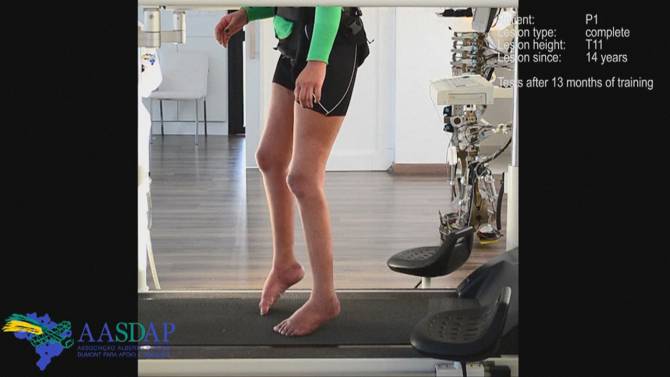
In an astonishing breakthrough, patients left paralysed by severe spinal cord injuries have recovered the ability to move their legs after training with an exoskeleton linked to their brain – with one even able to walk using two crutches.
Scientists developed the Walk Again Project, based in Sao Paulo, Brazil, thinking that they could enable paraplegics to move about using the exoskeleton controlled by their thoughts. But they were surprised to discover that during the training, the eight patients all started to regain the sense of touch and movement below the injury to their spine. It was previously thought that the nerves in seven of the patients’ spines had been completely severed.
But the researchers now believe that a few nerves survived and these were reactivated by the training, which may have rewired circuits in the brain. Writing in the journal Scientific Reports, they said: “While patient one was initially not even able to stand using braces when placed in an orthostatic posture, after 10 months of training the same patient became capable of walking using a walker, braces and the assistance of one therapist. “At this stage, this patient became capable of producing voluntary leg movements mimicking walking, while suspended overground.
Read more