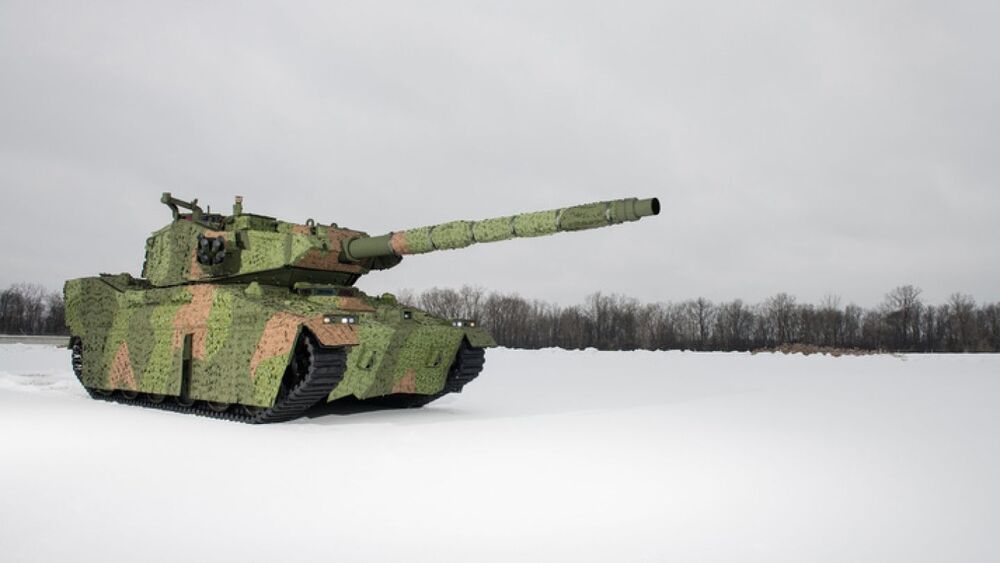
In a press release, the U.S. Army announced that initial Mobile Protected Firepower (MPF) prototypes arrived at Fort Bragg, North Carolina. The preproduction MPF vehicles will be put through their paces by paratroopers from the Army’s 82 Airborne.
“We are incredibly excited to see the MPF platform entering into this phase,” an Army Ground Combat Systems official stated, explaining that the “MPF represents an innovative and aggressive approach to system acquisition. The beginning of our SVA (soldier vehicle assessment) in January illustrates how hard the teams are working to keep the major events of this program on schedule,” despite the ongoing pandemic.
The Army awarded two initial prototyping contracts to both BAE Systems and General Dynamics back in 2018. The contracts, worth $376 million each, covered a total of 504 final production Mobile Protected Firepower vehicles, with initial deliveries scheduled for 2025.