Changing the destination for more than 1,500 satellites.


Researchers from North Carolina State University and the University of Texas at Austin have developed a technique for detecting types of malware that use a system’s architecture to thwart traditional security measures. The new detection approach works by tracking power fluctuations in embedded systems.
“Embedded systems are basically any computer that doesn’t have a physical keyboard – from smartphones to Internet of Things devices,” says Aydin Aysu, co-author of a paper on the work and an assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering at NC State. “Embedded systems are used in everything from the voice-activated virtual assistants in our homes to industrial control systems like those used in power plants. And malware that targets those systems can be used to seize control of these systems or to steal information.”
At issue are so-called micro-architectural attacks. This form of malware makes use of a system’s architectural design, effectively hijacking the hardware in a way that gives outside users control of the system and access to its data. Spectre and Meltdown are high-profile examples of micro-architectural malware.
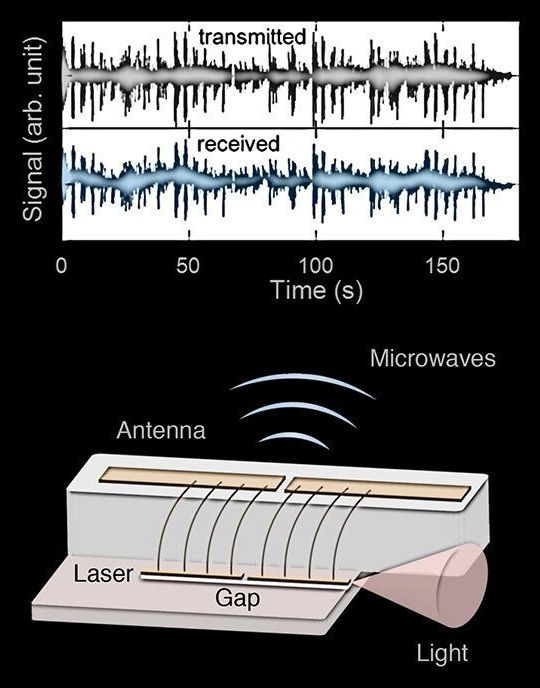
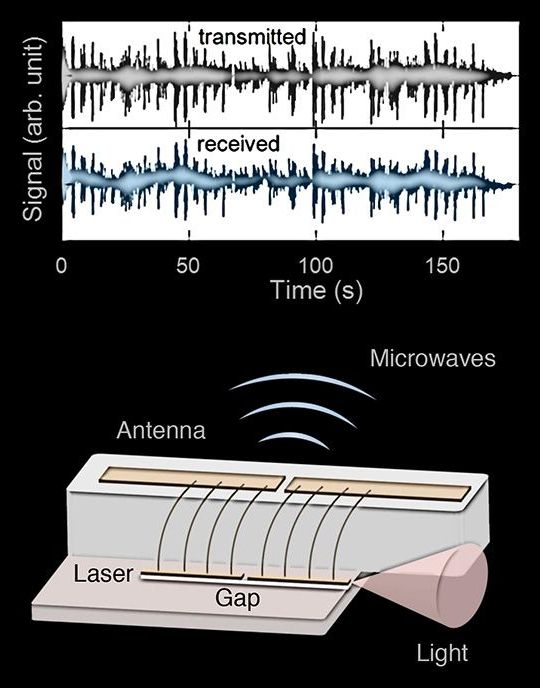
You’ve never heard Dean Martin like this.
Researchers from the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences transmitted a recording of Martin’s classic “Volare” wirelessly via a semiconductor laser—the first time a laser has been used as a radio frequency transmitter.
In a paper published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the researchers demonstrated a laser that can emit microwaves wirelessly, modulate them, and receive external radio frequency signals.

Chinese technology companies are increasingly important and dynamic international actors. They are making critical contributions in a range of areas, from cutting edge research to enabling connectivity for developing countries. Yet, their rapid expansion and growing influence also bring a range of strategic and policy challenges. The Australian Strategic Policy Institute’s International Cyber Policy Centre has created a public database to map the global expansion of 12 key Chinese tech companies working across the telecommunications, internet & biotech sectors. It’s a tool for journalists, researchers, NGOs, policymakers and the interested public to better understand the enormous scale, complexity and increasing reach of some of China’s tech giants. On this website you’ll find:

University of Copenhagen researchers have developed a nanocomponent that emits light particles carrying quantum information. Less than one-tenth the width of a human hair, the miniscule component makes it possible to scale up and could ultimately reach the capabilities required for a quantum computer or quantum internet. The research result puts Denmark at the head of the pack in the quantum race.
Teams around the world are working to develop quantum technologies. The focus of researchers based at the Center for Hybrid Quantum Networks (Hy-Q) at the University of Copenhagen’s Niels Bohr Institute is on developing quantum communication technology based on light circuits, known as nanophotonic circuits. The UCPH researchers have now achieved a major advancement.
“It is a truly major result, despite the component being so tiny,” says Assistant Professor Leonardo Midolo, who has been working towards this breakthrough for the past five years.

Keith Comito, interviewed by Adam Ford at the Undoing Aging 2019 conference in Berlin, discusses why solving the diseases of old age is a powerful cause.
How can solving aging reduce suffering? What are some common objections to the ideas of solving aging? How does Anti-Aging stack up against other cause…
Imagine being able to play a song on your computer just by thinking of its title. Or transmitting your thoughts to a friend over the internet without uttering a word. Scientists have now invented a ‘sewing machine’ capable of stitching electrodes into the brain, which may one day help to make such things a reality.
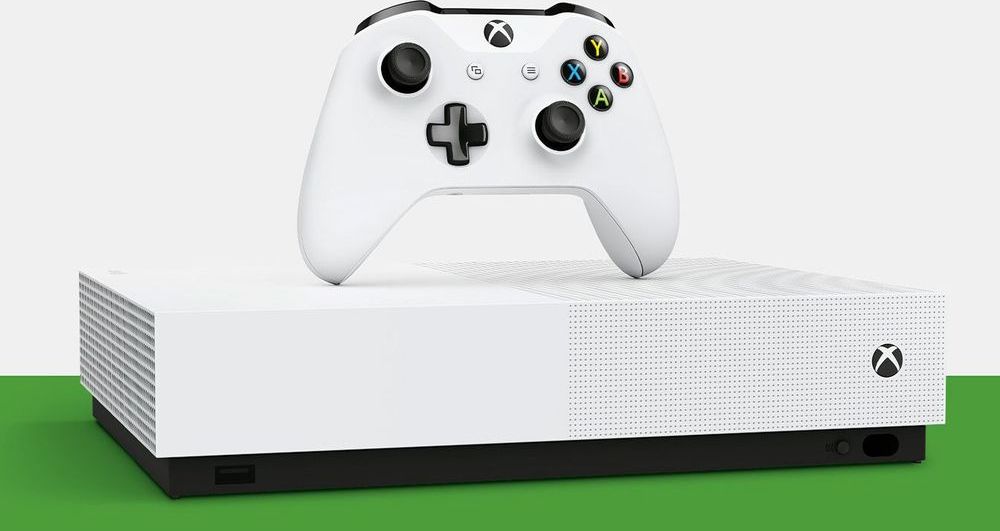

The rumors were true. Microsoft has announced an Xbox variant with no optical disc drive called the Xbox One S All-Digital Edition. It looks the same as any other Xbox One S with the important distinction that there’s no drive slot on the front. Microsoft will push game downloads, and it’s including a few of them free with the console. That might nudge some people to drop $250 on the device when it launches in a few weeks, but the pricing still seems too high.
Without the optical drive, Microsoft’s new game console won’t be able to play your existing game discs or Blu-ray movies. However, any digital Xbox content you own will be available on the All-Digital Edition. This seems mainly like a play to attract new gamers who don’t have a giant library of now-useless discs. It also ties neatly into the recently unveiled Game Pass subscription and xCloud game streaming tech.
The All-Digital Edition console comes with free downloads of Sea of Thieves, Forza Horizon 3, and Minecraft. Microsoft also stresses that all your games, saves, and backups are available in the cloud. You’ll just need a speedy internet connection to access them on short notice. You can at least pre-load new games on the All-Digital Edition to start playing them as soon as they’re live. That might be even faster than popping in a disc that requires installation and patching on launch day.
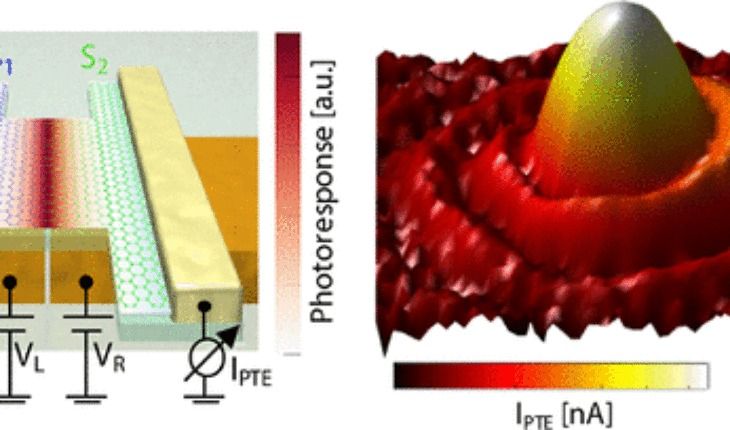
EU researchers have developed a graphene-enabled detector for terahertz light that is faster and more sensitive than existing room-temperature technologies. This can lead to a fully digital low-cost terahertz camera system. This could be as cheap as the camera inside the smartphone, since such a detector has proven to have a very low power consumption and is fully compatible with CMOS technology.
Detecting terahertz (THz) light is extremely useful for two main reasons. Firstly, THz technology is becoming a key element in applications regarding security (such as airport scanners), wireless data communication, and quality control, to mention just a few. However, current THz detectors have shown strong limitations in terms of simultaneously meeting the requirements for sensitivity, speed, spectral range, being able to operate at room temperature.
Secondly, it is a very safe type of radiation due to its low-energy photons, with more than a hundred times less energy than that of photons in the visible light range.