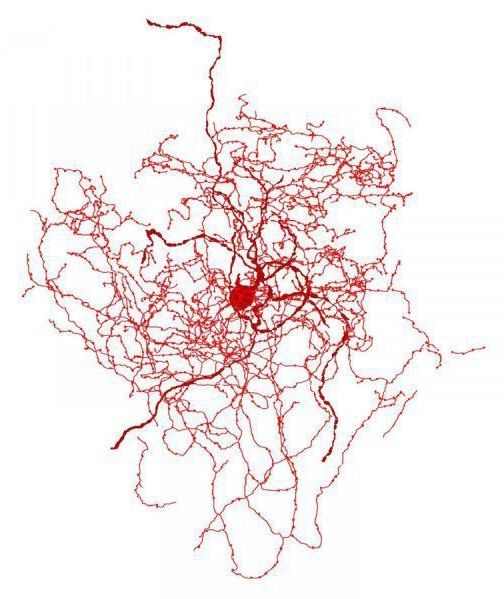
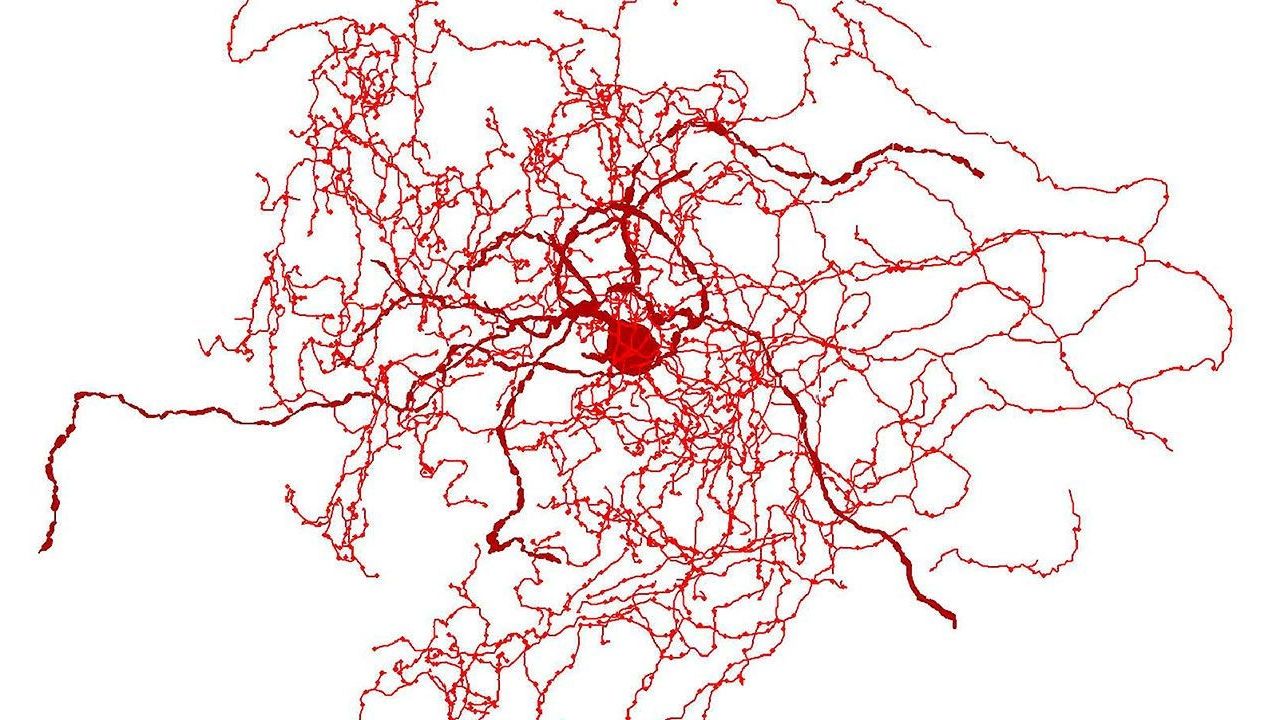
The neuron is not found within lab mice, possibly explaining why mouse studies often do not translate to human brains.

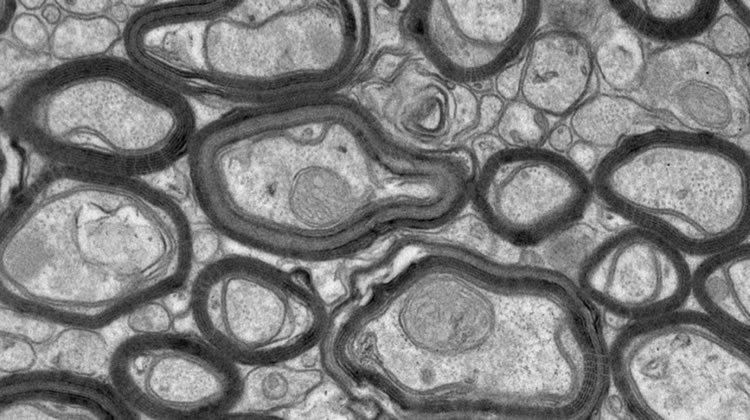
Researchers have found a way to rebuild damaged nerve coverings that cause Multiple Sclerosis.
Researchers successfully used a synthetic compound to stimulate a receptor pathway to promote remyelination in the brain. The technique may have significant beneficial implications for treating multiple sclerosis, researchers say.

When it comes to fundamental physics, things can get spooky. At least that’s what Albert Einstein said when describing the phenomenon of quantum entanglement—the linkage of particles in such a way that measurements performed on one particle seem to affect the other, even when separated by great distances. “Spooky action at a distance” is how Einstein described what he couldn’t explain.
While quantum mechanics includes many mysterious phenomena like entanglement, it remains the best fundamental physical theory describing how matter and light behave at the smallest scales. Quantum theory has survived numerous experimental tests in the past century while enabling many advanced technologies: modern computers, digital cameras and the displays of TVs, laptops and smartphones. Quantum entanglement itself is also the key to several next-generation technologies in computing, encryption and telecommunications. Yet, there is no clear consensus on how to interpret what quantum theory says about the true nature of reality at the subatomic level, or to definitively explain how entanglement actually works.
According to Andrew Friedman, a research scientist at the University of California San Diego Center for Astrophysics and Space Sciences (CASS), “the race is on” around the globe to identify and experimentally close potential loopholes that could still allow alternative theories, distinct from quantum theory, to explain perplexing phenomena like quantum entanglement. Such loopholes could potentially allow future quantum encryption schemes to be hacked. So, Friedman and his fellow researchers conducted a “Cosmic Bell” test with polarization-entangled photons designed to further close the “freedom-of-choice” or “free will” loophole in tests of Bell’s inequality, a famous theoretical result derived by physicist John S. Bell in the 1960s. Published in the Aug. 20 issue of Physical Review Letters, their findings are consistent with quantum theory and push back to at least 7.
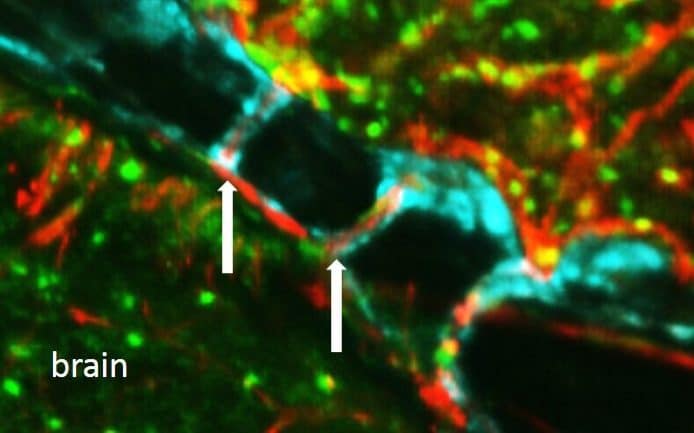
Hidden tunnels which link the human skull to the brain have been discovered by scientists, leading to hopes the breakthrough may help in stroke and Alzheimer’s research.
Researchers believe that the passages provide a quick channel for immune cells to reach the brain from the bone marrow in the skull.
Previously it was through that immune cells formed in the bone marrow of the limbs was transported up to the brain to clear out infection.
If you’ve ever experienced jet lag, you are familiar with your circadian rhythm, which manages nearly all aspects of metabolism, from sleep-wake cycles to body temperature to digestion. Every cell in the body has a circadian clock, but researchers were unclear about how networks of cells connect with each other over time and how those time-varying connections impact network functions.
In research published Aug. 27 in PNAS, researchers at Washington University in St. Louis and collaborating institutions developed a unified, data-driven computational approach to infer and reveal these connections in biological and chemical oscillatory networks, known as the topology of these complex networks, based on their time-series data. Once they establish the topology, they can infer how the agents, or cells, in the network work together in synchrony, an important state for the brain. Abnormal synchrony has been linked to a variety of brain disorders, such as epilepsy, Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
Jr-Shin Li, professor of systems science & mathematics and an applied mathematician in the School of Engineering & Applied Science, developed an algorithm, called the ICON (infer connections of networks) method, that shows for the first time the strength of these connections over time. Previously, researchers could only determine whether a connection existed between networks.

Jason Padgett grew up struggling in school — until one night in 2002 when he was attacked in a bar and everything changed. Padgett said after the incident, he was using areas of the brain he didn’t previously have access to; he experienced choppy vision, was drawing intricate shapes and was seeing complex mathematical objects everywhere. Dr. Darold Treffert, a world renowned expert on savants, later diagnosed Padgett with acquired savant syndrome, which explained Padgett’s new skills. Padgett joins Megyn Kelly TODAY to share his story.

A controversial new study in lab mice hints at sex-based differences in cosmic ray–induced cognitive decline.

Scientists at Harvard Medical School have discovered that a protein called TMC1 converts sound and head motion into electrical signals, thus enabling hearing and balance.
The findings were published this week in the journal Neuron.
Sensitivity to sound has been a powerful evolutionary force, but the precise molecular mechanisms that enable hearing have not been fully identified.
Today, we want to draw your attention to a recent study showing an association between the accumulation of Tau proteins, which are misfolded proteins that typically indicate Alzheimer’s disease and senescent cells.
Unfortunately, this journal paper is hidden behind a paywall, as is 70% of scientific data; this is an unacceptable situation for science and the sharing of knowledge. However, thanks to the work of Sci-Hub, a website that bypasses paywalls and offers free access to all scientific papers, you can read it without spending a dime.