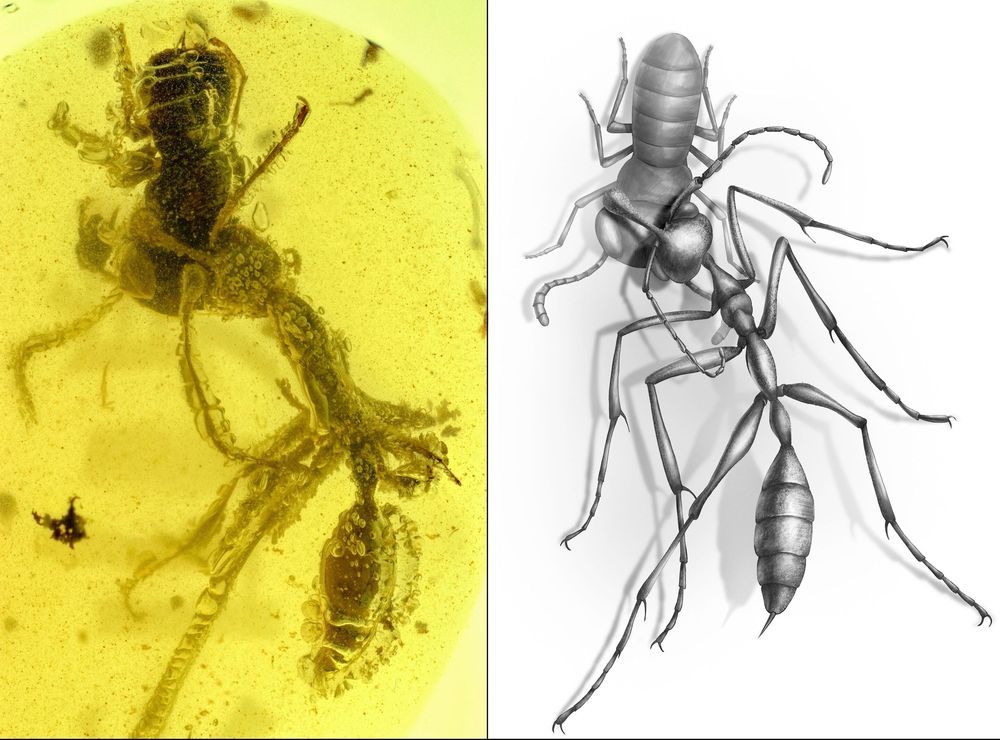
In findings published Aug. 6 in the journal Current Biology, researchers from New Jersey Institute of Technology (NJIT), Chinese Academy of Sciences and University of Rennes in France have unveiled a stunning 99-million-year-old fossil pristinely preserving an enigmatic insect predator from the Cretaceous Period—a ‘hell ant’ (haidomyrmecine)—as it embraced its unsuspecting final victim, an extinct relative of the cockroach known as Caputoraptor elegans.
The ancient encounter, locked in amber recovered from Myanmar, offers a detailed glimpse at a newly identified prehistoric ant species Ceratomyrmex ellenbergeri, and presents some of the first direct evidence showing how it and other hell ants once used their killer features—snapping their bizarre, but deadly, scythe-like mandibles in a vertical motion to pin prey against their horn-like appendages.
Researchers say the rare fossil demonstrating the hell ant’s feeding mode offers a possible evolutionary explanation for its unusual morphology and highlights a key difference between some of the earliest ant relatives and their modern counterparts, which today uniformly feature mouthparts that grasp by moving together laterally. The hell ant lineage, along with their striking predatory traits, are suspected to have vanished along with many other early ant groups during periods of ecological change around the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event 65 million years ago.