Nuclear fission — the physical process by which very large atoms like uranium split into pairs of smaller atoms — is what makes nuclear bombs and nuclear power plants possible. But for many years, physicists believed it energetically impossible for atoms as large as uranium (atomic mass = 235 or 238) to be split into two.
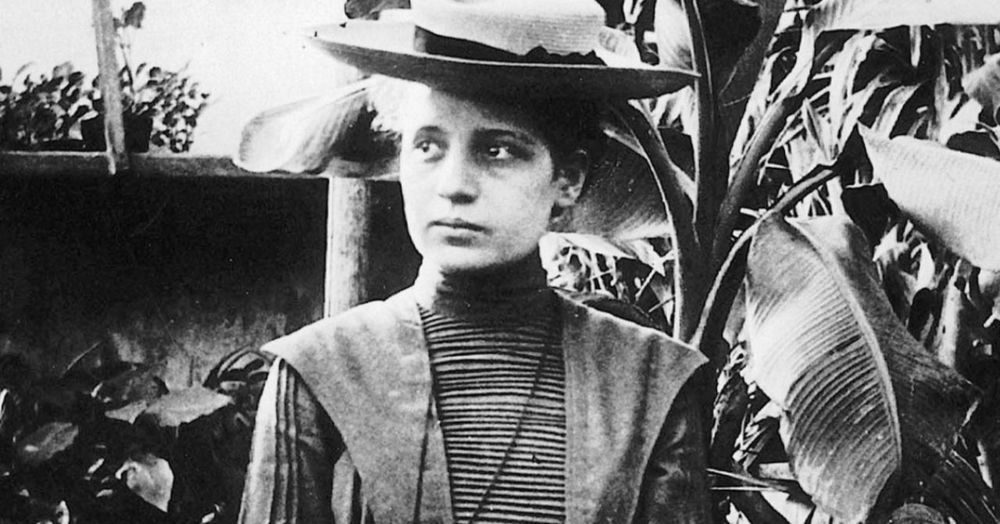
That all changed on Feb. 11, 1939, with a letter to the editor of Nature — a premier international scientific journal — that described exactly how such a thing could occur and even named it fission. In that letter, physicist Lise Meitner, with the assistance of her young nephew Otto Frisch, provided a physical explanation of how nuclear fission could happen.
It was a massive leap forward in nuclear physics, but today Lise Meitner remains obscure and largely forgotten. She was excluded from the victory celebration because she was a Jewish woman. Her story is a sad one.