Physicists have found “electron pairing,” a hallmark feature of superconductivity, at temperatures and energies well above the critical threshold where superconductivity happens.
Rice University’s Doug Natelson, co-corresponding author of a paper about the work in this week’s Nature, said the discovery of Cooper pairs of electrons “a bit above the critical temperature won’t be ‘crazy surprising’ to some people. The thing that’s more weird is that it looks like there are two different energy scales. There’s a higher energy scale where the pairs form, and there’s a lower energy scale where they all decide to join hands and act collectively and coherently, the behavior that actually brings about superconductivity.”
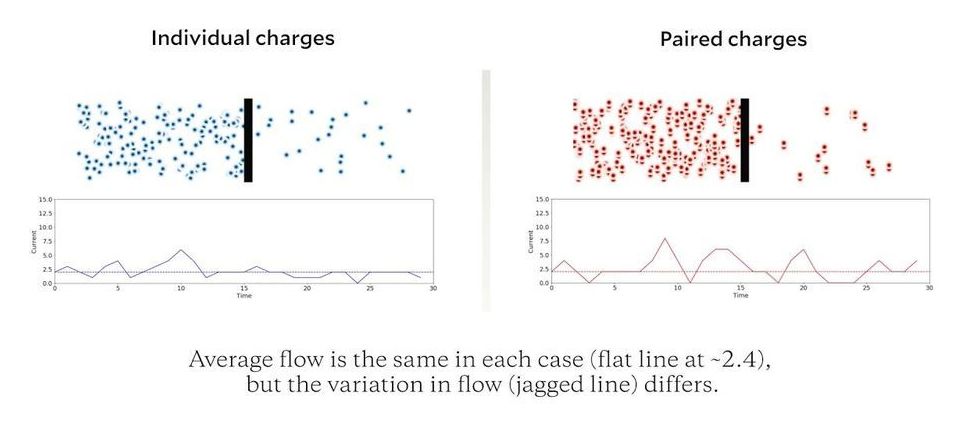
Electrical resistance is so common in the modern world that most of us take it for granted that computers, smartphones and electrical appliances warm up during use. That heating happens because electricity doesn’t flow freely through the metal wires and silicon chips inside the devices. Instead, flowing electrons occasionally bump into atoms or one another, and each collision produces a tiny bit of heat.