Category: innovation

Colliding lasers double the energy of proton beams
Researchers from Sweden’s Chalmers University of Technology and the University of Gothenburg present a new method which can double the energy of a proton beam produced by laser-based particle accelerators. The breakthrough could lead to more compact, cheaper equipment that could be useful for many applications, including proton therapy.
Proton therapy involves firing a beam of accelerated protons at cancerous tumours, killing them through irradiation. But the equipment needed is so large and expensive that it only exists in a few locations worldwide.
Modern high-powered lasers offer the potential to reduce the equipment’s size and cost, since they can accelerate particles over a much shorter distance than traditional accelerators — reducing the distance required from kilometres to metres. The problem is, despite efforts from researchers around the world, laser generated proton beams are currently not energetic enough. But now, the Swedish researchers present a new method which yields a doubling of the energy — a major leap forward.
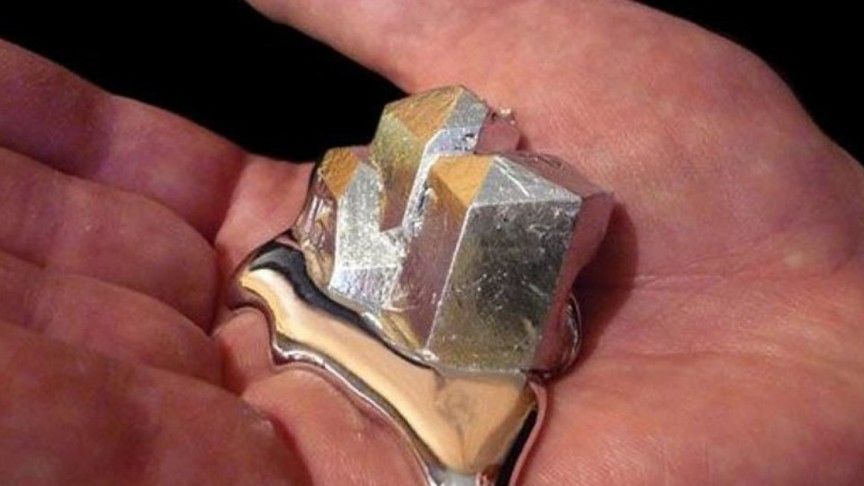

Scientists Have Created Shape Shifting Liquid Metal That Can Be Programmed
In a terrifying breakthrough similar to the metal morphing villain in Terminator 2, scientists at the University of Sussex and Swansea University have discovered a way to apply electrical charges to liquid metal and coax it into 3D shapes such as letters and even a heart.
This discovery has been called an “extremely promising” new kind of material that can be programmed to alter its shape.
Yutaka Tokuda, the Research Associate, working on this project at the University of Sussex, says: “This is a new class of programmable materials in a liquid state which can dynamically transform from a simple droplet shape to many other complex geometry in a controllable manner.
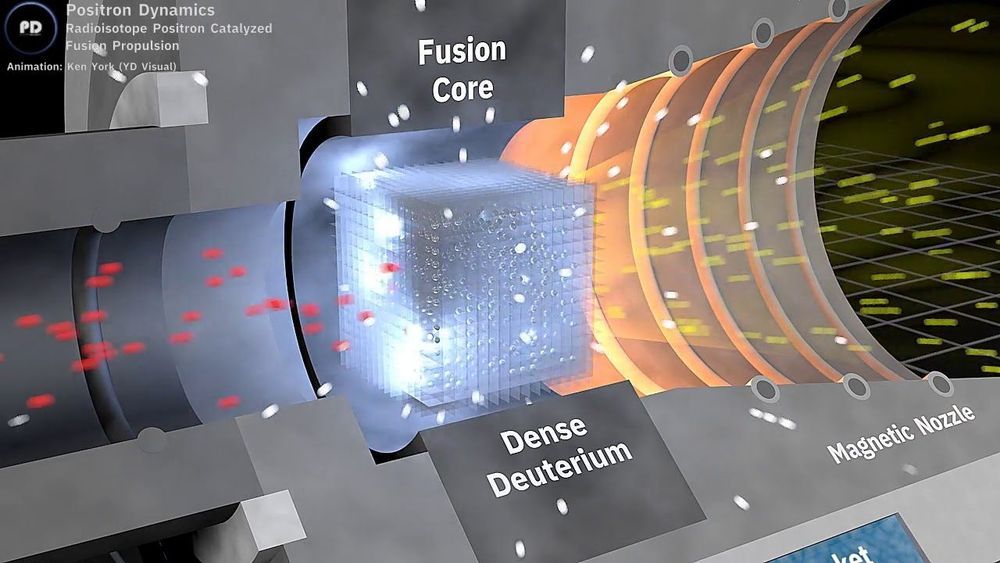
Going 1 Million Miles per Hour With Advanced Propulsion
Advanced propulsion breakthroughs are near. Spacecraft have been stuck at slow chemical rocket speeds for years and weak ion drive for decades. However, speeds over one million miles per hour before 2050 are possible. There are surprising new innovations with technically feasible projects.
NASA Institute for Advanced Concepts (NIAC) is funding two high potential concepts. New ion drives could have ten times better in terms of ISP and power levels ten thousand times higher. Antimatter propulsion and multi-megawatt ion drives are being developed.
Energy-free superfast computing invented by scientists using light pulses
Superfast data processing using light pulses instead of electricity has been created by scientists.
The invention uses magnets to record computer data which consume virtually zero energy, solving the dilemma of how to create faster data processing speeds without the accompanying high energy costs.
Today’s data centre servers consume between 2 to 5% of global electricity consumption, producing heat which in turn requires more power to cool the servers.
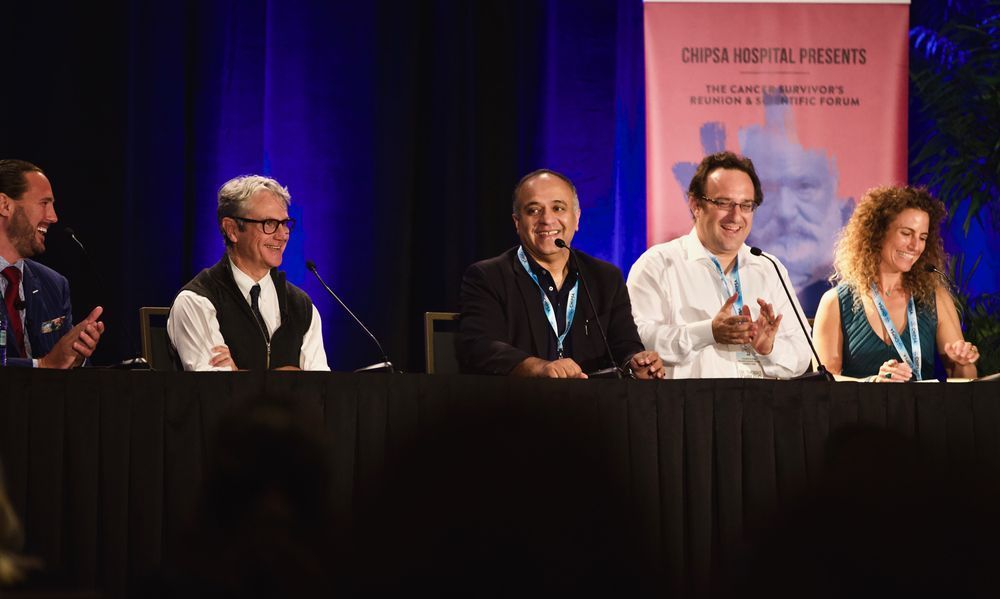

Alternative Cancer Treatments Brought to Legitimacy at Scientific Forum in San Diego
The world recently acknowledged the power of alternative cancer treatments by awarding the 2018 Nobel Prize in Medicine to Dr. James P. Allison and Dr. Tasuku Honjo for their work in immunotherapy. More specifically on checkpoint inhibitor therapies.
Until recently many in the scientific community had dismissed immunotherapy as a viable cancer treatment. Nevertheless, Allison and Honjo persevered and their breakthrough has allowed for the classification of new drugs and treatments that may help patients have run out of options.
Ironically, while many in the mainstream are barely learning of immunotherapy, a hospital in Mexico, CHIPSA Hospital, has been working with these treatments for over 38 year and often under fire from public ridicule that their treatments are strange and ineffective.
For The First Time, Scientists Turn Human Stem Cells Into Insulin-Producing Cells
May have posted this, but this is very cool. “We can now generate insulin-producing cells that look and act a lot like the pancreatic beta cells you and I have in our bodies,” explains one of the team, microphysiologist Matthias Hebrok from the University of California San Francisco (UCSF).
Although treatment of type 1 diabetes has come a long way since it was first described in Ancient Egypt, insulin injections and finger pricks are a daily part of life for many diabetics.
But researchers have just made a breakthrough that might one day make these technologies obsolete, by transforming human stem cells into functional insulin-producing cells (also known as beta cells) – at least in mice.
“We can now generate insulin-producing cells that look and act a lot like the pancreatic beta cells you and I have in our bodies,” explains one of the team, microphysiologist Matthias Hebrok from the University of California San Francisco (UCSF).

