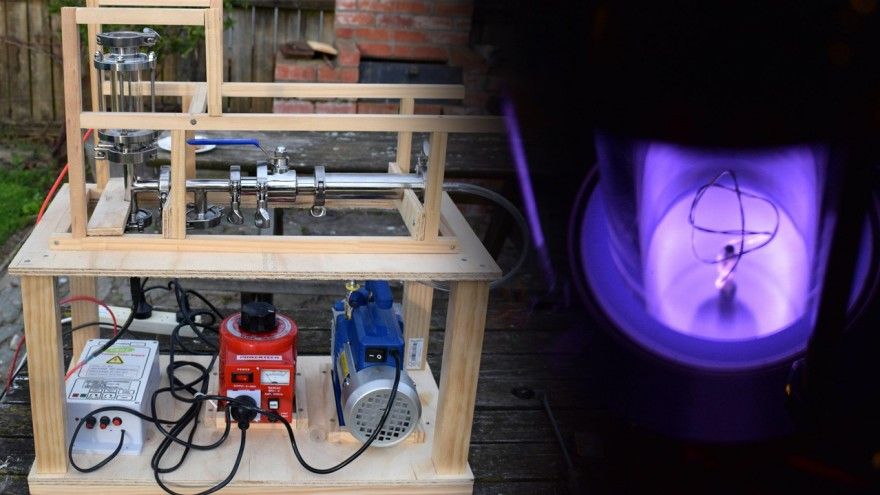
“We are sidestepping all of the scientific challenges that have held fusion energy back for more than half a century,” says the director of an Australian company that claims its hydrogen-boron fusion technology is already working a billion times better than expected.
HB11 Energy is a spin-out company that originated at the University of New South Wales, and it announced today a swag of patents through Japan, China and the USA protecting its unique approach to fusion energy generation.
Fusion, of course, is the long-awaited clean, safe theoretical solution to humanity’s energy needs. It’s how the Sun itself makes the vast amounts of energy that have powered life on our planet up until now. Where nuclear fission – the splitting of atoms to release energy – has proven incredibly powerful but insanely destructive when things go wrong, fusion promises reliable, safe, low cost, green energy generation with no chance of radioactive meltdown.