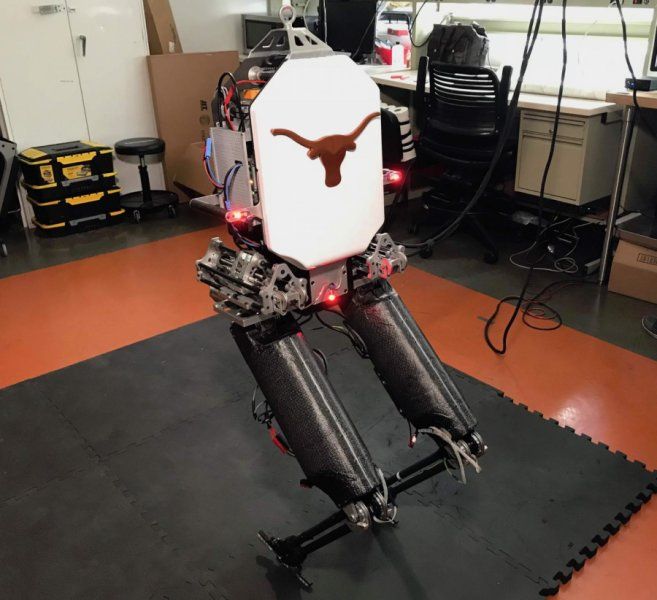
By translating a key human physical dynamic skill — maintaining whole-body balance — into a mathematical equation, the team was able to use the numerical formula to program their robot Mercury, which was built and tested over the course of six years. They calculated the margin of error necessary for the average person to lose one’s balance and fall when walking to be a simple figure — 2 centimeters.
“Essentially, we have developed a technique to teach autonomous robots how to maintain balance even when they are hit unexpectedly, or a force is applied without warning,” Sentis said. “This is a particularly valuable skill we as humans frequently use when navigating through large crowds.”
Sentis said their technique has been successful in dynamically balancing both bipeds without ankle control and full humanoid robots.