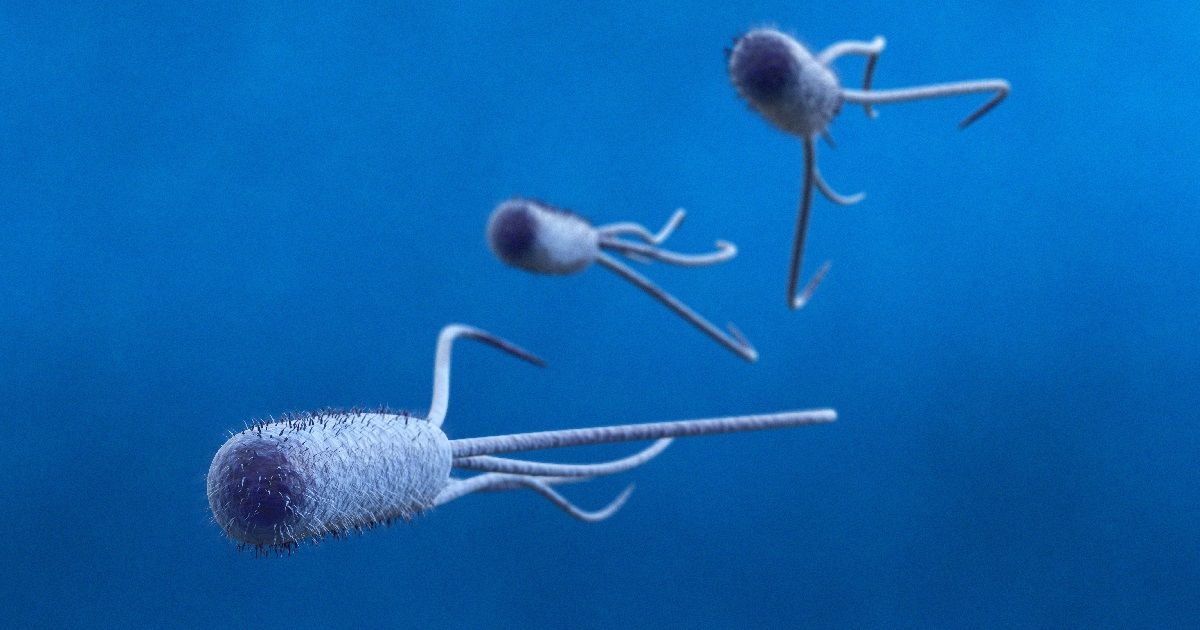
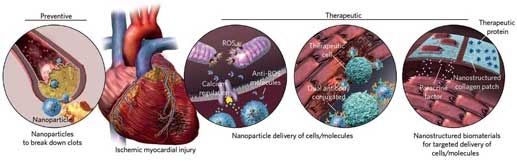
Summary: Nanodocs? #Swallow #the #doctor? The authors of a recent research study, says soon we will be able to “swallow the surgeon.” Using medical #nanobots to diagnose and treat disease from inside the body. Study authors documented recent advances in nanotechnology tools, such as nanodrillers, microgrippers, and microbullets – and show how #nanodocs have tremendous potential in the areas of precision surgery, detection, detoxification and targeted drug delivery.
Summary: Nanodocs? Swallow the doctor? The authors of a recent research study, say the concept of “swallow the surgeon” – or using medical nanobots to diagnose and treat disease from inside the body – may be closer than we think. Study authors document recent advances in nanotechnology tools, such as nanodrillers, microgrippers, and microbullets – and show how nanodocs have tremendous potential in the areas of precision surgery, detection, detoxification and targeted drug delivery. Cover photo: The old way to swallow the surgeon. Credit: R. Collin Johnson / Attributed to Stanford University.
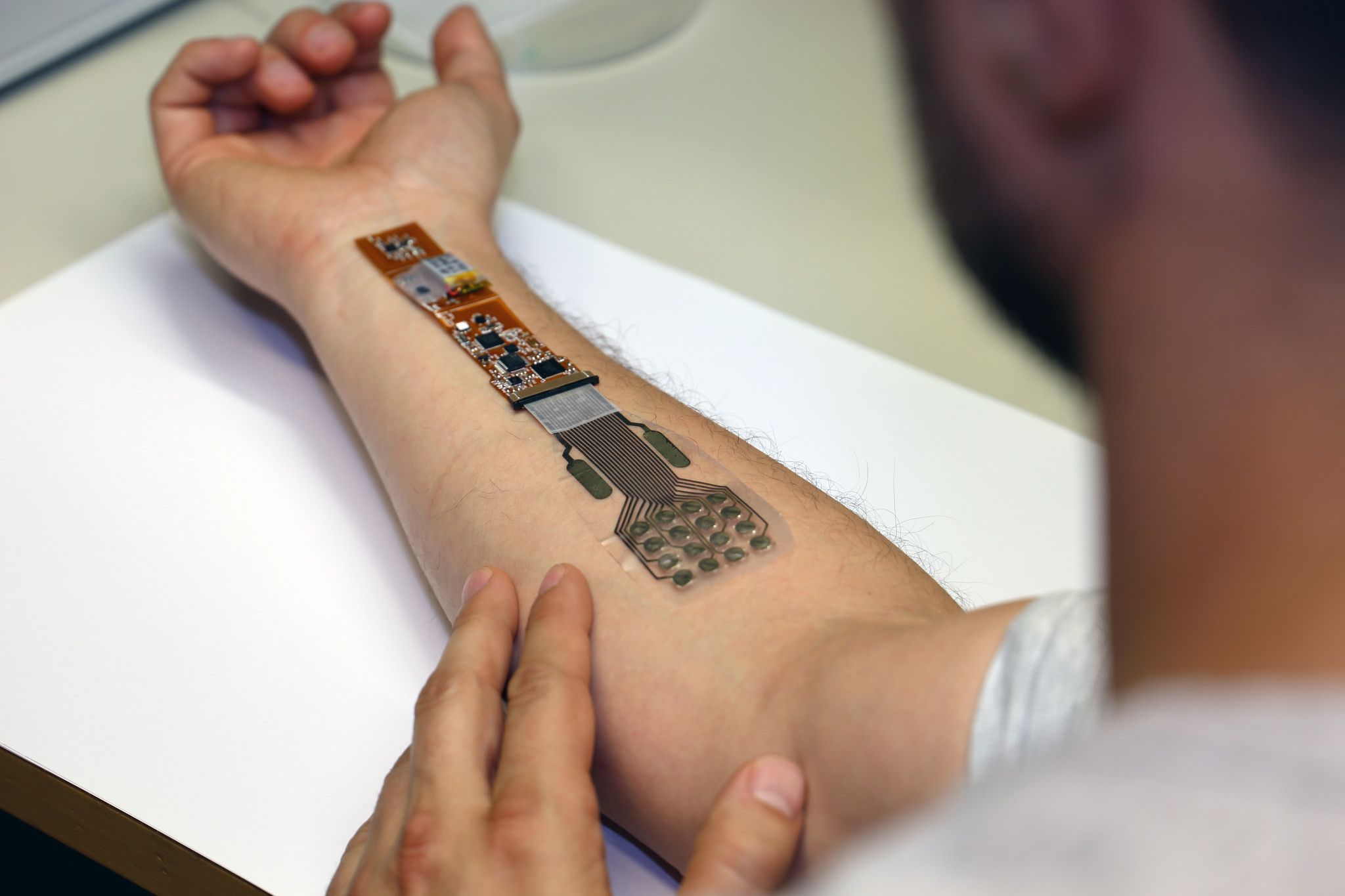
Imagine that you need to repair a defective heart valve, a major surgery. Instead of ripping your chest cut open, a doctor merely injects you with a syringe full of medical nanorobots, called nanodocs for short. You emerge from the ‘surgery’ unscathed, and your only external wound is the puncture hole from the injection.
According to a recent study published by nanorobotic engineers at the University of California San Diego (UCSD), the concept of ‘swallow the doctor’ may be closer to reality than we think.
Read more