Another huge leap forward in mass production of Quantum devices found.
Harnessing solid-state quantum bits, or qubits, is a key step toward the mass production of electronic devices based on quantum information science and technology. However, realizing a robust qubit with a long lifetime is challenging, particularly in semiconductors comprising multiple types of atoms.
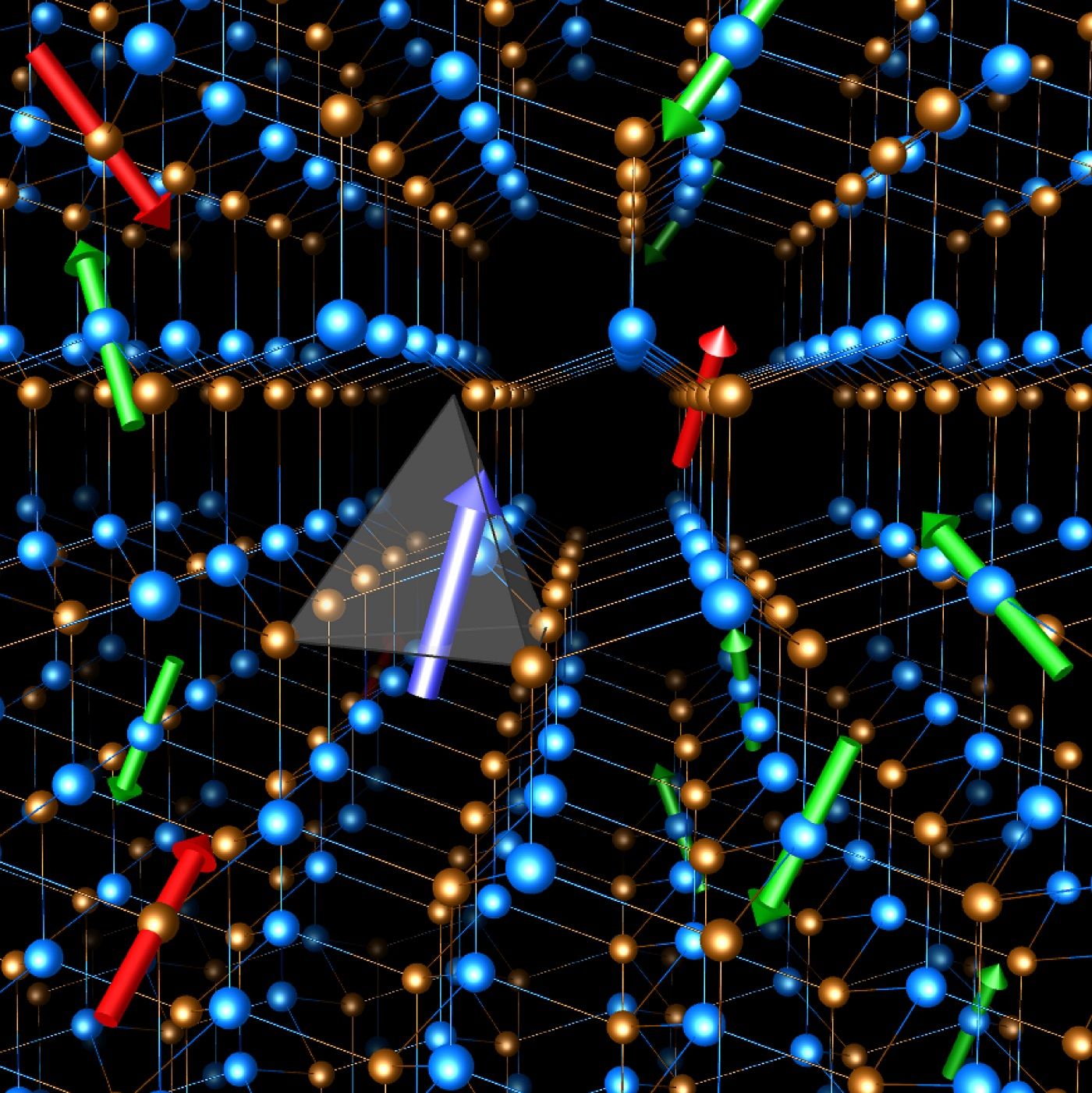
The close collaboration between experiments in Prof. David Awschalom’s group and theory and simulations in Prof. Giulia Galli’s group, both in the Institute for Molecular Engineering, has enabled a crucial step toward solid-state qubits in industrially important semiconductors. In a paper, published Sept. 29 in Nature Communications, the two groups showed that electron qubits bound to atom-like defects in a commercial silicon carbide wafer can exhibit the longest electronic coherence times ever measured in a natural crystal.
“Quantum coherence underlies all quantum information technologies, such as quantum communication and quantum sensing. However, the coherence time in materials is eventually limited by the magnetic noise produced by the fluctuating nuclear spins in a crystal,” said Hosung Seo, an IME postdoctoral researcher and the paper’s lead author.