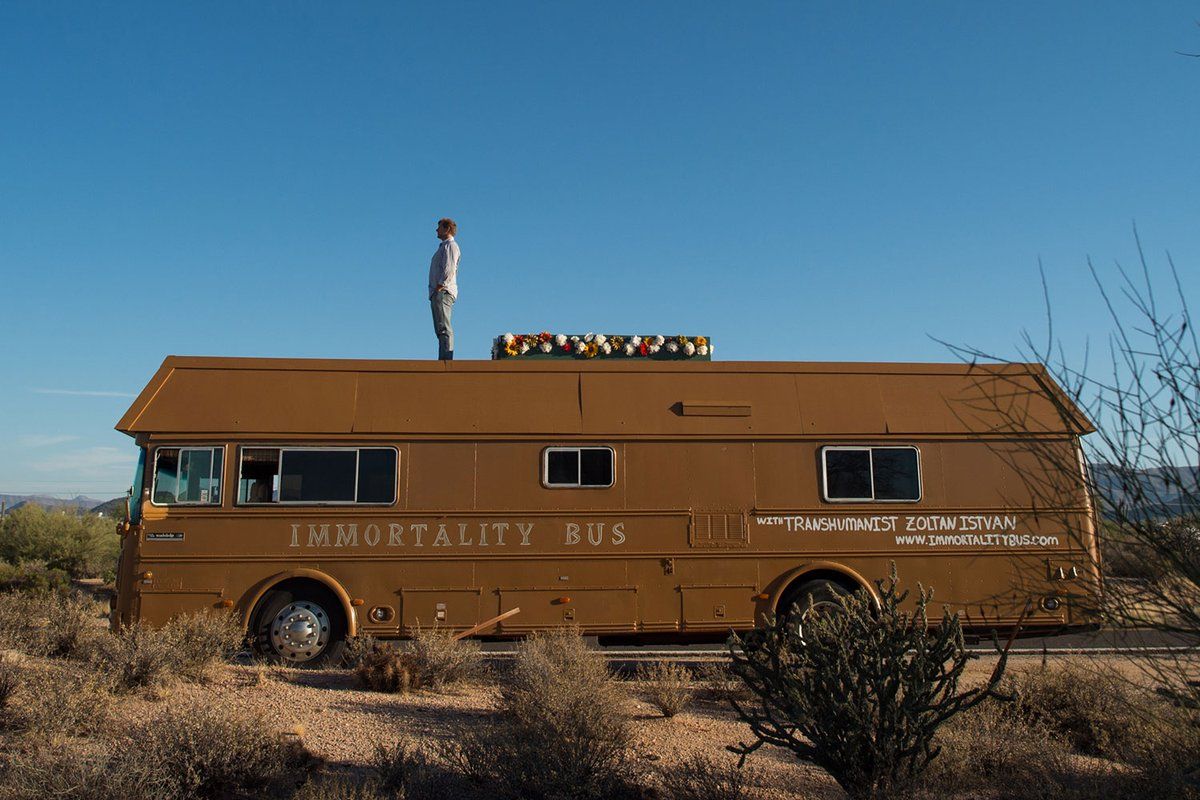
O n a recent evening at a start-up hub in Spitalfields, London, journalist and author Jamie Bartlett spoke to a small group of mostly under 40, mainly techie or creative professionals about his book Radicals: Outsiders Changing the World. The book, which Bartlett started to research in 2014, before Brexit and Trump, chronicles his time with a series of different radical groups, from the Psychedelic Society — who advocate the “careful use of psychedelics as a tool for awakening to the unity and interconnectedness of all things” — to Tommy Robinson, co-founder of the unabashedly far-right English Defence League, to the founder of Liberland, a libertarian nation on unclaimed land on the Serbian/Croatian border, to Zoltan Istvan, who ran as US transhumanist presidential candidate on a platform of putting an end to death. He campaigned by racing around America in a superannuated RV which he’d modified to look like a giant coffin, dubbed “the Immortality Bus.” His efforts were in vain, and illegal, as it turned out: his campaign was in breach of the US’ Federal Electoral Commission rules.
Bartlett’s book has been damned with faint praise — he has been called “surprisingly naive about politics,” and defining ‘radical’ so broadly as to make the term “meaningless.” The general consensus goes that Bartlett’s journey through the farthest-flung fringes of politics and society is entertaining and impressively dispassionate, but not altogether successful in making a clear or convincing case for radicals or radicalism. But at the talk that night Bartlett challenged what he sees as the complacent acceptance and defense of our current political and governmental systems, institutions and ideas, of the kind of technocratic centrism that prevailed throughout the global North until very recently. Perhaps they need some radical rethinking. Many of the radicals Bartlett spent time with may be flawed, crazy or wrong — literally, legally and morally — but they can also hold up mirrors and magnifying glasses to political and social trends. And sometimes, they can prophesize them…
Bartlett began the evening by saying, “If democracy were a business, it would be bankrupt.” A provocative statement, but one that he backs up. He pointed to research showing that only 30% of those born after 1980 believe that it is essential to live in a democracy. That rate drops steadily with age. A closer look at the research around peoples’ attitudes reveals widespread skepticism towards liberal institutions and a growing disaffection with political parties. Freedom House’s annual report for 2016 shows that as faith in democracy has declined so too have global freedoms — 2016 marks the “11th consecutive year of decline in global freedom.” While a lot of attention has been given to violent polarization, populism and nationalism rising out of anger at demographic and economic changes, Bartlett suggests that perhaps comfort and complacency are culprits too, and he is not the only one: only last week Financial Times columnist Janan Ganesh took up a similar theme.
What are the fringe ideas of today that might become ideas of the future? We cannot, of course, say, but Bartlett’s point is we should be paying much closer attention to the crazed hinterlands of human thought. In 2015 transhumanist Zoltan Istvan was talking about using technology to fundamentally change what it is to be human — to augment our fleshy bodies with steel and silicon. One of Istvan’s favored refrains is the transformative effect of artificial intelligence on the way that we work, and the way that we live. In the past six months, it has become near-impossible to read a newspaper or a magazine without stumbling across a take on how AI is set to change our economy. Istvan’s other hobby-horse is immortality, and using technology to drastically expand the human lifespan — ultimately to the point where it increases so fast that time can’t catch up with us and we reach a kind of “escape velocity.
Read more