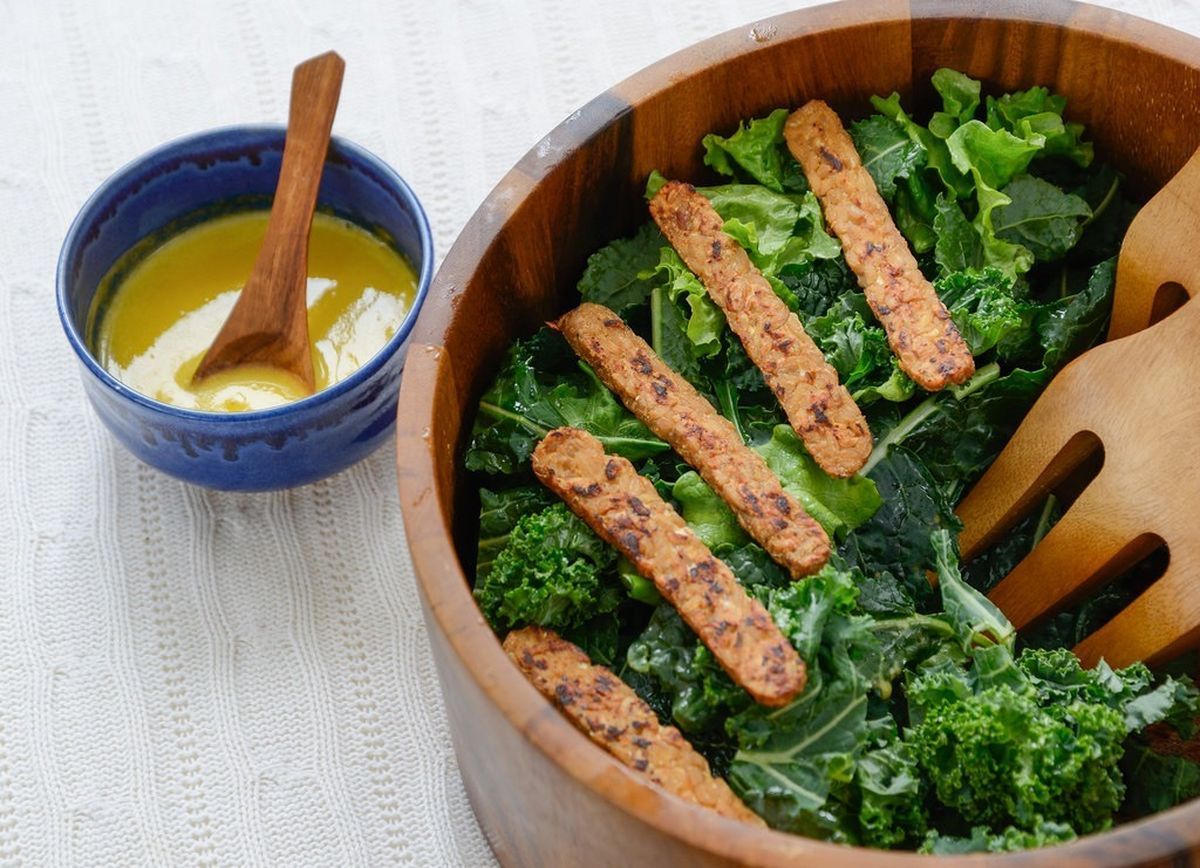
Want to preserve memory? Leafy greens, berries and orange juice may help.



Had a great time with my regenerative biology Q&A session with Ayersville (Ohio, USA) Schools 2nd graders and high school advanced anatomy class — so happy to see kids out there that are interested in these topics at such a young age — creating the future, one mind at a time — https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2_uu9f7nafc

If you asked most people about cadmium they’d probably know very little about it. But it is listed among the World Health Organisation’s ten chemicals of major public health concern, alongside substances such as lead and asbestos. As such, it is concerning to see it in such high quantities in so many household products. The health risk depends on how easily the cadmium can flake off or leach out and additional tests performed indicate that this is greatest for enamelled glassware.
High levels of the carcinogenic chemical cadmium can still be found in everyday household products like second-hand plastic toys, drinking glasses, alcoholic beverage bottles, ceramics and artists’ paints, according to new research by the University of Plymouth.
Cadmium was commonly used to give products a bright red, orange or yellow pigment, but over time the decoration on glass can start to flake and the glaze on ceramics fail.
Writing in Science of the Total Environment, scientists also suggest it is unintentionally finding its way into glass and other items through the recycling process.
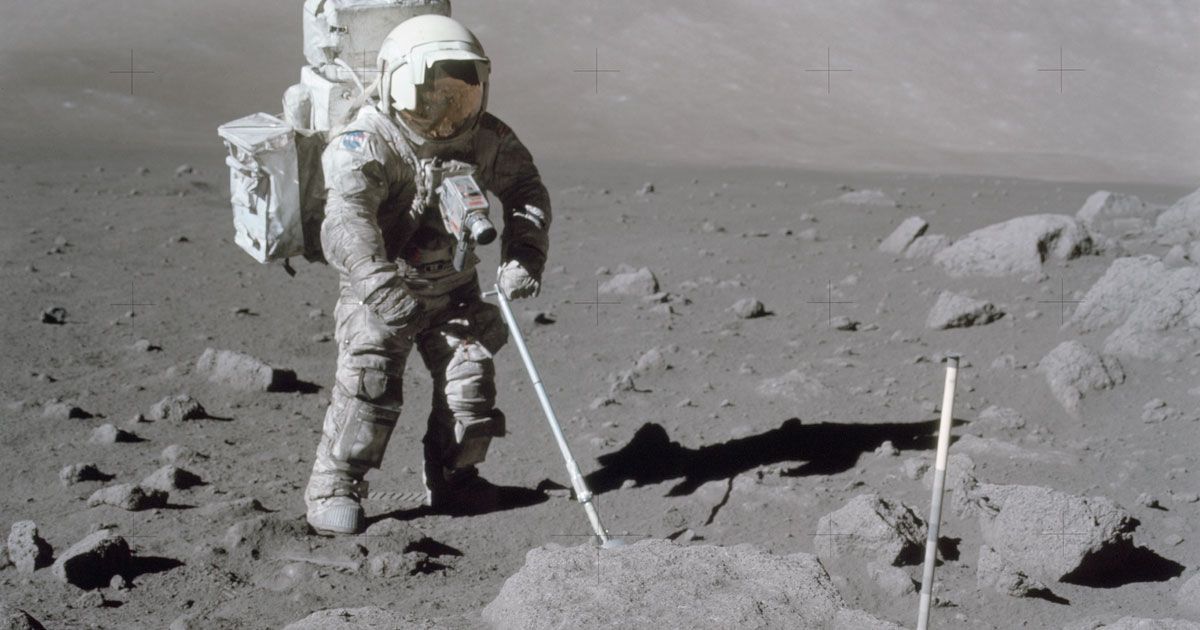

Space agencies are working hard to get humans back to the surface of the Moon. But it’s not exactly the most inviting place.
Astronauts during the Apollo 11 mission in 1969 may not have had any health incidents while they were gleefully bouncing around on the lunar surface, as a NASA mission report from the time points out. But they knew that lunar dust wasn’t their friend — it could irritate their lungs, cause their Moon buggies to overheat — it even started degrading their spacesuits.
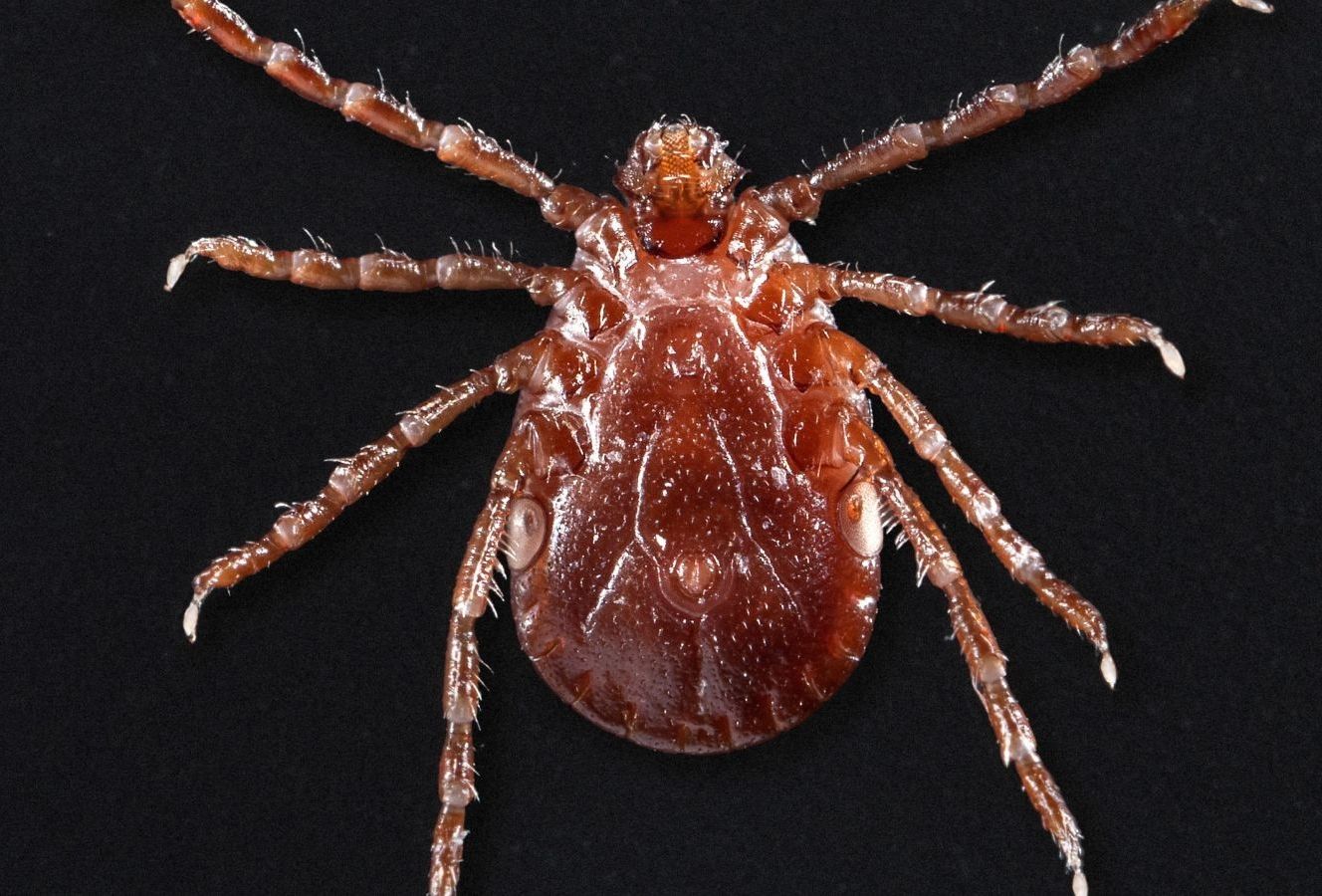

A disease-carrying, newly invasive tick to the United States, the Asian longhorned tick, is poised to spread across much of North America, suggests a new study published Thursday in the Journal of Medical Entomology. According to the study, the tick might be able to live anywhere from Southeastern Canada to most of the eastern half of the U.S. and even parts of the West Coast.
The Asian longhorned tick, or Haemaphysalis longicornis, made an unwelcome splash last year, when researchers and health officials discovered it on a pet sheep in New Jersey. Any hopes that the discovery was an isolated incident faded away this year, with sightings of the tick popping up again in New Jersey and eight other states this past spring and summer (Arkansas, Connecticut, Maryland, New York, North Carolina, Pennsylvania, Virginia, and West Virginia). Since 2017, the tick has been found on pets, farm animals, and at least two people in the U.S., and it’s possible that it might have made its way here at least as early as 2010.

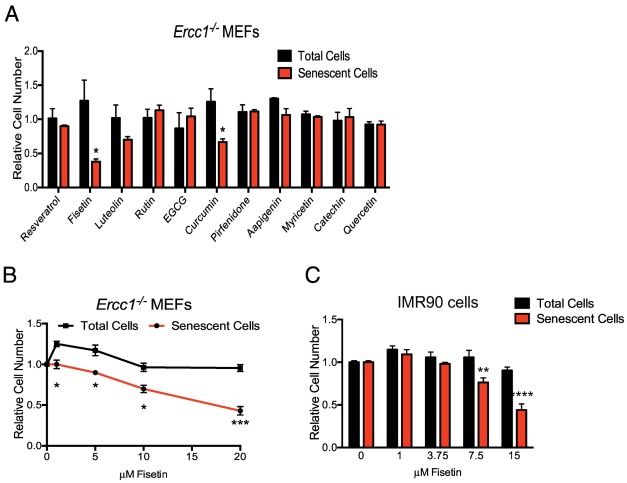
Of the 10 flavonoids tested, fisetin was the most potent senolytic. Acute or intermittent treatment of progeroid and old mice with fisetin reduced senescence markers in multiple tissues, consistent with a hit-and-run senolytic mechanism.
The natural product fisetin has senotherapeutic activity in mice and in human tissues. Late life intervention was sufficient to yield a potent health benefit. These characteristics suggest the feasibility to translation to human clinical studies.