The Buck institute is in the spotlight today.
Located in Novato, California, not too far from Mount Burdell Preserve and Olompali State Historic Park, is one of the world’s leading research centres for ageing and age-related diseases—the Buck Institute for Research on Aging.
Opened in 1999 thanks to the substantial bequest of American philanthropist Beryl Hamilton Buck, the Buck Institute set to fulfill her wishes that her patrimony be spent to “extend help towards the problems of the aged, not only the indigent but those whose resources cannot begin to provide adequate care.” Over the years, the Institute has certainly honoured its commitment: The Buck can boast some of the most eminent experts on ageing among its research staff, and a number of laboratories that push forward our understanding of age-related pathologies every day—such as the Campisi Lab and the Kennedy Lab, just to name a few.
The Buck’s approach to investigating ageing is a multifaceted one. The institute rightfully acknowledges the necessity to bring together experts from disparate fields of science—from physics to engineering, from mathematics to anthropology—in order to properly understand the complex networks of biochemical processes underlying ageing and ultimately leading to pathology. Biochemistry, molecular endocrinology, proteomics, genomic stability, and cell biology are only some of the areas of investigation of the Buck, and the medical conditions researched by their teams range from Huntington’s disease to ischemia, to Parkinson’s, to cancer and Alzheimer’s. The three main questions the Buck set to answer are why do ageing tissues lose their regeneration capacity, why do stem cells fail to function with ageing, and how do tissues change during ageing so that they no longer support normal regenerative processes.
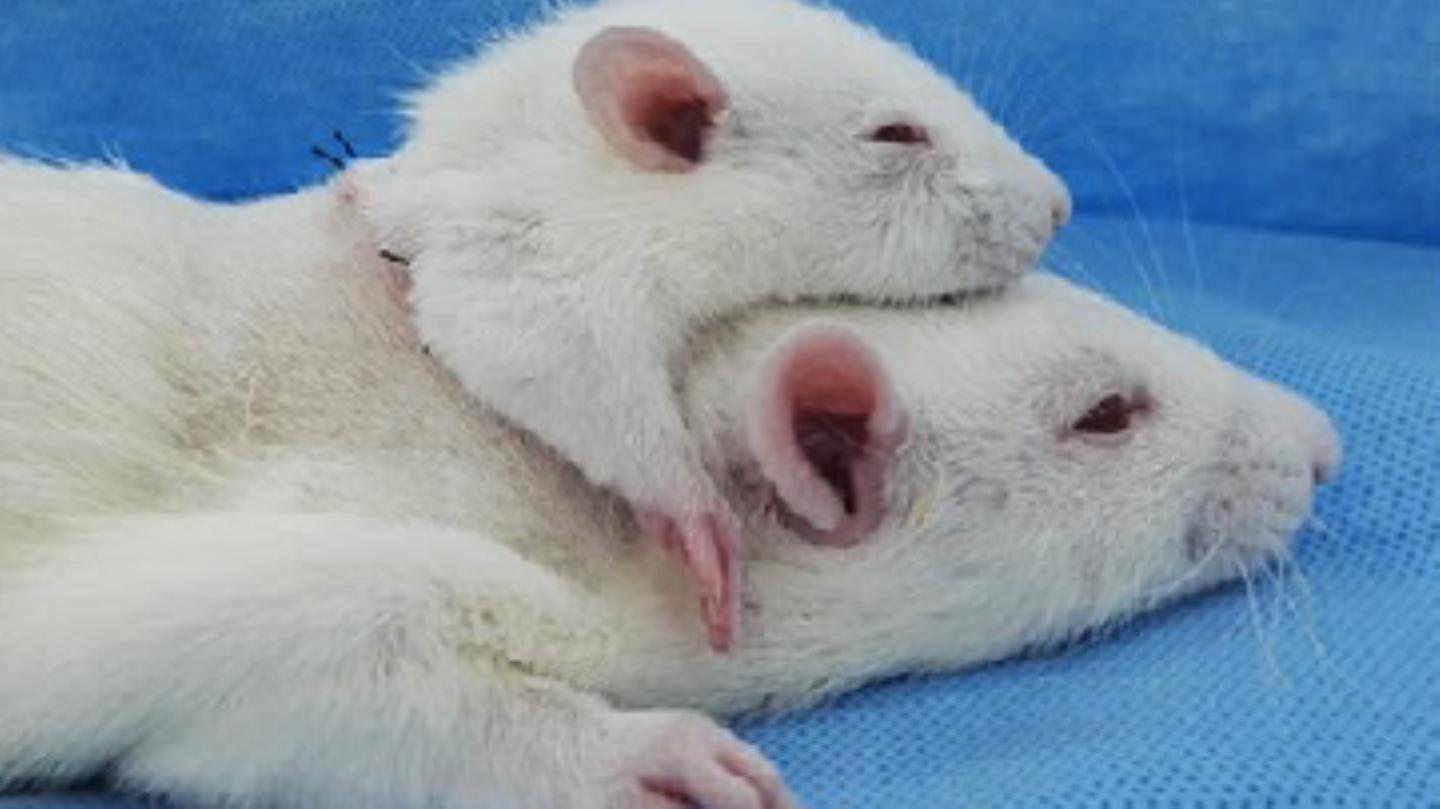





 Researches successfully avoided brain-damaging blood loss while the donor head was being attached to the recipient rat.
Researches successfully avoided brain-damaging blood loss while the donor head was being attached to the recipient rat.
