Quantum entanglement, one of the most intriguing features of multi-particle quantum systems, has become a fundamental building block in both quantum information processing and quantum computation. If two particles are entangled, no matter how far away they are separated, quantum mechanics predicts that measurement of one particle leads to instantaneous wave-function collapse of the other particle.
Such “spooky action at a distance” is non-intuitive, and in 1935, Einstein attempted to use entanglement to criticize quantum mechanics to suggest that the quantum description of physical reality is incomplete. Einstein believed that no information could travel faster than light, and suggested that there might be some local hidden variable theories that could explain the world in a deterministic way, if and only if they obey realism and locality. In 1964, J. S. Bell showed that the debate can be experimentally resolved by testing an inequality; by measuring correlations between entangled parties, the result calculated from local hidden variable theories should be constrained by the Bell inequality, which, on the other hand, can be violated in the predictions of quantum mechanics.
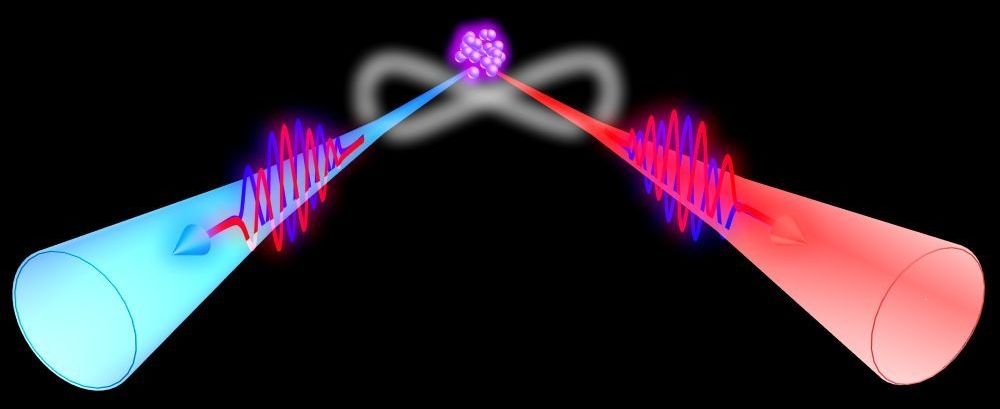
By reducing the velocity of light dramatically, researchers at the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology implemented a Bell Test and were able to generate frequency-bin entangled narrowband biphotons from spontaneous four-wave mixing (SFWM) in cold atoms with a double-path configuration, where the phase difference between the two spatial paths can be controlled independently and nonlocally.