Converting to electric is inevitable says the R&D Chief. 🚗
#engineering
The shift to electric transportation is imminent. Hyundai just shut down the engine division that was its pride for almost four decades.
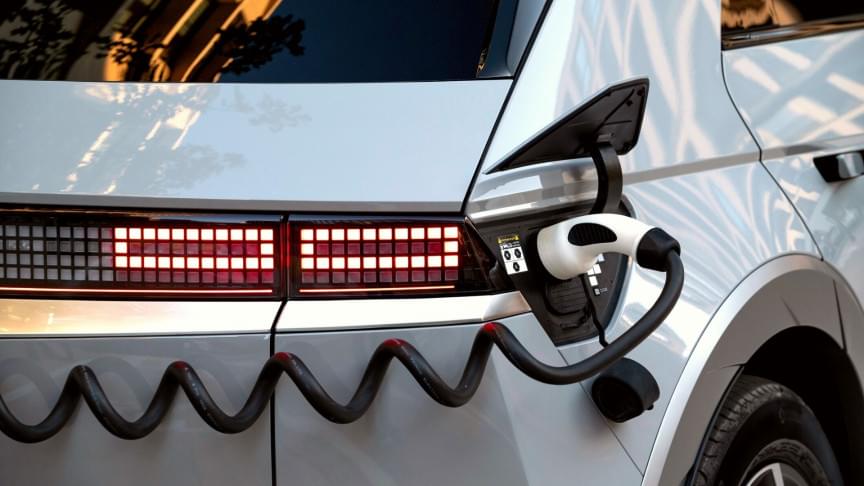


While rotating at up to 10 degrees per second!
The technological competition between the United States and China is growing at breakneck speeds.
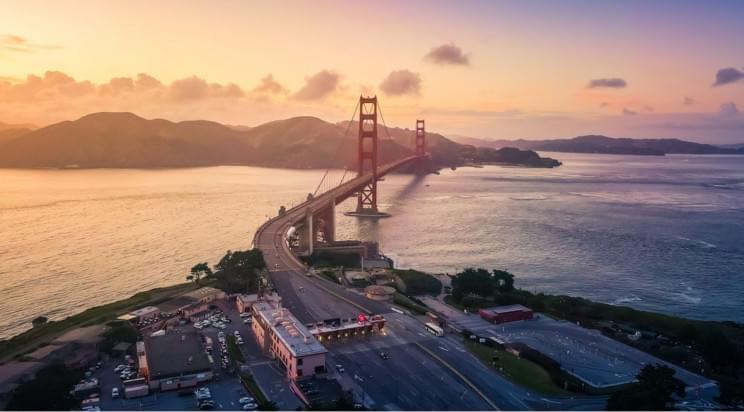
A small and relatively low-cost satellite by China can allegedly take high-resolution images of cities in mere seconds, The South China Morning Post first reported. The images are allegedly so detailed that they can be used to identify specific military vehicles and weapons.
An impressive act proving this statement was performed by Beijing-3, a small commercial satellite launched by China in June. Beijing-3 conducted an in-depth scan of the San Francisco Bay, which corresponds to roughly 1,470 sq mi (3,800 sq km), within 42 seconds, according to scientists involved in the satellite project who published the results this month in the Chinese peer-reviewed journal Spacecraft Engineering.
Full Story:
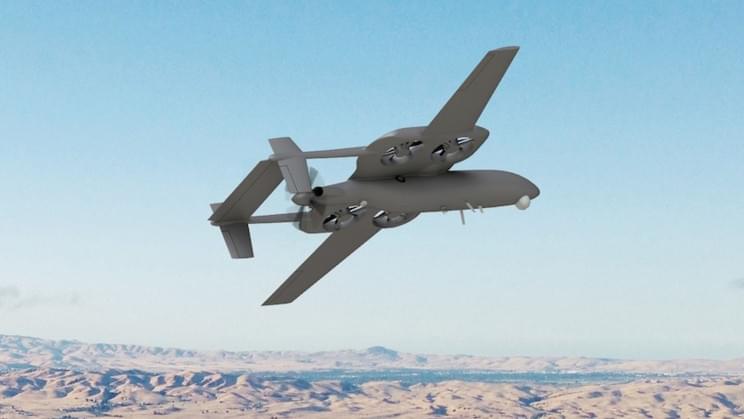

It burns about half the fuel of the same-sized rotorcraft.
In 1989, Vox conceptualized fixed-wing vertical take-off and landing airframes (VTOL), along with a plethora of sketches that looked straight out of a sci-fi movie, for a way to innovate the idea. Several prototypes and component tests later, the aircraft is in its final stages of assembly, and testing is expected to start next year.
Revolving around the concept of increasing the safety and convenience of the passenger, this hybrid aircraft can also fly three times faster than a helicopter.
“Our aircraft can travel at turboprop speeds and land on nearly any helipad in the world,” Brian Morgan, the COO and EVP of engineering at Vox, told Robb Report. “Like any helicopter, it provides the flexibility and ease of point-to-point travel, but at two to three times the speed, with more comfort and the ability to fly above the weather, all while burning about half the fuel of the same-sized rotorcraft performing the same mission,” he said.
Full Story:

Created as an analogy for Quantum Electrodynamics (QED) — which describes the interactions due to the electromagnetic force carried by photons — Quantum Chromodynamics (QCD) is the theory of physics that explains the interactions mediated by the strong force — one of the four fundamental forces of nature.
A new collection of papers published in The European Physical Journal Special Topics and edited by Diogo Boito, Instituto de Fisica de Sao Carlos, Universidade de Sao Paulo, Brazil, and Irinel Caprini, Horia Hulubei National Institute for Physics and Nuclear Engineering, Bucharest, Romania, brings together recent developments in the investigation of QCD.
The editors explain in a special introduction to the collection that due to a much stronger coupling in the strong force — carried by gluons between quarks, forming the fundamental building blocks of matter — described by QCD, than the electromagnetic force, the divergence of perturbation expansions in the mathematical descriptions of a system can have important physical consequences. The editors point out that this has become increasingly relevant with recent high-precision calculations in QCD, due to advances in the so-called higher-order loop computations.
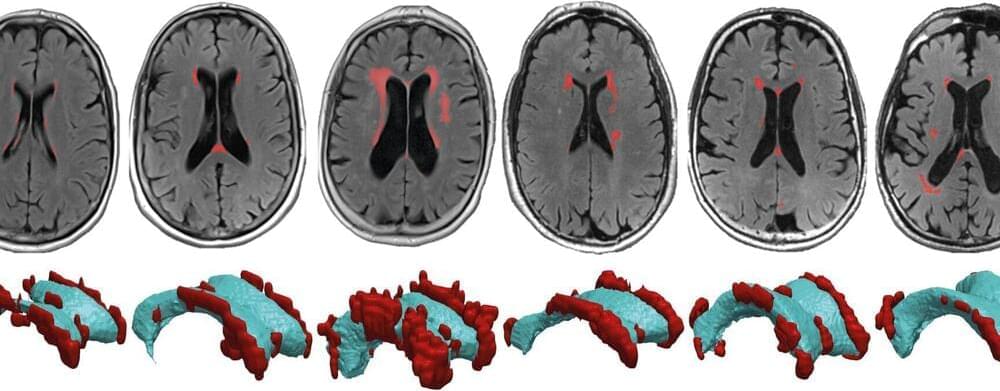
Researchers at Stevens Institute of Technology show that strain on ventricular walls explains where lesions develop in the aging brain.
As our brains age, small lesions begin to pop up in the bundles of white matter that carry messages between our neurons. The lesions can damage this white matter and lead to cognitive deficits. Now, researchers at Stevens Institute of Technology and colleagues not only provide an explanation for the location of these lesions but also how they develop in the first place.
The work, led by Johannes Weickenmeier, an assistant professor of mechanical engineering at Stevens, highlights the importance of viewing the brain as more than neural circuitry that underpins how thoughts are formed, and memories created. It’s also a physical object that’s prone to glitches and mechanical failures. “The brain is susceptible to wear and tear in vulnerable areas,” Weickenmeier said. “Especially in an aging brain, we need to look at its biomechanical properties to better understand how things can start to go wrong.”

Researchers have discovered that using a thin-film coating of copper or copper compounds on surfaces could enhance copper’s ability to inactivate or destroy the SARS-CoV-2 virus responsible for COVID-19.
In a study that began soon after the pandemic hit in March 2020, University of Waterloo engineering graduate students investigated how six different thin metal and oxide coatings interacted with HCov-229E, a coronavirus that is genetically like SARS-CoV-2 but safer to work with.
“While there was already some data out there on the lifetime of the virus on common-touch surfaces like stainless steel, plastics and copper, the lifetime of the virus on engineered coatings was less understood,” said Kevin Mussleman, the Waterloo mechanical and mechatronics engineering professor who led the study.

😀
A levitating vehicle might someday explore the moon, asteroids, and other airless planetary surfaces.
Aerospace engineers at MIT
MIT is an acronym for the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. It is a prestigious private research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts that was founded in 1861. It is organized into five Schools: architecture and planning; engineering; humanities, arts, and social sciences; management; and science. MIT’s impact includes many scientific breakthroughs and technological advances.

And it’s a hybrid mix of hydrogen and electric power.
Global mining company Anglo American is experimenting with hydrogen to power the giant mining trucks.
Mining trucks consume 35.3 gallons (134 liters) of diesel per hour with their enormous weight of around 220 metric tonnes and therefore emitting vast amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
In order to reduce the mining industry’s carbon footprint, Anglo American is focused on mining trucks.
The company is collaborating with several partners, such as Engie, NPROXX, First Mode, Williams Advanced Engineering, Ballard, ABB, Nel, and Plug Power, to develop a hybrid mining vehicle, fueled with hydrogen and electricity.
The truck will be hybrid, with a hydrogen fuel cell providing roughly half of the power and the other half by a battery pack.
The truck can also harvest regenerative energy created when driving downhill and braking, which is stored in the battery and extends the range of the vehicle.
Instead of using diesel as a source of power for the motor, hydrogen enters the fuel cell and mixes with oxygen to create water in a chemical reaction catalyzed by platinum, which generates the necessary electricity to power the motors that drive the wheels.
Full Story:

Thyme and oregano possess an anti-cancer compound that suppresses tumor development, but adding more to your tomato sauce isn’t enough to gain significant benefit. The key to unlocking the power of these plants is in amplifying the amount of the compound created or synthesizing the compound for drug development.
Researchers at Purdue University achieved the first step toward using the compound in pharmaceuticals by mapping its biosynthetic pathway, a sort of molecular recipe of the ingredients and steps needed.
“These plants contain important compounds, but the amount is very low and extraction won’t be enough,” said Natalia Dudareva, a Distinguished Professor of Biochemistry in Purdue’s College of Agriculture, who co-led the project. “By understanding how these compounds are formed, we open a path to engineering plants with higher levels of them or to synthesizing the compounds in microorganisms for medical use.