Bacillus probiotics health benefits have been until now quite poorly studied in the elderly population. This study aimed to assess the effects of Bacillus subtilis CU1 consumption on immune stimulation and resistance to common infectious disease (CID) episodes in healthy free-living seniors.
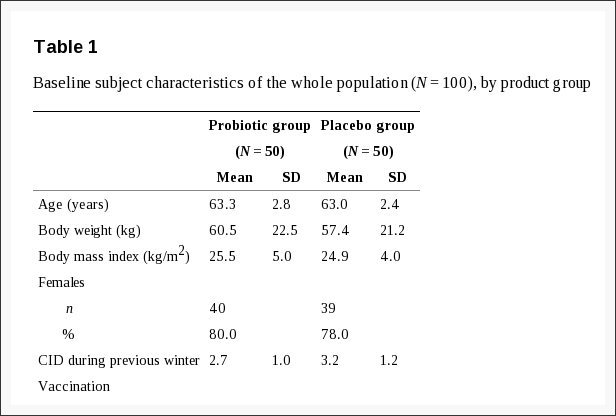
One hundred subjects aged 60–74 were included in this randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-arms study. Subjects consumed either the placebo or the probiotic (2.10B. subtilis CU1 spores daily) by short periodical courses of 10 days intermittently, alternating 18-day course of break. This scheme was repeated 4 times during the study. Symptoms of gastrointestinal and upper/lower respiratory tract infections were recorded daily by the subjects throughout the study (4 months). Blood, saliva and stool samples were collected in a predefined subset of the first forty-four subjects enrolled in the study. B. subtilis CU1 supplementation did not statistically significantly decrease the mean number of days of reported CID symptoms over the 4-month of study (probiotic group: 5.1 (7.0) d, placebo group: 6.6 (7.3) d, P = 0.2015). However, in the subset of forty-four randomized subjects providing biological samples, we showed that consumption of B.