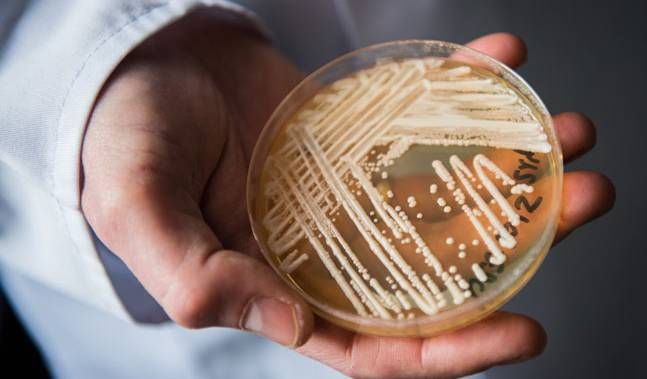
Drug-resistant fungi are appearing around the globe, and some are known to cause illness in humans.


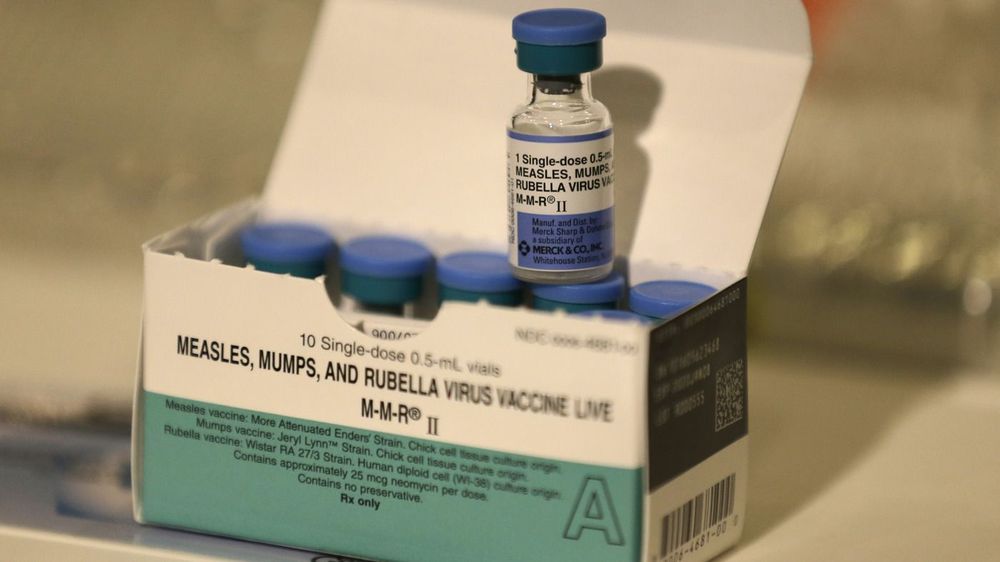
The number of new measles cases in the United States rose again this month, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said on Monday, bringing the total number to 555 in 2019. This year’s outbreak is on course to be the worst since the country eliminated measles as an endemic disease in 2000.
Health authorities reported 90 additional cases as of April 11, with outbreaks in New York, Washington, California, New Jersey and Michigan, up from 78 the week before. Those cases were largely linked to travelers returning from countries seeing outbreaks of their own, including Israel, Ukraine and the Philippines.
The disease then spread through populations in which large numbers of people are unvaccinated, the C.D.C. said.
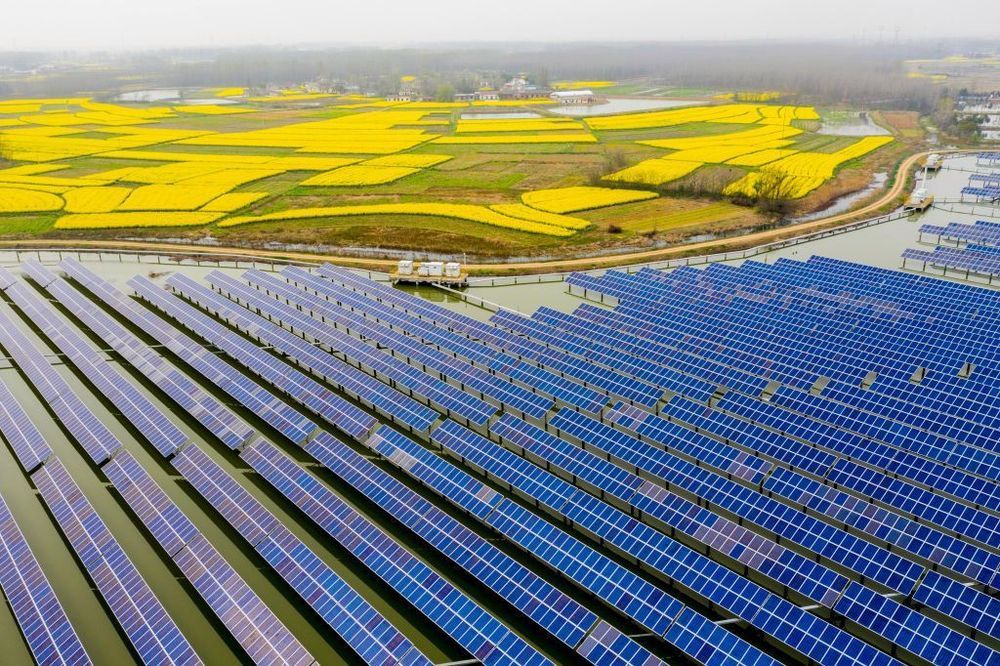


In fact, according to IRENA’s new report, the most cost-effective strategy to achieve a “climate-safe future” — keeping global warming below 2 degrees Celsius (3.6 degrees Fahrenheit) — is an accelerated energy transition to renewables and energy efficiency coupled with electrification of key sectors like transportation.
This Renewable Energy Roadmap (REmap) scenario “would also save the global economy up to USD 160 trillion cumulatively over the next 30 years in avoided health costs, energy subsidies and climate damages.”
At the same time, IRENA reports, “every dollar spent on energy transition would pay off up to seven times.”
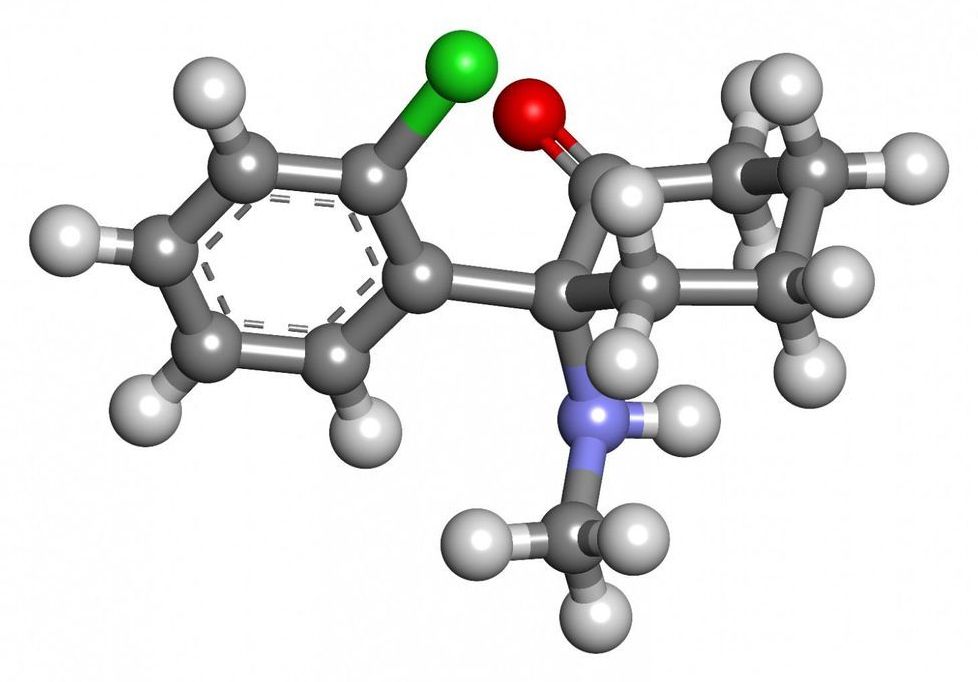
Researchers have identified ketamine-induced brain-related changes that are responsible for maintaining the remission of behaviors related to depression in mice—findings that may help researchers develop interventions that promote lasting remission of depression in humans. The study, funded by the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), part of the National Institutes of Health, appears in the journal Science.
Major depression is one of the most common mental disorders in the United States, with approximately 17.3 million adults experienced a major depressive episode in 2017. However, many of the neural changes underlying the transitions between active depression, remission, and depression re-occurrence remain unknown. Ketamine, a fast-acting antidepressant which relieves depressive symptoms in hours instead of weeks or longer, provides an opportunity for researchers to investigate the short- and long-term biological changes underlying these transitions.
“Ketamine is a potentially transformative treatment for depression, but one of the major challenges associated with this drug is sustaining recovery after the initial treatment,” said study author Conor Liston, M.D., Ph.D., of Weill Cornell Medicine, New York City.

From smog-sucking bikes to electric taxis and paint made of car exhaust, designers and architects are stepping up to address air pollution—the world’s single largest health risk. But a new air filter making the rounds in Oslo, Paris, Brussels, and Hong Kong shows that nature may be our best ally in this battle.
Essentially a moss-covered wall, each CityTree removes CO2, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter from the air while also producing oxygen. A single tree is able to absorb 250 grams of particulate matter a day and remove 240 metric tons of CO2 each year—a level roughly on par with the air purification impact of 275 urban trees. Thirteen feet tall, with a metal frame, the CityTrees are easily installed in a public space, and they even have built-in seating at their base.

Scientists say they’ve developed a new “quantum material” that could one day transfer information directly from human brains to a computer.
The research is in early stages, but it invokes ideas like uploading brains to the cloud or hooking people up to a computer to track deep health metrics — concepts that until now existed solely in science fiction.
New York City on Tuesday ramped up the battle against the spread of a measles outbreak in a Brooklyn hot spot, declaring a public health emergency and calling for mandatory vaccinations.
Mayor Bill de Blasio said the emergency covers four Brooklyn ZIP codes, including most of Williamsburg and Borough Park, which have seen more than 285 cases of the measles since October.
“We cannot allow this dangerous disease to make a comeback here in New York City. We have to stop it now,” de Blasio said at a news conference. “We have a situation now where children are in danger. We have to take this seriously,” he added.

It’s the first-ever quantification of the damage caused by plastic pollution on a global scale.
Global plastic pollution and the damage it causes to marine ecosystems now has a price tag attached to it. A team of researchers from the UK and Norway analyzed the many ways in which plastic pollution damages or destroys natural resources, and came up with a staggering figure – $2.5 billion – as the annual cost to society.
Much of our current understanding about plastic pollution is on a local level that cannot be interpreted easily on a global scale; and yet, this is a global threat. An estimated 8 million tons of plastic enter the oceans annually, and because of its material persistence and ability to disperse widely, must be viewed from a broader perspective if we hope to tackle it effectively. The researchers, whose study was just published in Marine Pollution Bulletin, looked at the many ways in which marine ecosystems benefit the planet, including food provision for billions of people, carbon storage, waste detoxification, and cultural benefits (recreational and spiritual). When these benefits are threatened by the presence of plastic, it “has the potential to significantly impact the wellbeing of humans across the globe, owing to the loss of food security, livelihoods, income and good health.”