Researchers hope to create a new “green revolution” by improving photosynthesis.


Burdening occurrence of dengue fever across the Asia-Pacific region has prompted the demand for effective vaccines and medications to supress this viral malaise. While several pharmaceutical companies are striving to develop a cure for dengue, the fever’s incidence rate in Asia-Pacific is rising at an alarming rate. A recent report published by Future Market Insights predicts that in 2017, an estimated 70.3% of global dengue vaccines market will be dominated by Asia-Pacific. Through 2027, the region will continue to be the largest market for dengue vaccines, procuring a majority revenue share and projecting revenue growth at a 17.4% CAGR.
Request to View Sample of Research Report @ https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/sample/rep-gb-1763
Future Market Insights also observes Latin America as the second-largest market for dengue vaccines, and is expected to rake in US$ 288.7 Mn towards the end of 2027. The report, titled “Dengue Vaccines Market: Global Industry Analysis and Opportunity Assessment, 2017–2027,” expects that more and more pharmaceutical giants from across the globe will be partaking in the market’s growth in the years to come. Currently, the market is witnessing active participation of French drugmaker, Sanofi S.A., while vaccines being formulated by companies such as Biological E. Limited, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, GlaxoSmithKline plc, Merck & Co. Inc., Vabiotech, Butantan Institute, and Panacea Biotech Ltd. are under multiple phases of development.



Why do protected areas have to be interconnected?
With its annual report “Environment Frontiers”, the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) outlines the challenges that will have a decisive influence on the natural foundations of life on our planet in the future. In their report 2018/2019, the authors call “Ecological Networking: Bridges to Greater Biodiversity” one of the great challenges of the future.



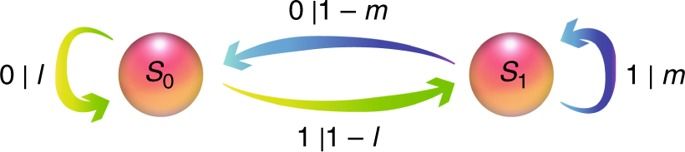
Simulations of stochastic processes play an important role in the quantitative sciences, enabling the characterisation of complex systems. Recent work has established a quantum advantage in stochastic simulation, leading to quantum devices that execute a simulation using less memory than possible by classical means. To realise this advantage it is essential that the memory register remains coherent, and coherently interacts with the processor, allowing the simulator to operate over many time steps. Here we report a multi-time-step experimental simulation of a stochastic process using less memory than the classical limit. A key feature of the photonic quantum information processor is that it creates a quantum superposition of all possible future trajectories that the system can evolve into. This superposition allows us to introduce, and demonstrate, the idea of comparing statistical futures of two classical processes via quantum interference. We demonstrate interference of two 16-dimensional quantum states, representing statistical futures of our process, with a visibility of 0.96 ± 0.02.
