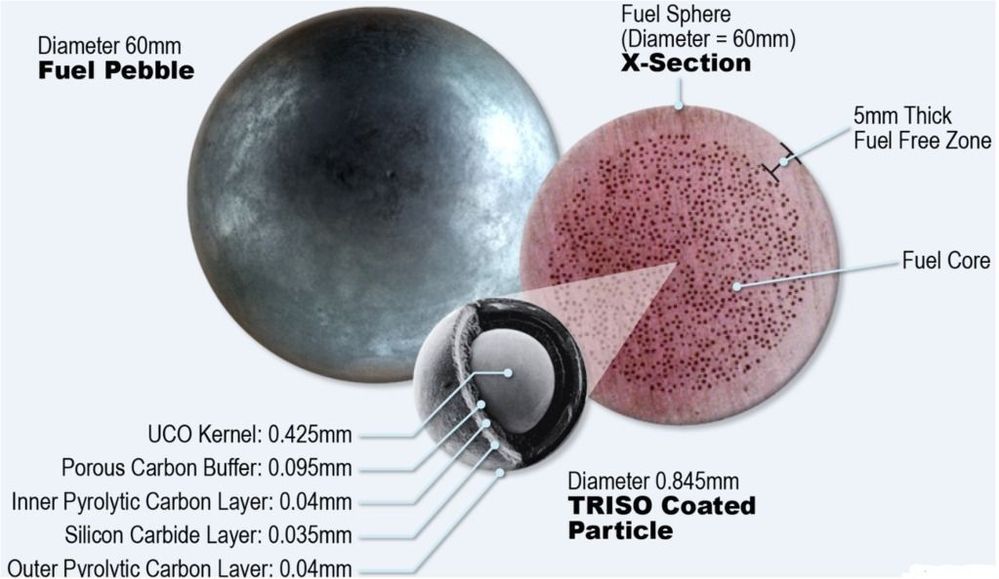
Circa 2018 o,.,o.
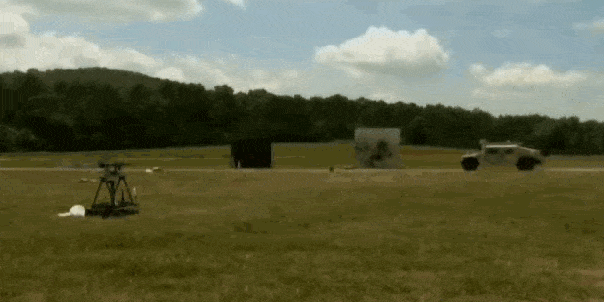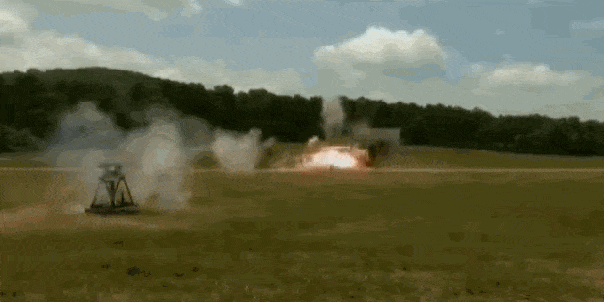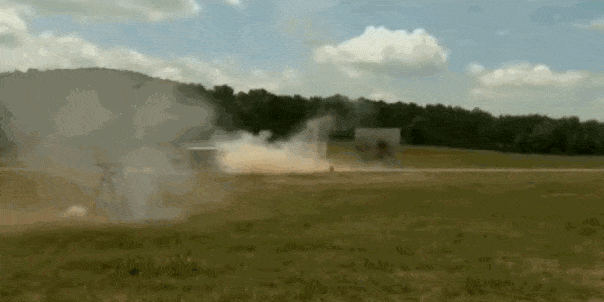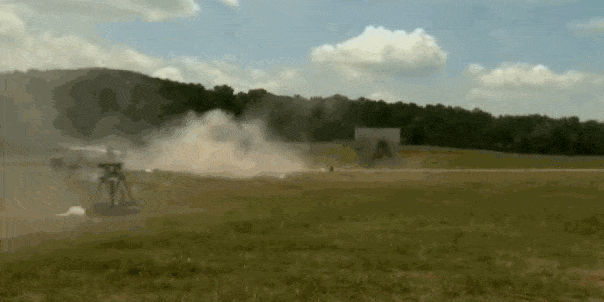
The U.S. Army is testing a system designed to protect military vehicles smaller than tanks from attacks. The “Iron Curtain” uses a combination of sensors and downward-firing projectiles to stop incoming rockets and missiles from striking vehicles by setting off their shaped charge warheads. The result could be vehicles as small Humvees protected from anti-tank guided weapons.
The proliferation of anti-tank weapons with shaped charges has made the modern battlefield very deadly for any vehicle daring to cross it. High explosive, anti-tank (HEAT) warheads are found on everything from shoulder-fired rocket propelled grenade launchers of the Taliban to Kornet-EM anti-tank guided missiles arming the Russian Army. Defeating them is one of the Army’s top concerns, and a brigade of Abrams tanks equipped with the Israeli Trophy active protection system (APS) is headed to Europe in the near future.