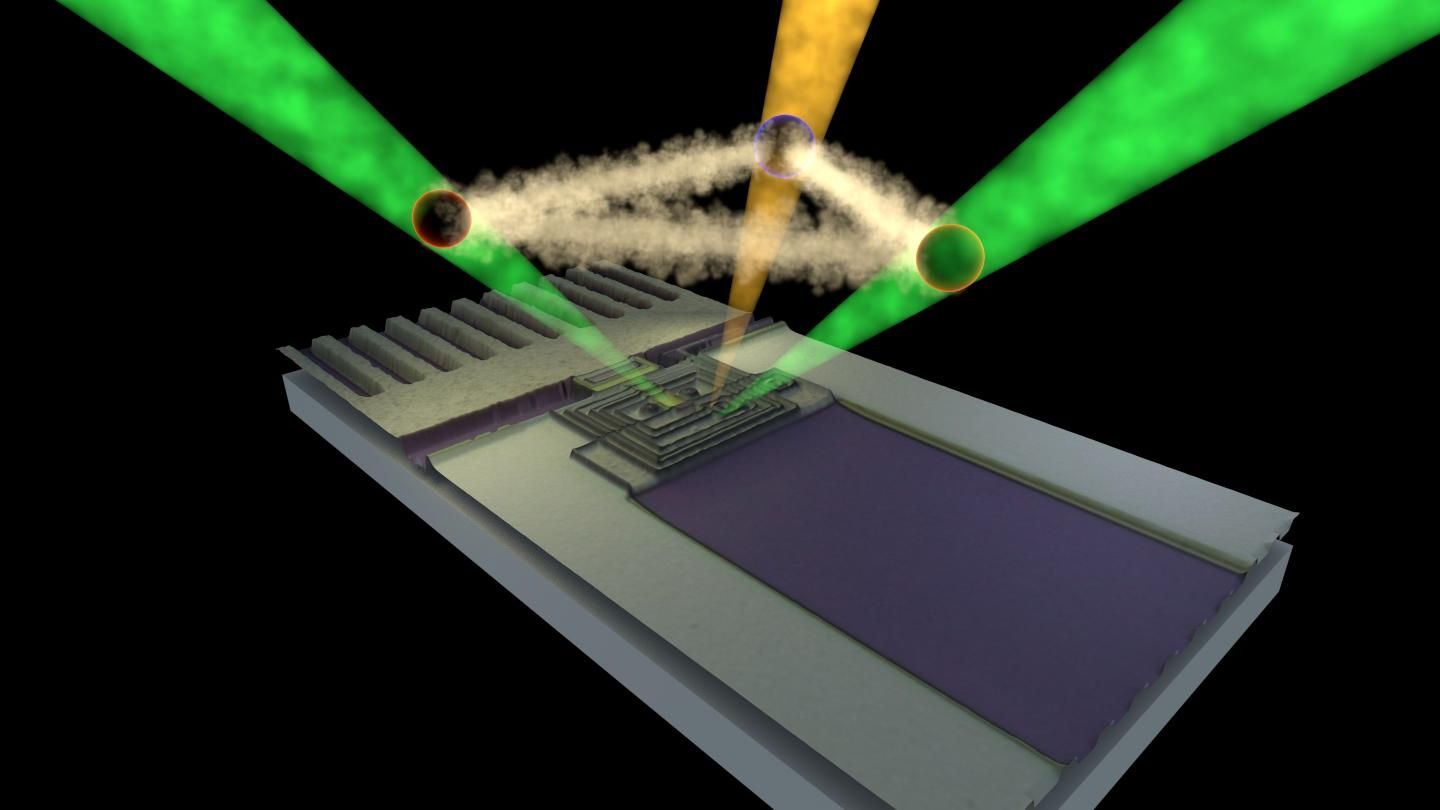
Researchers at Aalto University have demonstrated the suitability of microwave signals in the coding of information for quantum computing. Previous development of the field has been focusing on optical systems. Researchers used a microwave resonator based on extremely sensitive measurement devices known as superconductive quantum interference devices (SQUIDs). In their studies, the resonator was cooled down and kept near absolute zero, where any thermal motion freezes. This state corresponds to perfect darkness where no photon — a real particle of electromagnetic radiation such as visible light or microwaves — is present.
However, in this state (called quantum vacuum) there exist fluctuations that bring photons in and out of existence for a very short time. The researchers have now managed to convert these fluctuations into real photons of microwave radiation with different frequencies, showing that, in a sense, darkness is more than just absence of light.
They also found out that these photons are correlated with each other, as if a magic connection exists between them.