Improvements help the technique rival x-ray crystallography.





Are we governed by donkeys? COP26 was just a farce of vested interests kissing the butts of fossil fuel legacy industries that are so out of date that they cannot compete anymore and need underhand, secret handshake deals just to keep themselves in the luxury they enjoy…at our expense. So here is my Manifesto for the next decade. It is time to start voting for the right people and harassing your representatives to get them to make the right decisions that will benefit the majority, not a few CEO’s who are so corrupt it is like the plot of a new film…
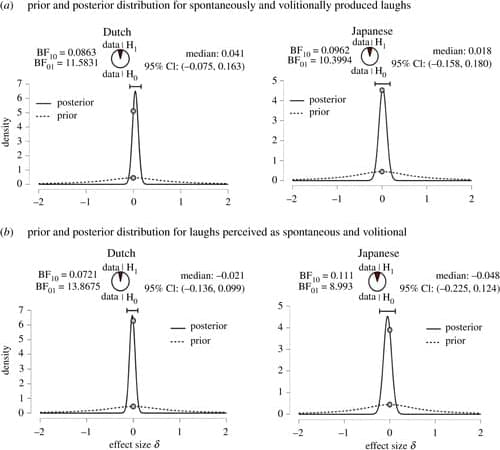
Laughter is a ubiquitous social signal. Recent work has highlighted distinctions between spontaneous and volitional laughter, which differ in terms of both production mechanisms and perceptual features. Here, we test listeners’ ability to infer group identity from volitional and spontaneous laughter, as well as the perceived positivity of these laughs across cultures. Dutch (n = 273) and Japanese (n = 131) participants listened to decontextualized laughter clips and judged (i) whether the laughing person was from their cultural in-group or an out-group; and (ii) whether they thought the laughter was produced spontaneously or volitionally. They also rated the positivity of each laughter clip. Using frequentist and Bayesian analyses, we show that listeners were able to infer group membership from both spontaneous and volitional laughter, and that performance was equivalent for both types of laughter. Spontaneous laughter was rated as more positive than volitional laughter across the two cultures, and in-group laughs were perceived as more positive than out-group laughs by Dutch but not Japanese listeners. Our results demonstrate that both spontaneous and volitional laughter can be used by listeners to infer laughers’ cultural group identity.
This article is part of the theme issue ‘Voice modulation: from origin and mechanism to social impact (Part II)’.
Laughter is a frequently occurring and socially potent nonverbal vocalization, which is frequently used to signal affiliation, reward or cooperative intent, and often helps to maintain and strengthen social bonds [1,2]. A key distinction is whether laughs are spontaneous or volitional [3,4]. Spontaneous and volitional laughs are thought to be generated by different vocal production mechanisms. We often laugh spontaneously with little volitional control, which is thought to typically reflect an internal emotional state. Yet laughter can also be produced with volitional modulation of vocal output, which is more likely to express polite agreement in conversation [5,6]. Recent research has shown that listeners’ ability to differentiate individual speakers is impaired for spontaneous, as compared to volitional, laughter [7,8].


By analyzing data from the global online intelligence platform BuiltWith, my colleagues and I have been exploring new ways to measure a nation’s actual digital footprint – from the bottom-up. We have developed two new experimental measures of national digital infrastructure – one focused on domestic digital infrastructure (DDI) and another that looks at a nation’s online export ambitions (DXI).
We plan to develop these further and explore how they may be used to feature in a future index of Digital Economic Investment next year.
This first measure: Digital Domestic Infrastructure (DDI), has a domestic focus and simply looks at the number of websites in each country using the top-level country domain as a simple filter for geography. We digital infrastructure consists of much more than websites and online services but that is a useful guide at a national scale into a nations investments and assets in the digital economy. We’ve also filtered for domains that are hosted by or invest in paid technologies (a data feature BuiltWith offers), so as to distinguish active websites from those that are idle or redirected – typically held by domain squatters. This also removes counts of hobby or personal websites as, while there’s an amazing array of free, open source technologies to be used in building digital services online, most commercial services now have at least one form of paid technology in their mix.

Nova Scotia sanctuary for captive whales to open 2023.
The Whale Sanctuary Project says it is not possible to release whales straight from captivity into the ocean, because they have never experienced life in the ocean.
The organisation says the sanctuary would give them “lifetime care” in a “natural setting that’s as close as possible to what they would experience in the wild”.

Facebook’s vision of the Metaverse has been criticized by both consumers & other companies for its obvious dystopian outlook. But one of the most prominent Augmented Reality Companies in the world, Niantic has shown a much better looking futuristic vision of the metaverse. One in which the real world would only get augmented instead of completely replaced like in Meta’s vision of it. Niantic’s Lightship platform and future augmented reality glasses are meant to be a look into a future where privacy and social interactions are of uttermost importance and the dystopian nightmare future wouldn’t be a big problem. Let’s see what companies such as Apple or niantic think of this.
–
TIMESTAMPS:
00:00 The unfortunate fate of the Metaverse.
02:01 What is this future going to look like?
03:59 Facebook’s Creepy Vision of the Workplace.
06:29 A possible solution by Niantic.
08:35 Last Words.
–
#facebook #meta #metaverse