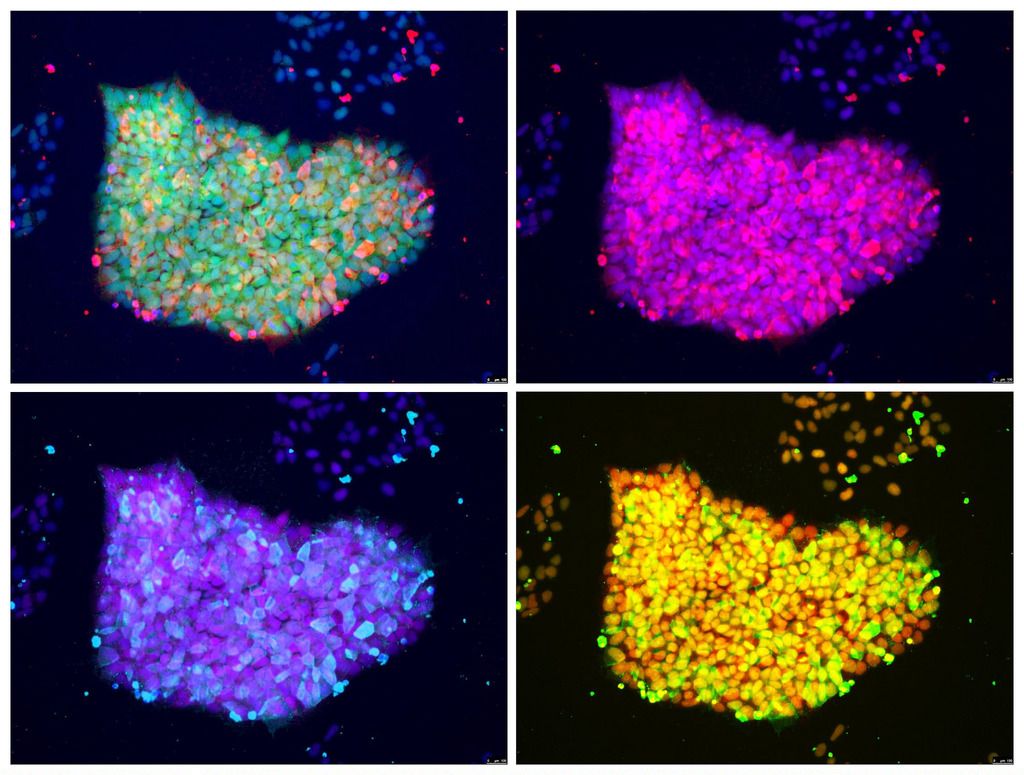
Researchers from North Carolina State University, the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University have developed a synthetic version of a cardiac stem cell. These synthetic stem cells offer therapeutic benefits comparable to those from natural stem cells and could reduce some of the risks associated with stem cell therapies. Additionally, these cells have better preservation stability and the technology is generalizable to other types of stem cells.
Stem cell therapies work by promoting endogenous repair; that is, they aid damaged tissue in repairing itself by secreting “paracrine factors,” including proteins and genetic materials. While stem cell therapies can be effective, they are also associated with some risks of both tumor growth and immune rejection. Also, the cells themselves are very fragile, requiring careful storage and a multi-step process of typing and characterization before they can be used.
Ke Cheng, associate professor of molecular biomedical sciences at NC State, associate professor in the joint biomedical engineering program at NC State and UNC, and adjunct associate professor at the UNC Eshelman School of Pharmacy, led a team in developing the synthetic version of a cardiac stem cell that could be used in off-the-shelf applications.
Read more