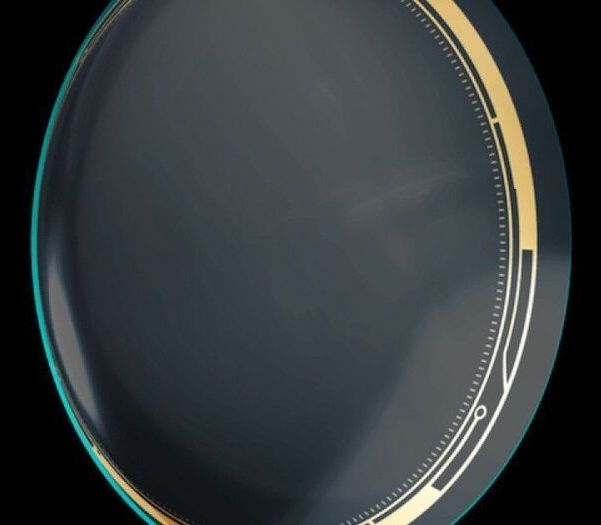
SMART CONTACT LENSES are coming during this decade, probably within a few years. This company claims it is ready to launch one that will 1) give night vision to the wearer; 2) record video of what you see with your eyes in real time; 3) zoom magnification up to 60 times larger than regular vision, so if you see something far away, you can see what it is; 4) display “augmented” images on your visual field. This means you will be able to see everything normally, BUT can see a text of the weather, or map directions, etc. Eventually, such contact lenses will replace the smart phone, and you will dial, talk, etc, without use of your hands. I would like this to interface with instant language translation, to make learning a language five times faster!
This innovation, called iLens, looks unbelievable on paper. Associated with a smartphone via Bluetooth, this concept would allow you to record your daily memories in video. A telephoto camera embedded in the lens would allow you to zoom digitally up to 60x to enhance your eyesight and discover details invisible to the naked eye. This digital feat would also allow you to see perfectly in the dark.
ILens would also display augmented reality information, for instance to keep a certain distance from others, or practical information regarding air quality or the weather.
Another interesting feature is that iLens would warn you if you’ve spent too much time in front of a screen and would encourage you to take breaks to avoid eye strain.