Sharing for fellow researchers and others who have interest in GBM news.
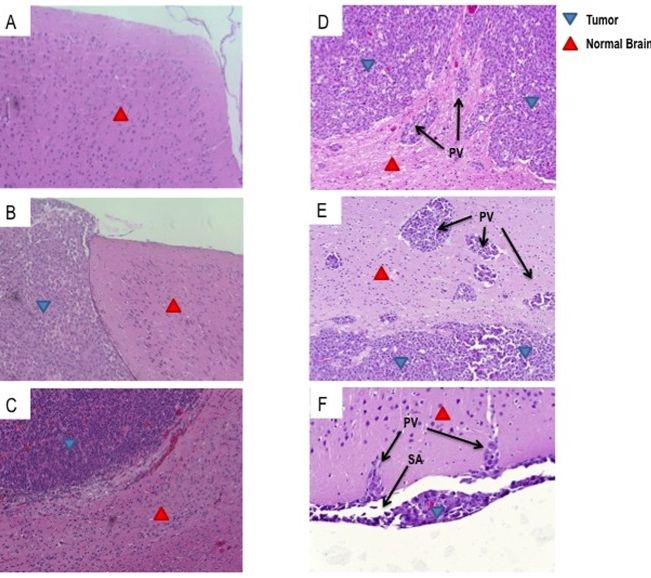
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most common primary malignant brain tumor in adults and is uniformly lethal. T-cell-based immunotherapy offers a promising platform for treatment given its potential to specifically target tumor tissue while sparing the normal brain. However, the diffuse and infiltrative nature of these tumors in the brain parenchyma may pose an exceptional hurdle to successful immunotherapy in patients. Areas of invasive tumor are thought to reside behind an intact blood brain barrier, isolating them from effective immunosurveillance and thereby predisposing the development of “immunologically silent” tumor peninsulas. Therefore, it remains unclear if adoptively transferred T cells can migrate to and mediate regression in areas of invasive GBM. One barrier has been the lack of a preclinical mouse model that accurately recapitulates the growth patterns of human GBM in vivo. Here, we demonstrate that D-270 MG xenografts exhibit the classical features of GBM and produce the diffuse and invasive tumors seen in patients. Using this model, we designed experiments to assess whether T cells expressing third-generation chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) targeting the tumor-specific mutation of the epidermal growth factor receptor, EGFRvIII, would localize to and treat invasive intracerebral GBM. EGFRvIII-targeted CAR (EGFRvIII+ CAR) T cells demonstrated in vitro EGFRvIII antigen-specific recognition and reactivity to the D-270 MG cell line, which naturally expresses EGFRvIII. Moreover, when administered systemically, EGFRvIII+ CAR T cells localized to areas of invasive tumor, suppressed tumor growth, and enhanced survival of mice with established intracranial D-270 MG tumors. Together, these data demonstrate that systemically administered T cells are capable of migrating to the invasive edges of GBM to mediate antitumor efficacy and tumor regression.
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most common form of primary malignant brain tumor in adults and remains one of the most deadly neoplasms. Despite multimodal therapy including maximal surgical resection, radiation, and temozolomide (TMZ), the median overall survival is less than 15 months [1]. Moreover, these therapies are non-specific and are ultimately limited by toxicity to normal tissues [2]. In contrast, immunotherapy promises an exquisitely precise approach, and substantial evidence suggests that T cells can eradicate large, well-established tumors in mice and humans [3] –[7].
Chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) represent an emerging technology that combines the variable region of an antibody with T-cell signaling moieties, and can be genetically expressed in T cells to mediate potent, antigen-specific activation. CAR T cells carry the potential to eradicate neoplasms by recognizing tumor cells regardless of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) presentation of target antigen or MHC downregulation in tumors, factors which allow tumor-escape from treatment with ex vivo expanded tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) [8] and T-cell receptor (TCR) gene therapy [9], [10].
Read more