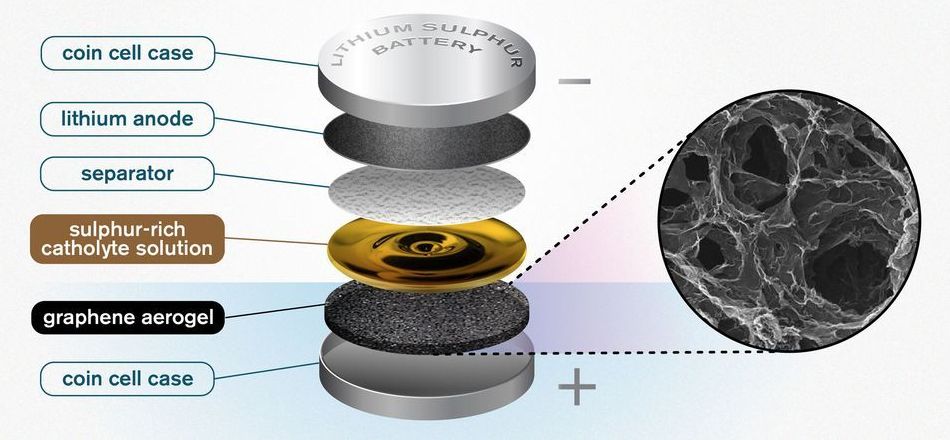
To meet the demands of an electric future, new battery technologies will be essential. One option is lithium sulphur batteries, which offer a theoretical energy density more than five times that of lithium ion batteries. Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, recently unveiled a promising breakthrough for this type of battery, using a catholyte with the help of a graphene sponge.
The researchers’ novel idea is a porous, sponge-like aerogel made of reduced graphene oxide that acts as a free-standing electrode in the battery cell and allows for better and higher utilisation of sulphur.
A traditional battery consists of four parts. First, there are two supporting electrodes coated with an active substance, which are known as an anode and a cathode. In between them is an electrolyte, generally a liquid, allowing ions to be transferred back and forth. The fourth component is a separator, which acts as a physical barrier, preventing contact between the two electrodes whilst still allowing the transfer of ions.
Read more