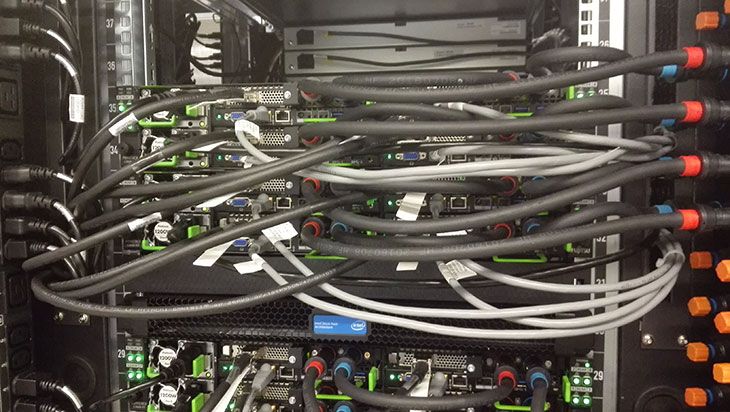
A new supercomputer has been deployed at the Jülich Supercomputing Center (JSC) in Germany. Called QPACE3, the new 447 Teraflop machine is named for “QCD Parallel Computing on the Cell.”
QPACE3 is being used by the University of Regensburg for a joint research project with the University of Wuppertal and the Jülich Supercomputing Center for numerical simulations of quantum chromodynamics (QCD), which is one of the fundamental theories of elementary particle physics. Such simulations serve, among other things, to understand the state of the universe shortly after the Big Bang, for which a very high computing power is required.
The demand for high performance computers to solve complex applications has risen exponentially, but unfortunately so has their consumption of power. Many supercomputers require more than a megawatt of electricity to operate and annual electricity costs can easily run into millions of Euros. The energy supply is therefore a significant part of the operating costs of a data center. According to recent analyst studies, this represents the second-largest factor in addition to personnel and maintenance costs. The upcoming boom with (3D) video streaming, augmented reality, image recognition and artificial intelligence is driving up the demand for data center capabilities, thereby placing new challenges in the power supply sector.