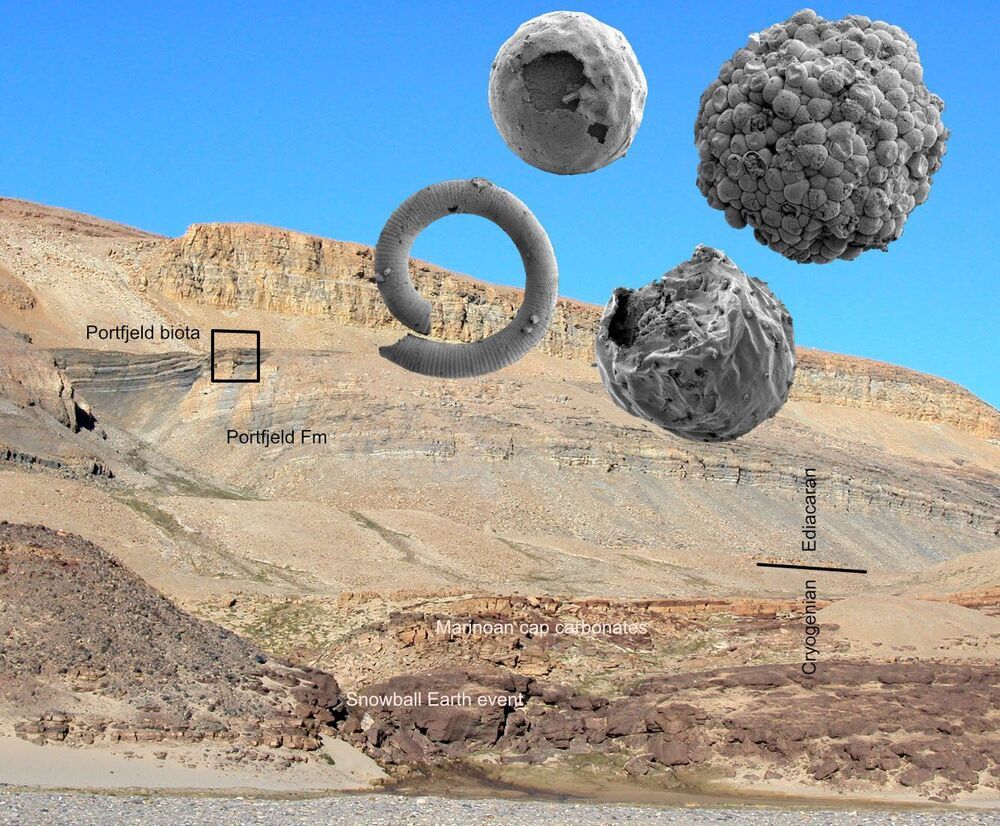
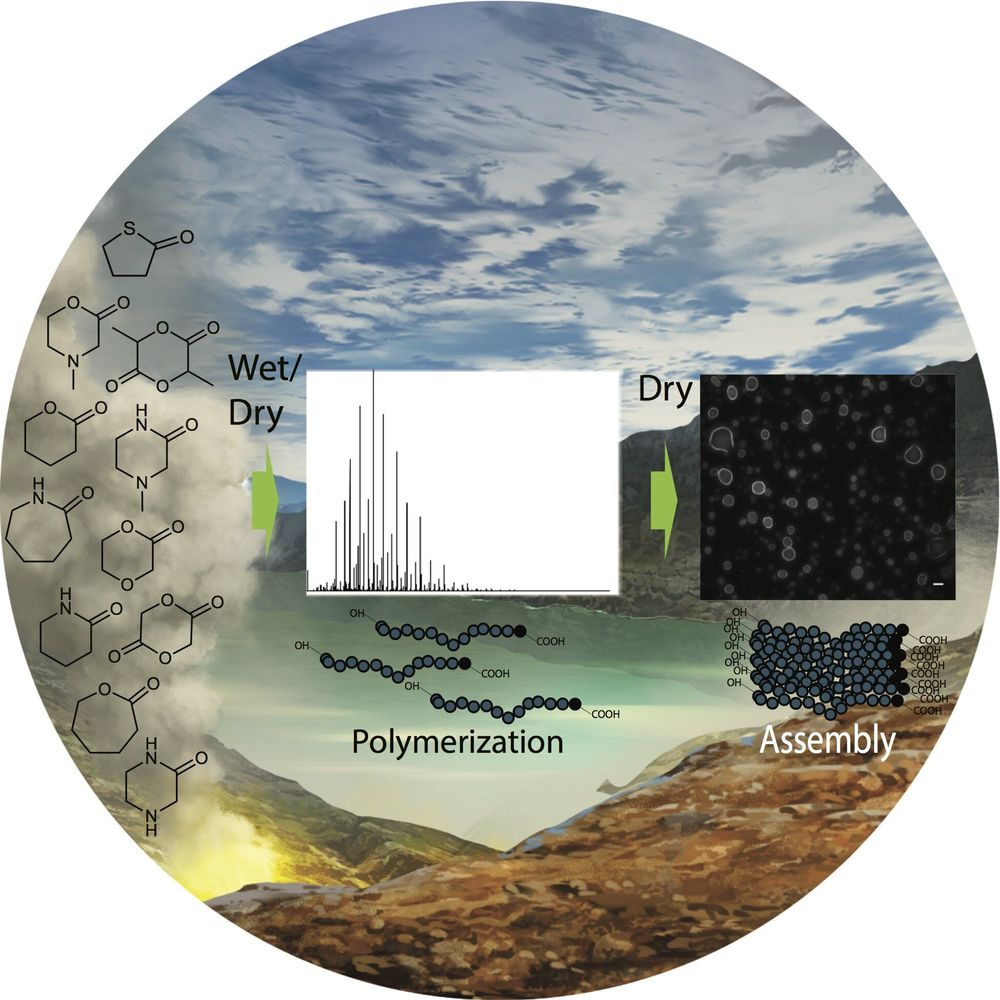
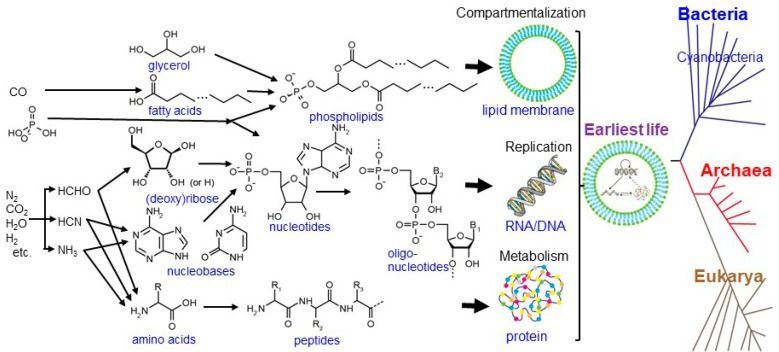
When we apprehend reality as the entirety of everything that exists including all dimensionality, all events and entities in their respective timelines, then by definition nothing exists outside of reality, not even “nothing.” It means that the first cause for reality’s existence must lie within ontological reality itself, since there is nothing outside of it. This self-causation of reality is perhaps best understood in relation to the existence of your own mind. Self-simulated reality transpires as self-evident when you relate to the notion that a phenomenal mind, which is a web of patterns, conceives a certain novel pattern and simultaneously perceives it. Furthermore, the imminent natural God of Spinoza, or Absolute Consciousness, becomes intelligible by applying a scientific tool of extrapolation to the meta-systemic phenomenon of radical emergence and treating consciousness as a primary ontological mover, the Source if you will, not a by-product of material interactions.
#OntologicalHolism #ontology #holism #cosmology #phenomenology #consciousness #mind #evolution