🌈🌈Mini air conditioning fan water cooling small fan small student portable 📣📣USB dual battery rechargeable dormitory bed office desktop📣📣 ultra-quiet electric fan cooling cooler spray humidifier❄❄
✨Get Yours Now: https://bit.ly/3fpZR4F

🌈🌈Mini air conditioning fan water cooling small fan small student portable 📣📣USB dual battery rechargeable dormitory bed office desktop📣📣 ultra-quiet electric fan cooling cooler spray humidifier❄❄
✨Get Yours Now: https://bit.ly/3fpZR4F

Army researchers developed a new way to protect and safeguard quantum information, moving quantum networks a step closer to reality.
Quantum information science is a rapidly growing interdisciplinary field exploring new ways of storing, manipulating and communicating information. Researchers want to create powerful computational capabilities using new hardware that operates on quantum physics principles.
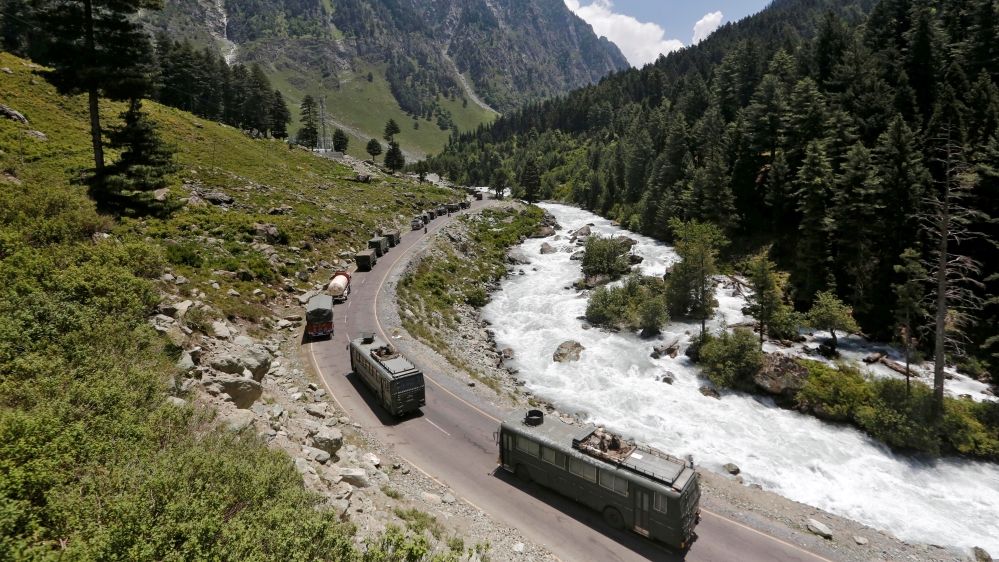
For the Army, the new quantum paradigms could potentially lead to transformational capabilities in fast, efficient and secure collecting, exchanging and processing vast amounts of information on dynamic battlefields of the future.
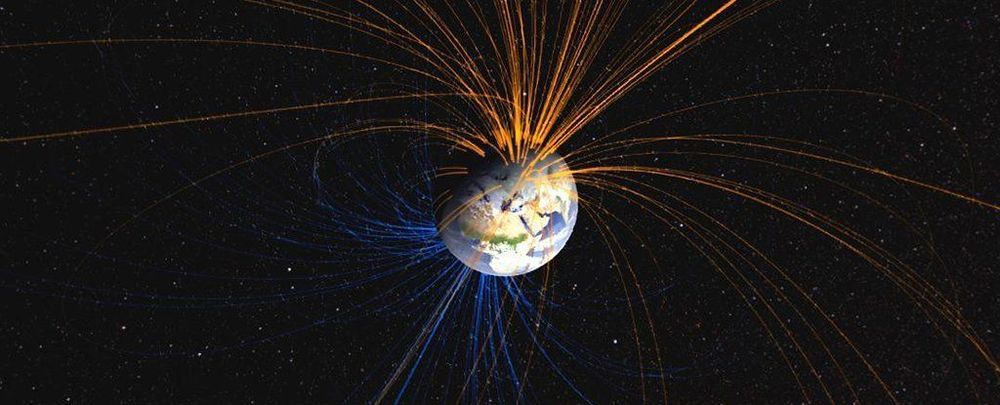
The Earth’s magnetic field flips, every few hundred thousand years or so on average, which means magnetic north becomes magnetic south and vice versa (the planet doesn’t actually turn upside down). New research suggests this change of direction can happen up to 10 times faster than previously thought.
That’s big news for scientists studying how the magnetic field shifts affect life on Earth, how our planet has evolved over time, and how we might be better able to predict the next reversal in the coming years.
Past palaeomagnetic studies have shown that the magnetic field could change direction at up to 1 degree a year, but the latest study suggests that movements of up to 10 degrees annually are possible.


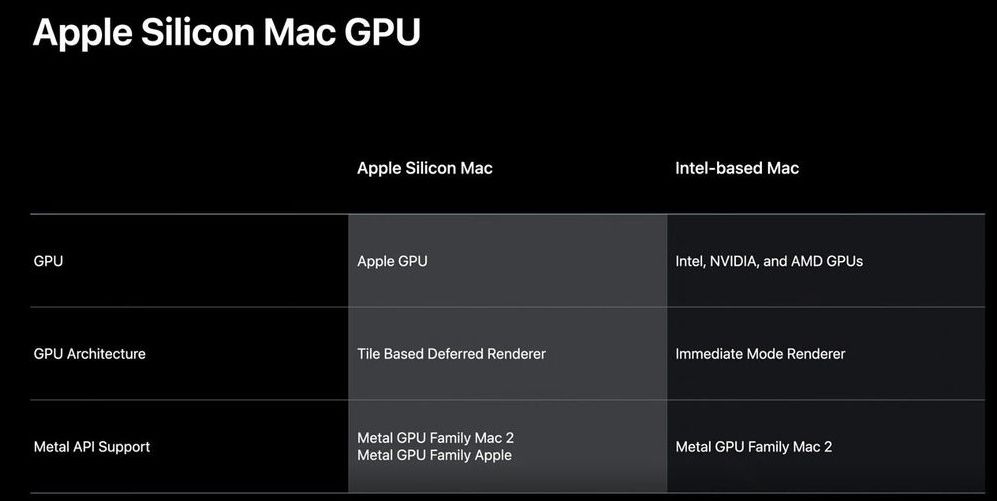
In the next big step toward complete silicon independence, Apple is planning to dump AMD as a supplier of discrete GPUs in the near future, closely following its decision to dump Intel and the x86 machine architecture in favor of its own SoCs based on the Arm machine architecture. The company is developing its own line of discrete GPUs under the “Metal GPU Family,” a name borrowed from its own Metal graphics API.
This explosive bit of information comes from a WWDC 2020 presentation slide posted by Longhorn (@never_released) on Twitter. The slide suggests that along with the processor, Apple is making a clean break with its graphics hardware. The SoCs powering client-segment Macs, such as future iMacs or MacBooks, could feature iGPUs based on this graphics architecture, while larger platforms such as MacBook Pros, Mac Pros, and iMac Pros of the future could feature Apple’s own discrete GPUs.



The decision to invest in a company can rely on a lot of guesswork, but Kim Polese, co-founder and chairman of CrowdSmart, is using artificial intelligence to turn qualitative information into quantitative data—and reduce bias along the way.
“When we’re talking about using collective intelligence, augmented collective intelligence, what we’re really talking about is using a combination of human and machine intelligence to improve the way that diligence is done,” Polese said this past Wednesday at a Barron’sInvesting in Tech panel. The founder of an artificial-intelligence platform designed to predict a company’s potential for success, Polese detailed how the CrowdSmart platform works, and how it could help remove bias from the diligence process.
The system draws on the insights of a group of 25 or more people, selected for their different levels of expertise, to evaluate prospective investments, explained Polese, who said her career in Silicon Valley began 30 years ago at the first artificial-intelligence company to go public.
