By Kim Thurler, Tufts University
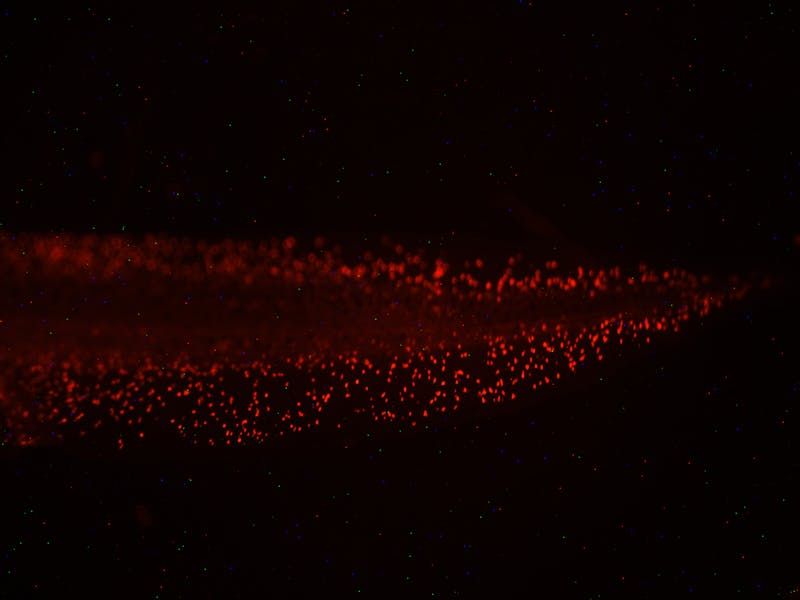
(MEDFORD/SOMERVILLE, Mass.) — Changing the natural electrical signaling that exists in cells outside the nervous system can improve resistance to life-threatening bacterial infections, according to new research from Tufts University biologists. The researchers found that administering drugs, including those already used in humans for other purposes, to make the cell interior more negatively charged strengthens tadpoles’ innate immune response to E. coli infection and injury. This reveals a novel aspect of the immune system – regulation by non-neural bioelectricity – and suggests a new approach for clinical applications in human medicine. The study is published online May 26, 2017, in npj Regenerative Medicine, a Nature Research journal.
“All cells, not just nerve cells, naturally generate and receive electrical signals. Being able to regulate such non-neural bioelectricity with the many ion channel and neurotransmitter drugs that are already human-approved gives us an amazing new toolkit to augment the immune system’s ability to resist infections,” said the paper’s corresponding author Michael Levin, Ph.D., Vannevar Bush Professor of Biology and Director of the Allen Discovery Center at Tufts and the Tufts Center for Regenerative and Developmental Biology in the School of Arts and Sciences. Levin is also an Associate Faculty member of the Wyss Institute of Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University.