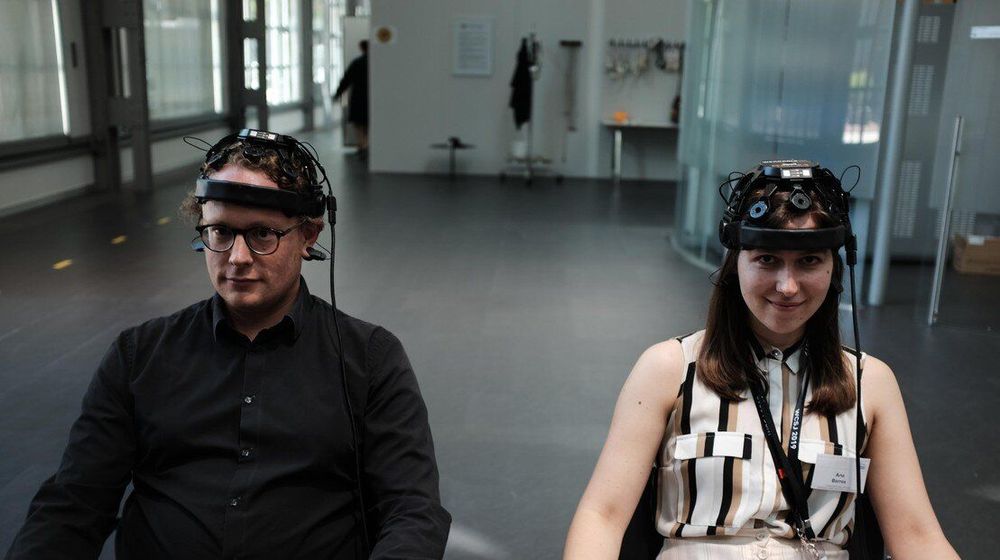
Data from Mental Work project, conducted as an experimental artwork at EPFL’s Artlab, indicates that BMI is robust and accessible to the general public, spurring new research collaborations in Switzerland on user experience.
Brain-machine interfaces are rarely found outside of medical clinics, where the disabled receive hours or days of training in order to operate wheelchairs with their minds. Now the largest-ever BMI experiment Mental Work, conducted as an experimental artwork at EPFL’s Artlab, has provided preliminary evidence that training time can be shortened, the use of dry electrodes are a robust solution for public BMI and that user performance tends to improve within a relatively short period of time. The still-to-be-published results suggest that BMI may soon reach a much larger and more diverse population. A new collaboration between the Foundation Campus Biotech Geneva, the EPFL and the HEIG-VD in Yverdon will build on the promising results will build on the promising results of Mental Work to further develop user-friendly and publicly accessible interfaces to interact with the physical and digital world using only one’s mind.
“This is the first demonstration that installation art can be used as an experimental platform for breakthrough science,” says Jonathon Keats, the artist and experimental philosopher who conceptualized Mental Work.