SpaceX called off the launch of its latest Starlink satellite mission Friday (June 26) to allow more time for preflight checks.
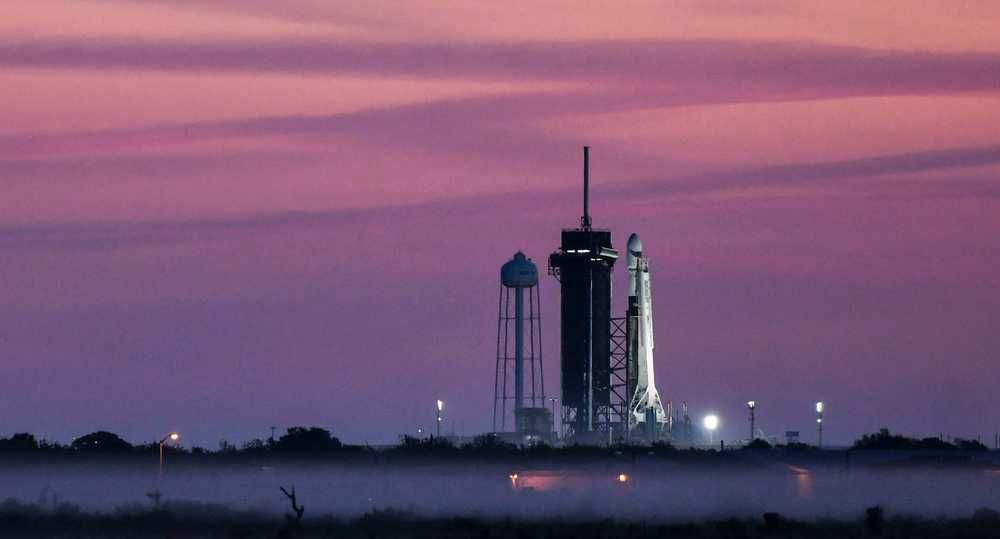





The weather forecast appears to be trending slightly toward favorable conditions for the Space Coast’s next launch from Kennedy Space Center.
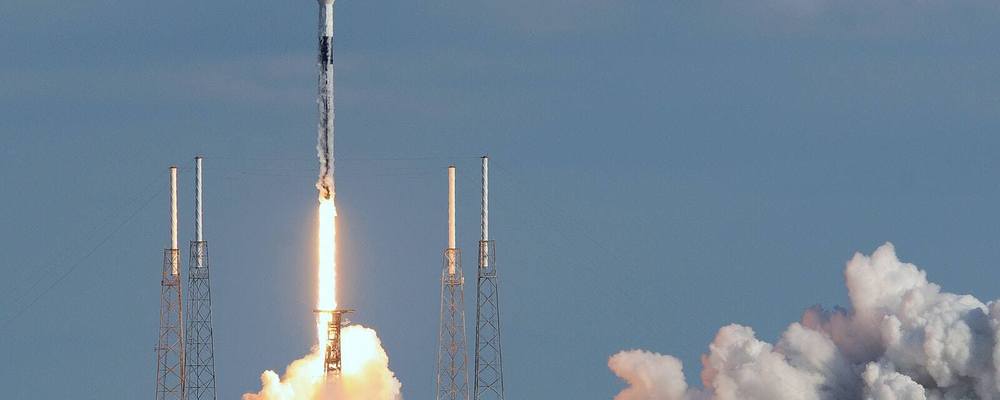
If schedules hold, a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket will likely encounter 60% “go” conditions for its 5:22 p.m. Tuesday liftoff from pad 39A, the Space Force’s 45th Weather Squadron said Saturday. The 230-foot rocket will carry about 60 Starlink satellites for the company’s tenth internet constellation mission.
Showers and thunderstorms are expected Tuesday but should move mostly inland just before the launch time.

Elon Musk’s SpaceX has applied to offer high-speed internet to Canadians living in remote areas by beaming it to them via satellites.
The Globe and Mail newspaper first reported that space exploration company SpaceX applied with Canada’s telecom regulator, the Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission (CRTC), for what’s known as a Basic International Telecommunications Services, or BITS, licence.

Qualcomm today announced its RB5 reference design platform for the robotics and intelligent drone ecosystem. As the field of robotics continues to evolve towards more advanced capabilities, Qualcomm’s latest platform should help drive the next step in robotics evolution with intelligence and connectivity. The company has combined its 5G connectivity and AI-focused processing along with a flexible peripherals architecture based on what they are calling “mezzanine” modules. The new Qualcomm RB5 platform promises an acceleration in the robotics design and development process with a full suite of hardware, software and development tools. The company is making big promises for the RB5 platform, and if current levels of ecosystem engagement are any indicator, the platform will have ample opportunities to prove itself.
Targeting robot and drone designs meant for enterprise, industrial and professional service applications, at the heart of the platform is Qualcomm’s QRB5165 system on chip (SOC) processor. The QRB5165 is derived from the Snapdragon 865 processor used in mobile devices, but customized for robotic applications with increased camera and image signal processor (ISP) capabilities for additional camera sensors, higher industrial grade temperature and security ratings and a non-Package-on-Package (POP) configuration option.
To help bring highly capable artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities to bear in these applications, the chip is rated for 15 Tera Operations Per Second (TOPS) of AI performance. Additionally, as it is critical that robots and drones can “see” their surroundings, the architecture also includes support for up to seven concurrent cameras and a dedicated computer vision engine meant to provide enhanced video analytics. Given the sheer amount of information that the platform can generate, process and analyze, the platform also has support for a communications module boasting 4G and 5G connectivity speeds. In particular, the addition of 5G to the platform will allow high speed and low latency data connectivity to the robots or drones.

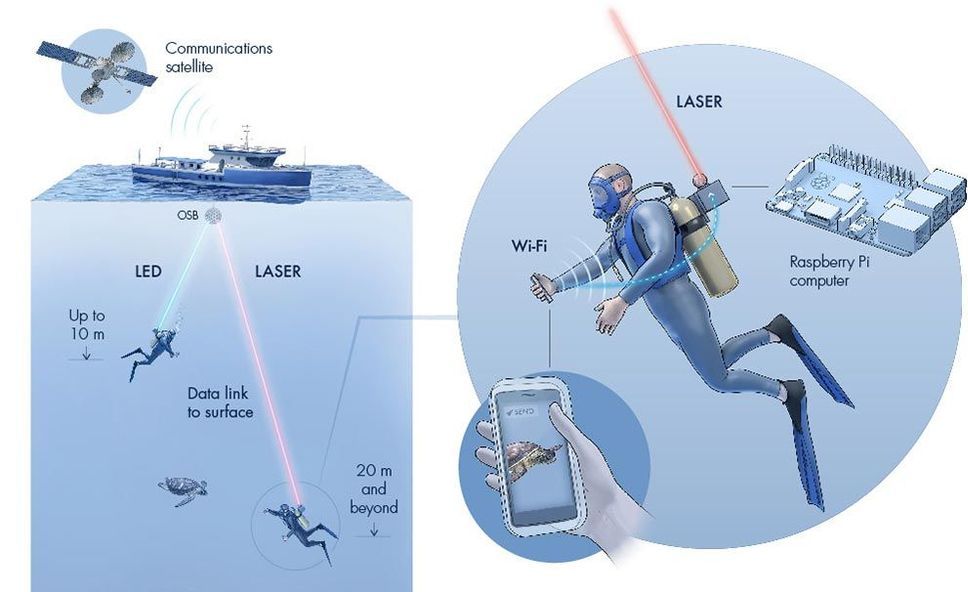
Aquatic internet that sends data through light beams could enable divers to instantly transmit footage from under the sea to the surface.
The internet is an indispensable communication tool, connecting tens of billions of devices worldwide, and yet we struggle to connect to the web from under water. “People from both academia and industry want to monitor and explore underwater environments in detail,” explains the first author, Basem Shihada. Wireless internet under the sea would enable divers to talk without hand signals and send live data to the surface.
Underwater communication is possible with radio, acoustic and visible light signals. However, radio can only carry data over short distances, while acoustic signals support long distances, but with a very limited data rate. Visible light can travel far and carry lots of data, but the narrow light beams require a clear line of sight between the transmitters and receivers.

