Construction work is still ongoing on China’s massive Raffles City Chongqing project but its most notable feature, the “horizontal skyscraper,” has now opened to visitors. The stunning skybridge boasts a park and a glass-bottomed observation point.



Slack and Amazon announced a big integration late yesterday afternoon. As part of the deal, Slack will use Amazon Chime for its call feature, while reiterating its commitment to use AWS as its preferred cloud provider to run its infrastructure. At the same time, Amazon has agreed to offer Slack as an option for all internal communications.
“Some parts of Amazon had licensed Slack before, but this is the first time it will be offered as an option to all employees,” an Amazon spokesperson told TechCrunch.
Make no mistake, this is a big deal as the SaaS communications tool increases its ties with AWS, but this agreement could also be about slighting Microsoft and its rival Teams product by making a deal with a cloud rival. In the past, Slack CEO Stewart Butterfield has had choice words for Microsoft saying the Redmond technology giant sees his company as an “existential threat.”
Solar photovoltaic (PV) systems have a utilization (or capacity) factor of 15–20% worldwide. We propose to enhance the energy yield in a software-defined manner by complementing commodity solar PV systems with cloud-based IoT-controlled reflectors. We also propose designs for brownfield and greenfield settings in solar farms. We study a number of practical engineering issues including effect of solar azimuth, shadowing effects, ground coverage ratio (GCR) tradeoff, constraints on angular control etc. Our designs can raise solar PV energy yield between 50–100% with modest tradeoffs on operational complexity, land requirements (ground coverage ratio) etc. The software-defined IoT control allows a variety of current and future operational or business constraints to be flexibly factored in to tradeoff these factors versus economic gain (eg: levelized cost of energy, LCOE). The paper presents both simulation and experimental evidence for our system. We are actively piloting this technology with solar PV developers and engineering, procurement, construction (EPC) companies in emerging markets.

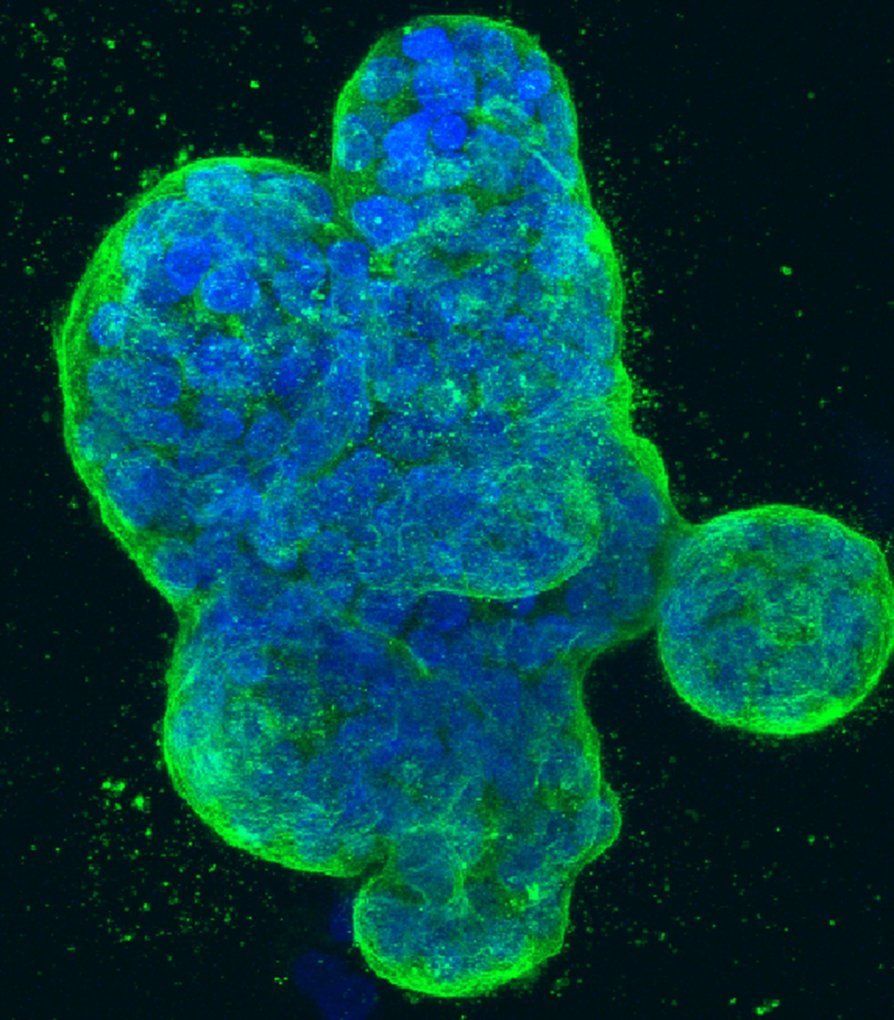
Researchers at Tulane University School of Medicine identified a gene that causes an aggressive form of breast cancer to rapidly grow. More importantly, they have also discovered a way to “turn it off” and inhibit cancer from occurring. The animal study results have been so compelling that the team is now working on FDA approval to begin clinical trials and has published details in the journal Scientific Reports.
The team led by Dr. Reza Izadpanah examined the role two genes, including one whose involvement in cancer was discovered by Tulane researchers, play in causing triple negative breast cancer (TNBC). TNBC is considered to be the most aggressive of breast cancers, with a much poorer prognosis for treatment and survival. Izadpanah’s team specifically identified an inhibitor of the TRAF3IP2 gene, which was proven to suppress the growth and spread (metastasis) of TNBC in mouse models that closely resemble humans.
In parallel studies looking at a duo of genes—TRAF3IP2 and Rab27a, which play roles in the secretion of substances that can cause tumor formation —the research teams studied what happens when they were stopped from functioning. Suppressing the expression of either gene led to a decline in both tumor growth and the spread of cancer to other organs. Izadpanah says that when Rab27a was silenced, the tumor did not grow but was still spreading a small number of cancer cells to other parts of the body. However, when the TRAF3IP2 gene was turned off, they found no spread (known as “metastasis” or “micrometastasis”) of the original tumor cells for a full year following the treatment. Even more beneficial, inhibiting the TRAF3IP2 gene not only stopped future tumor growth but caused existing tumors to shrink to undetectable levels.

Meet Gita, a mobile-carrier that follows people on the go.
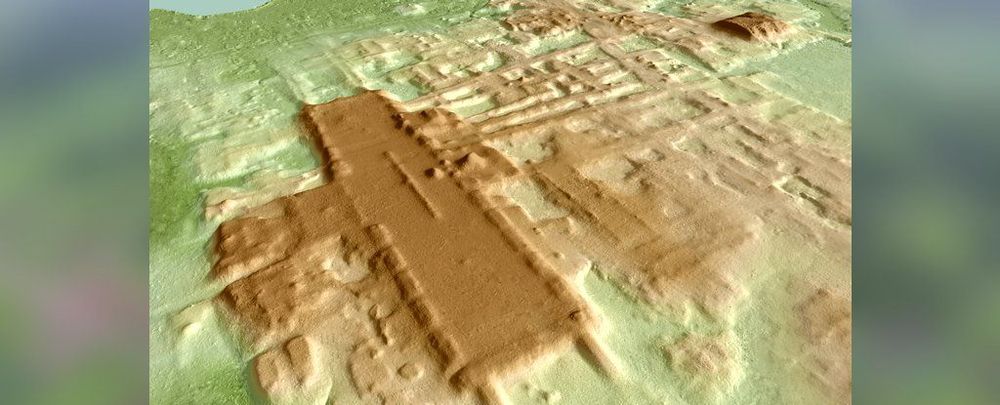


A giant, sprawling structure almost a mile long has been discovered at the southern tip of Mexico, with researchers saying it may represent the oldest and largest monument of the ancient Maya civilisation ever found.
The site, called Aguada Fénix, is located in the state of Tabasco, at the base of the Gulf of Mexico. It’s so vast for its age, the find is making archaeologists recalibrate their timelines on the architectural capabilities of the mysterious Maya.
Before now, the Maya site of Ceibal (aka Seibal) was thought to be the oldest ceremonial centre, dating back to around 950 BCE.
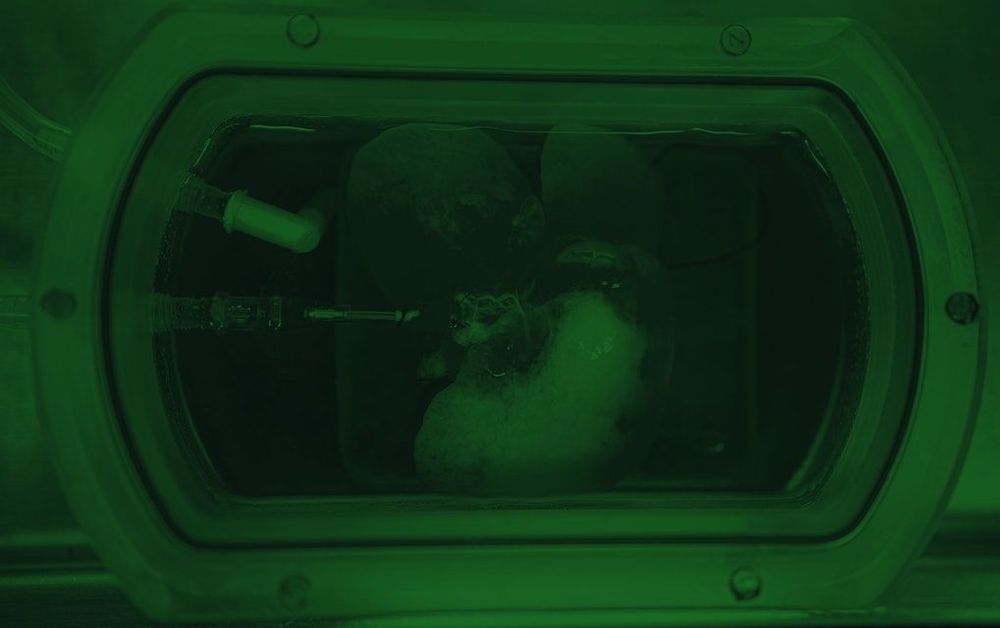

In a fascinating new study, scientists created fully-functional mini-livers out of human skin cells, then successfully transplanted them into rats.
The research is a proof-of-concept for potentially revolutionary technology and provides a glimpse of an organ donor free future.
