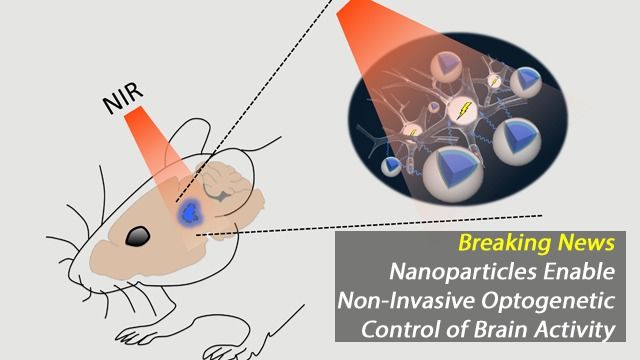
So will we ever be able to do this or is this just a pipe dream? Plenty has been written about the future and what we may be able to do one day, but not much attention gets paid to the hurdles we have yet to overcome. Forget all the techno-babble, philosophy, and transhumanism – how close is this brave new world to our present time?
“Any way you look at it, all the information that a person accumulates in a lifetime is just a drop in a bucket.”
Taken from 1995’s Ghost in the Shell, this sentence perfectly sums up the complexity and ambiguity of the human mind and the brain. Despite enormous advances, our ignorance on what lies within our cranium remains vast and sometimes unyielding. Those drops, and their relation to the bucket, are profoundly enigmatic.
We understand how different parts of the brain communicate and often what they specialize in, but what exactly is a “thought” made of? Where, amongst the 86 billion neurons in our brain, do they come from, and where do they go? What, scientifically speaking, is consciousness – is it a single entity or the sum of trillions of permutations? Is it the addition or average of all those firing neurons?