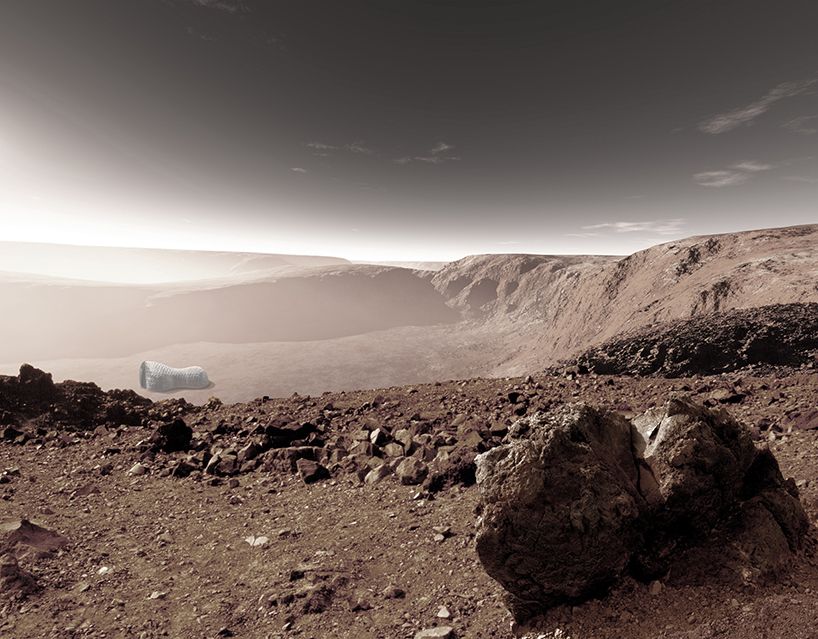
New home proposal for a Martian habitat, designed by marek podlaha and antónia pohanková, uses a prefabricated spaceship as the center of the structure.



More films about China: https://rtd.rt.com/tags/china/
- Technology and innovation hub, Shenzhen is known as China’s “silicon valley” and “the city of the future”.
- Once a fishing village, in just 50 years it grew into a megacity packed with skyscrapers.
- It hosts international technology exhibitions and forums and attracts creators and investors from around the world, contributing to its population boom.
- Inventors and engineers working here, create helpful robots, hybrid cars and smart car parks.
China has a saying; to see the past, visit Beijing, to see the present, go to Shanghai but for the future, it’s Shenzhen. Shenzhen has transformed itself from a tiny fishing village to a megacity in just 50 years, its population tripling since the 1990s. The city is a magnet for tech-savvy and inventive dreamers from all across China and the world, because of them Shenzhen has become the “silicon valley” of China, a true technology and innovation hub.
The sprawling metropolis is famed for its skyscrapers, hybrid cars, solar energy and for being home to a great many hi-tech companies. UBTECH is one of them; its focus is on making robots an indispensable part of everyday life. Its key product is the android – a human-like robot that can help out in the workplace and around the home as well as becoming both teacher and playmate for kids.
Shenzhen municipal government encourages citizens to switch to eco-friendly, hybrid cars that use both fuel and solar energy. The vehicles are made by a local manufacturer, BYD. Public transport here is hybrid too helping maintain the city’s ecological reputation, which is among the best in China. The city’s rapid growth demands new solutions for optimising space. Shenzhen is one of the top 10 cities in the world for having the most skyscrapers. Today, its engineers are working on a solution to the ever present problem of parking by developing smart car parks that can automatically place cars in tight spaces while the driver simply walks away.
The technological achievements of the city’s many companies are regularly showcased at popular international exhibitions and forums.
SUBSCRIBE TO RTD Channel to get documentaries firsthand! http://bit.ly/1MgFbVy
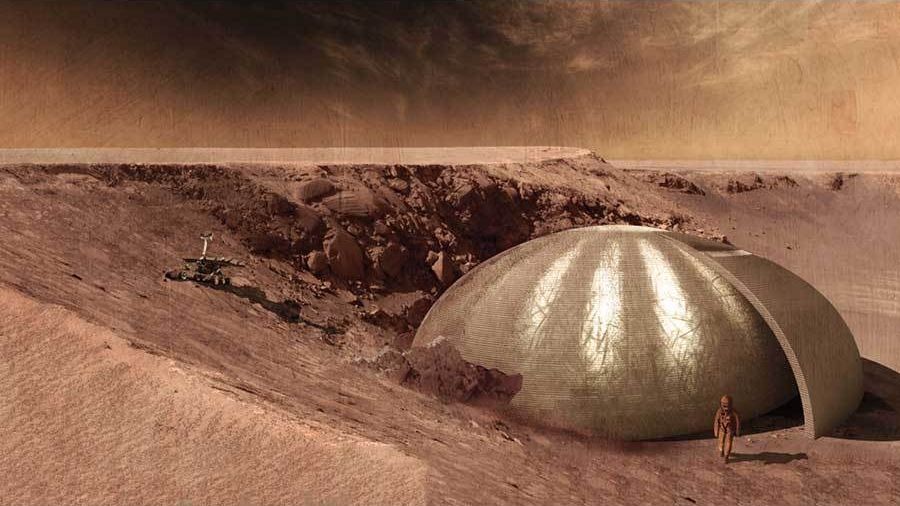

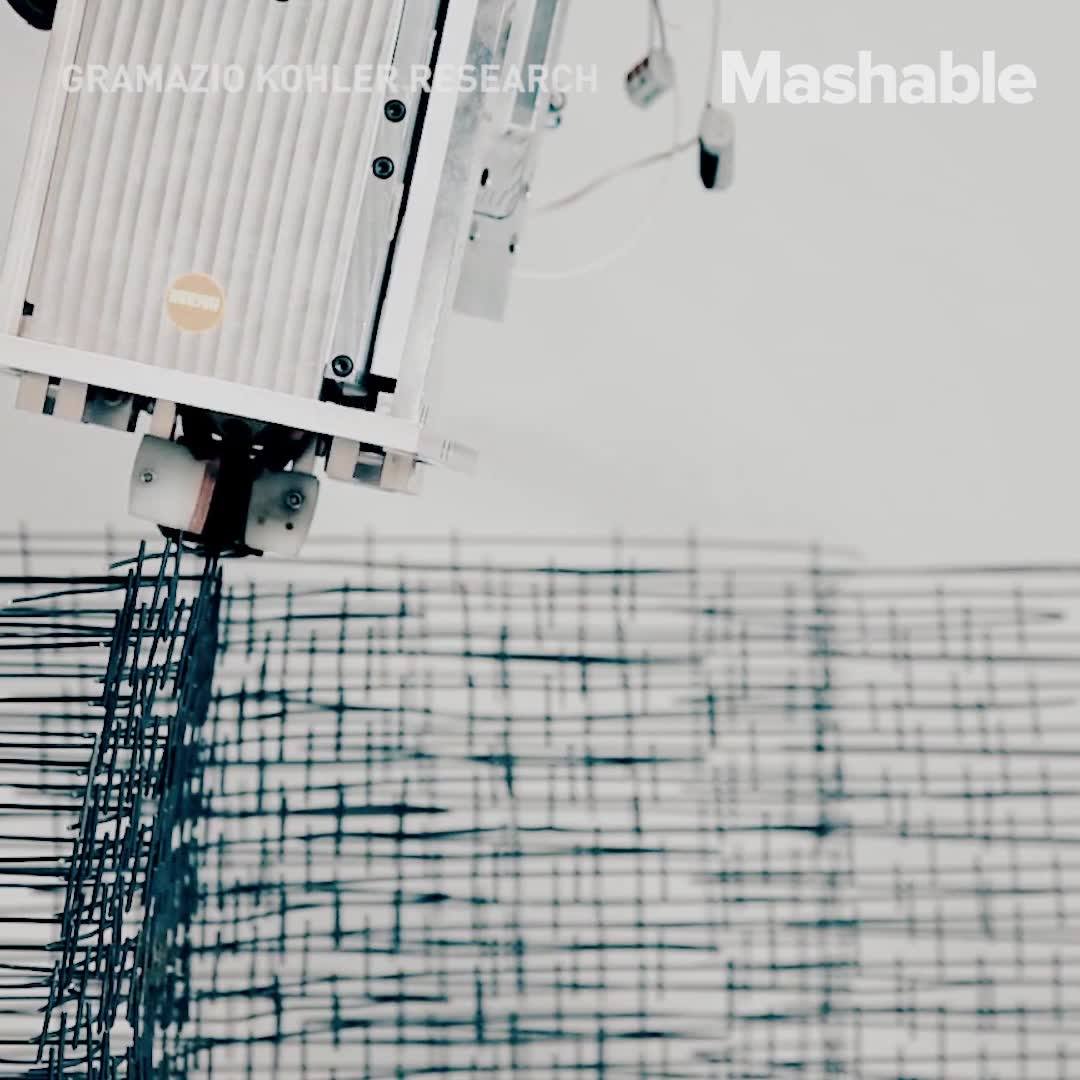
At a test facility in rural Illinois, engineers fabricate structural segments for buildings. But instead of using typical assembly techniques, here at this dirt-floor arena with tightly controlled conditions, teams employ robotic nozzles to extrude domes, beams and cylinders using material chosen for its similarity to the regolith found on the surface of the planet Mars.
The activity comprises part of the 3D-Printed Mars Habitat Design Challenge, which focuses on how to go about building structures on Mars to eventually house human explorers. It’s a component of the NASA Centennial Challenges, a contest series that solicits the public to solve the practical problems of future space exploration. The third phase of the challenge, underway now, focuses on creating stable structural members using an additive manufacturing process based on basaltic rock geologically similar to what is found on Mars.
“This leg of the competition is focused on the materials, specifically the indigenous Mars regolith,” explains Tony Kim, deputy program manager for NASA’s Centennial Challenge. “All of the teams are approaching it differently.” Previous phases of the challenge focused on conceptual designs for habitats and proof-of-concept 3D-printed shapes. But this showdown emphasizes pure structural strength, as the 3D-printed cylinders, beams and domes will be subjected to loading until they fail.
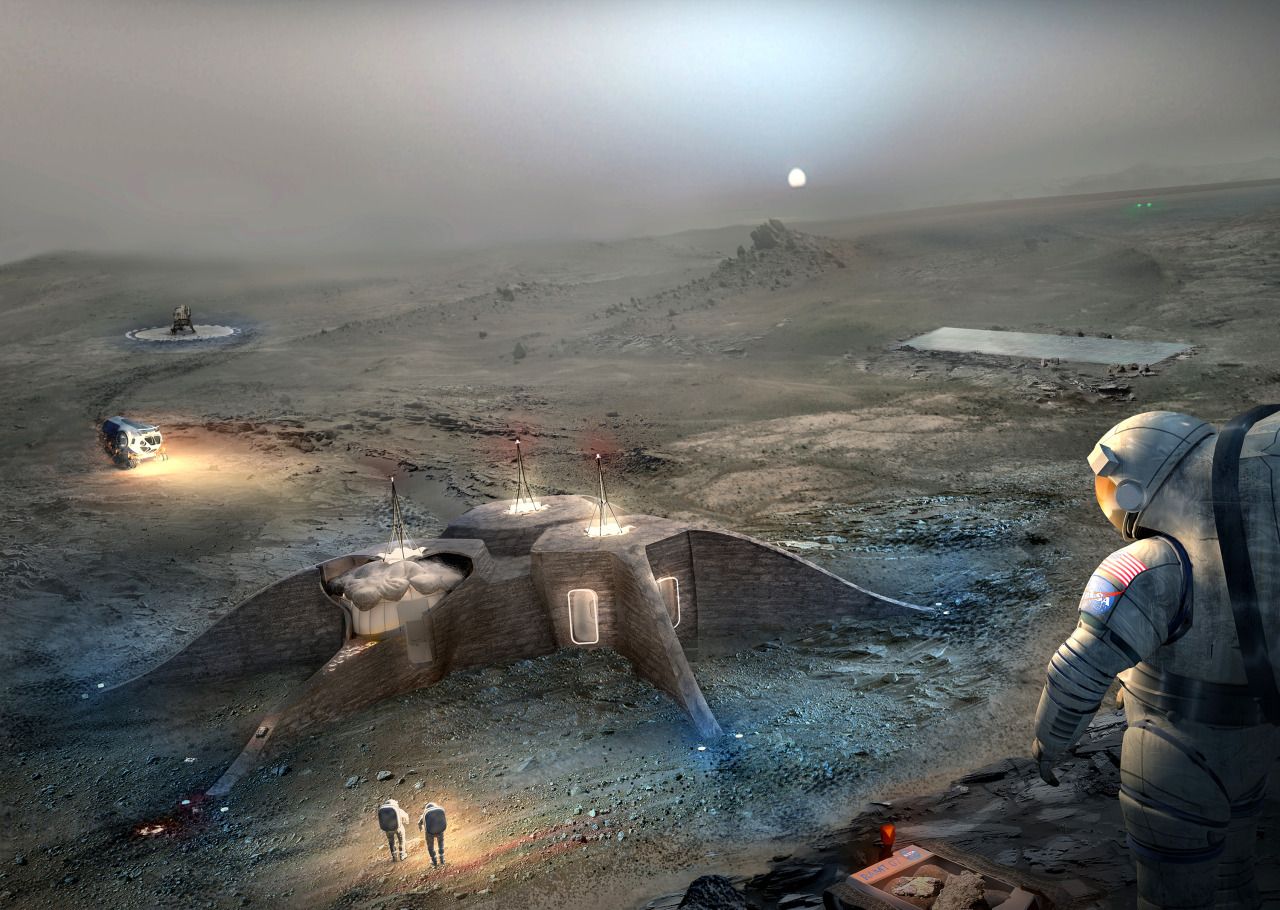

As part of its support for the application 3D printing technology to deep space exploration, NASA has awarded a $250,000 prize to a joint team consisting of members from Foster+Partners California and Branch Technology (based in Chattanooga, Tennessee).
NASA’s competition, which has now reached level three of its second phase, aims to “advance construction technology needed to create sustainable housing solutions for Earth and beyond”, most notably with the aim of accommodating astronauts on Mars and building human colonies in outer space.
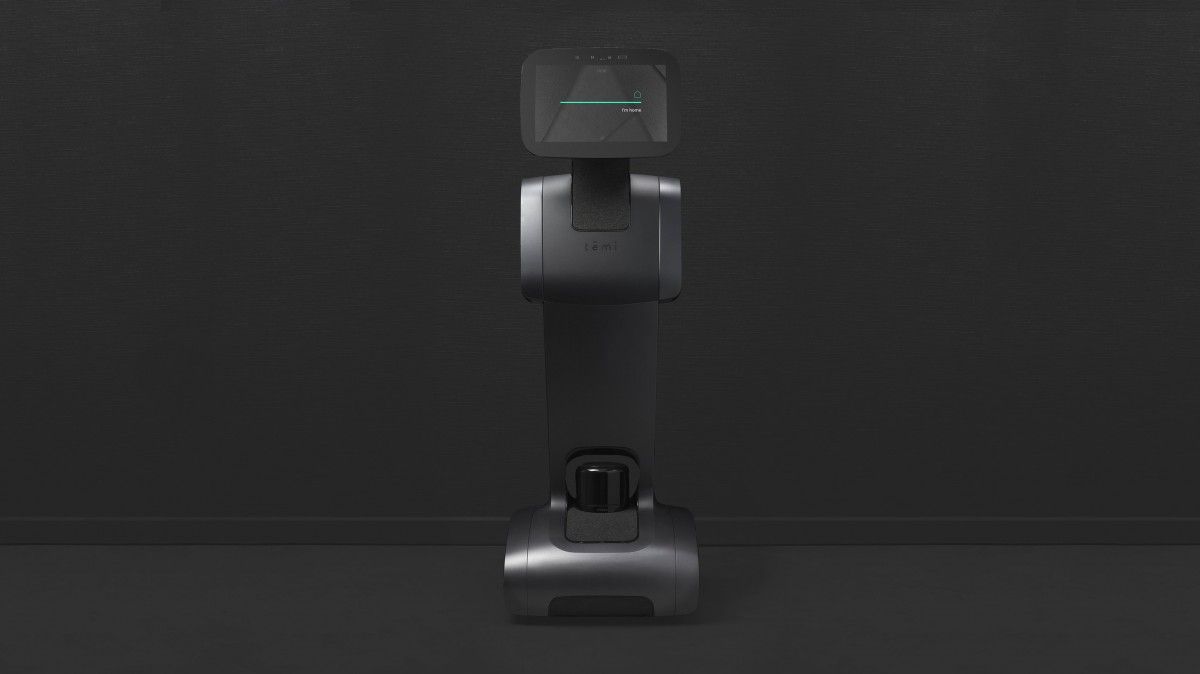

Say hello to Temi. Wired reports that this sleek, 3-foot robot with a tablet for a face is essentially a kind of travelling AI butler for your home—a Siri or Alexa, only on wheels. It will come rolling when you holler. It can use facial recognition to follow people around, so they can watch TV or Skype as they stroll. And it taps Google’s artificial intelligence to help answer your questions. A run of 1,000 robots will be made available November by its maker, Roboteam, and it’s planned to cost under $1,500 when it launches widely next year. But, as we’ve argued in the past, these kinds of domestic robots are more a source of entertainment than much practical use, and are certainly not the kinds of practical machines that may one day be able to take over some of your household chores. For now, you might be better off carrying your phone around the home—especially if you have stairs.

https://youtube.com/watch?v=-5jcq3RlxJQ
Cell by Cell
3D-printing technology has made significant strides over the past several years. What started as a tool for producing small objects can now be used to craft food, build houses, and even construct “space fabric.”
One of the tech’s most impressive applications, however, is the creation of artificial tissues and organs, a process known as 3D bioprinting, and now, a team of researchers from the University of Oxford has developed a new method that takes 3D bioprinting to the next level. They published their work in the journal Nature Communications.
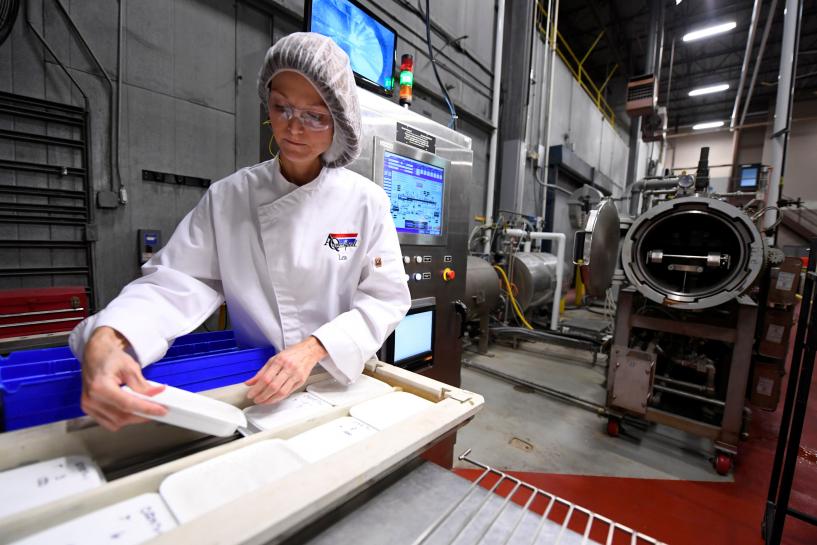

SAN FRANCISCO (Reuters) — Amazon.com Inc is exploring a technology first developed for the U.S. military to produce tasty prepared meals that do not need refrigeration, as it looks for new ways to muscle into the $700 billion U.S. grocery business.
The world’s biggest online retailer has discussed selling ready-to-eat dishes such as beef stew and a vegetable frittata as soon as next year, officials at the startup firm marketing the technology told Reuters.
The dishes would be easy to stockpile and ship because they do not require refrigeration and could be offered quite cheaply compared with take-out from a restaurant.
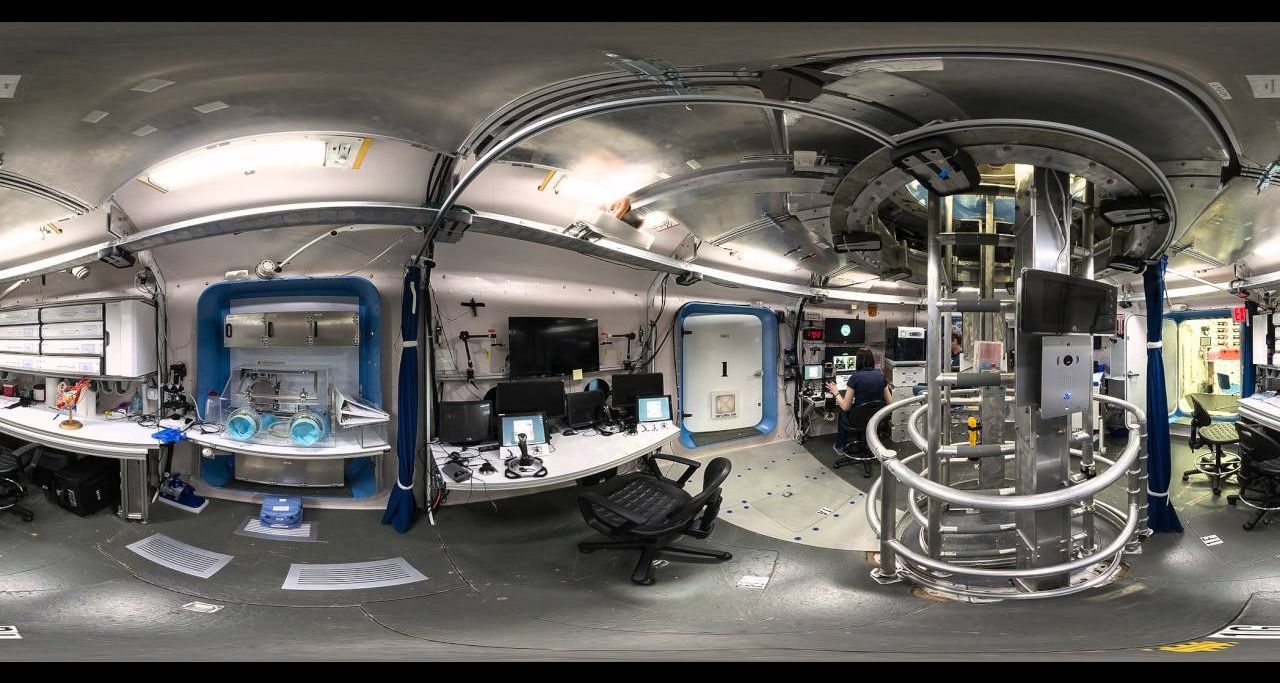

Ever wonder how astronauts will live on other worlds? Welcome to the Human Exploration Research Analog, or HERA, a habitat at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston built to simulate the isolation of missions to deep space. You can take a tour of the HERA habitat with NASA interns in this new video in the style of the MTV series “Cribs.”
“HERA is a unique three-story habitat designed to serve as an analog for isolation, confinement, and remote conditions in exploration scenarios,” NASA officials explained in a video description. “This video gives a tour of where crew members live, work, sleep, and eat during the analog missions.”

Nextbigfuture wrote about the designs for an improved nuclear thermal rocket by John Bucknell. John has worked as a senior engineer on the SpaceX Raptor rocket. John provides high quality qualified work to his rocket designs and to his proposed space habitat.
Nextbigfuture comments had some technical observations about Project Timberwind and a comment from John himself that his design improves on flaws in the last major nuclear thermal rocket experiments. There were also comments and discussion about Star Trek and communism and O’Neill space stations.
Reddit futurology had two comments. One positive comment by the submitter and a negative comment complaining that the factual title was hype./a The title was trying to condense the concept that John’s habitat would have full Earth gravity and full radiation shielding. Colonies on the surface of Mars would have 38% of Earth gravity and colonies on the surface of the moon would have 16% of Earth gravity. Living in the current International space station is a microgravity environment with more radiation. It is well known that long term exposure to lower gravity is a problem. Muscles weaken bones thin out stress is placed on blood vessels Serious effort is needed to exercise while in low gravity to reduce effects and physiotherapy is needed to recover from the stays in orbit or on the Moon where there is low or no-gravity. Yet the title “Constructing full earth like conditions in Space with technology proven in the sixties” is claimed to be hype.