This is what the first Mars colony could be living in 🔴 🚀.
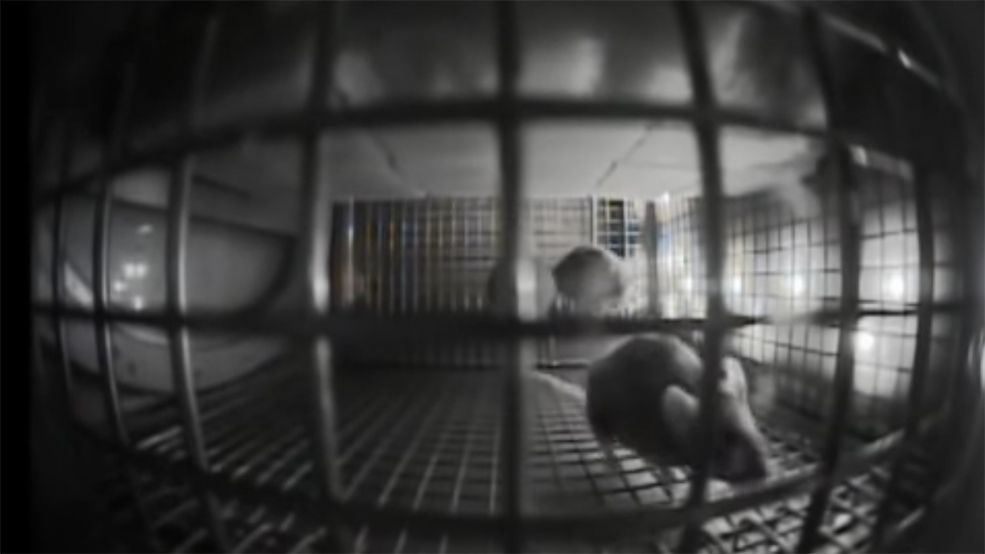



The behavior of 20 mice on the International Space Station is helping shed some light on how humans might adapt to living in space.
The female mice were flown out on the International Space Station aboard an uncrewed SpaceX Dragon capsule and spent up to 37 days floating in NASA’s Rodent Habitat. Video footage show that the mice immediately began their usual grooming, feeding, huddling and socializing, but within 10 days of leaving Earth, younger mice began to run in circles around their cage.


Most Hackaday readers are no doubt familiar with the Faraday cage, at least in name, and nearly everyone owns one: if you’ve ever stood watching a bag of popcorn slowly revolve inside of a microwave, you’be seen Michael Faraday’s 1836 invention in action. Yet despite being such a well known device, the average hacker still doesn’t have one in their arsenal. But why?
It could be that there’s a certain mystique about Faraday cages, an assumption that their construction requires techniques or materials outside the realm of the home hacker. While it’s true that building a perfect Faraday cage for a given frequency involves math and careful attention to detail, putting together a simple model for general purpose use and experimentation turns out to be quick and easy.
As an exercise in minimalist hacking I recently built a basic Faraday cage out of materials sourced from Home Depot, and thought it would be interesting to not only describe its construction but give some ideas as to how one can put it to practical use in the home lab. While it’s hardly a perfect specimen, it clearly works, and it didn’t take anything that can’t be sourced locally pretty much anywhere in the world.
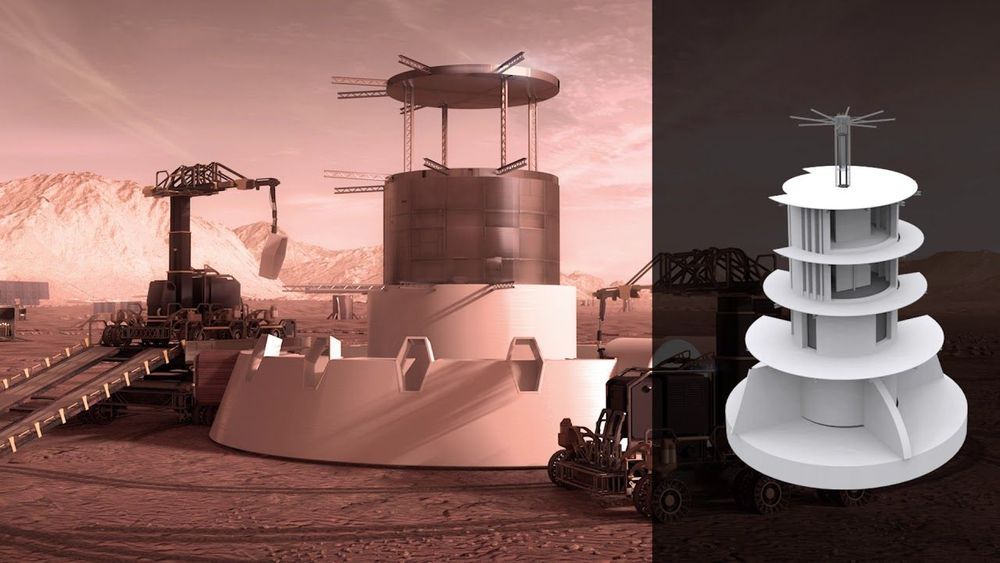
It’s a fascinating competition that paints an incredibly detailed picture of what the future of Moon or even Mars exploration could look like one day — and we’ve never been closer to that future.
READ MORE: Top Three Teams Share $100,000 Prize in Complete Virtual Construction Level of 3D-Printed Habitat Challenge [NASA]
More on the Challenge: Here Are The Finalists For NASA’s Mars Habitat Design Competition.

Climate change is a sprawling, complex problem. But there is an astonishingly simple way to make a difference: plant more trees. Trees scrub pollution from the air, reduce erosion, improve water quality, provide homes for animals and insects, and enhance our lives in countless other ways.
It turns out that ecosystem restoration is also an emerging business opportunity. A new report from the World Resources Institute and the Nature Conservancy says governments around the world have committed to reviving nearly 400 million acres of wilderness — an area larger than South Africa. As countries push to regrow forests, startups are dreaming up new, faster ways to plant trees. For some innovators, like NASA veteran Dr. Lauren Fletcher, that means using drones.
Fletcher said his conversion from stargazer to eco-warrior was driven by his worry about climate change, which has been dramatically worsened by deforestation. To tackle the problem, he created BioCarbon Engineering, which he describes as an ecosystem restoration company. Working with colleagues, he came up with a 30-pound unmanned aerial vehicle nicknamed “Robin.” It can fly over the most rugged landscapes on earth, planting trees in precise locations at the rate of 120 per minute.

SILVER SPRING, Md. — Blue Origin has studied repurposing upper stages of its future New Glenn launch vehicle to serve as habitats or for other applications as part of a series of NASA-funded commercialization studies.
Brett Alexander, vice president of government sales and strategy at Blue Origin, said the company looked at ways it could make use of the second stage of New Glenn rather than simply deorbiting the stage at the end of each launch, but emphasized the company currently had no firm plans to reuse those stages at this time.
That study was part of a series of study contracts awarded by NASA last August to study future concepts to support commercial human spaceflight in low Earth orbit. “We focused there on the reuse of the second stage of New Glenn and what we might be able to do with that volume and capacity once we’re on orbit,” he said during a panel discussion about low Earth orbit commercialization at the American Astronautical Society’s Goddard Memorial Symposium here March 20.


Marine microorganisms in the Southern Ocean may find themselves in a deadly vise grip by century’s end as ocean acidification creates a shallower horizon for life, new University of Colorado Boulder research finds.
The modeling study, published today in the journal Nature Climate Change, forecasts that at current carbon dioxide emission rates, the depth at which some shelled organisms can survive will shrink from an average of 1,000 meters today to just 83 meters by the year 2100, a drastic reduction in viable habitat.
The steep drop, which could happen suddenly over a period as short as one year in localized areas, could impact marine food webs significantly and lead to cascading changes across ocean ecosystems, including disruptions of vital global fisheries.