The future for hydrogen fuel? 😃
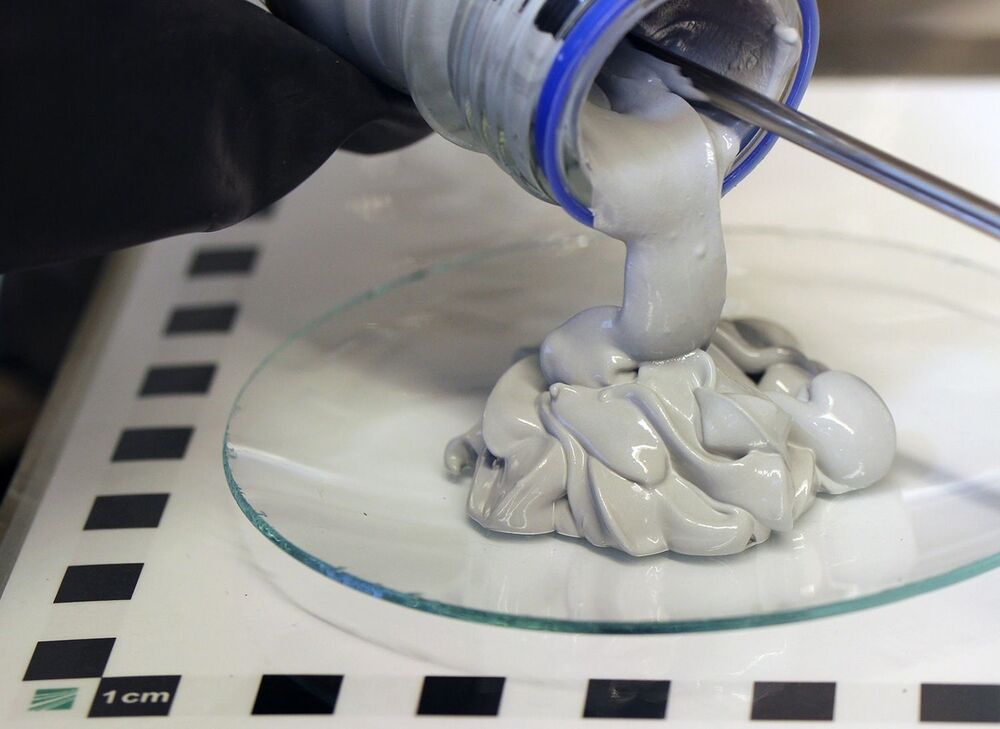
Researchers have developed a magnesium-based POWERPASTE that stores hydrogen energy at 10 times the density of a lithium battery, ideal for small vehicles.

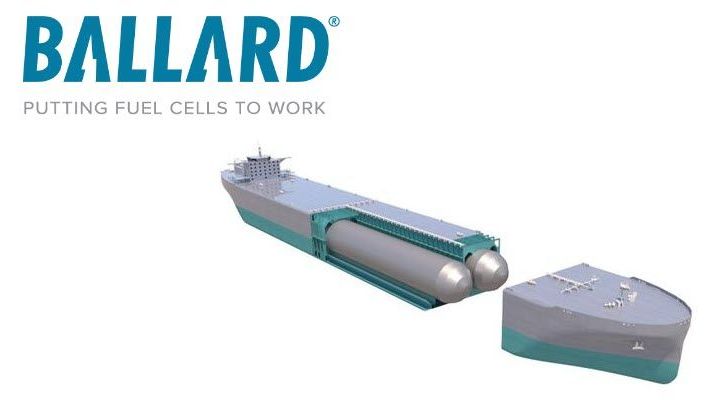
VANCOUVER, CANADA and WEST PERTH, AUSTRALIA – Ballard Power Systems (NASDAQ: BLDP; TSX: BLDP) today announced that it has signed a non-binding Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) with Global Energy Ventures (ASX: GEV; www.gev.com) – a provider of integrated compressed shipping solutions for the transportation of energy to regional markets, headquartered in Australia – for the development of a new fuel cell-powered ship, called C-H2 Ship, designed to transport compressed green hydrogen.

The power required for a small-scale demonstration of the C-H2 Ship is expected to be under 10 megawatts (MW). At full scale, the C-H2 Ship will have a propulsion power requirement of approximately 26MW, and a containment system for storage of 2000 tons of compressed green hydrogen.
GEV will be responsible for design approvals, development, financing, and operation of C-H2 Ship, along with integration of the required power system. Ballard will be responsible for design of the fuel cell system for the C-H2 Ship, based on its FCwaveTM technology, and will assist GEV with integration of the fuel cell system into the vessel’s design. Ballard’s FCwaveTM system will obtain its hydrogen fuel from the compressed green hydrogen stored onboard and transported by the vessel.

Could there be a new kind of light in the universe? Since the late 19th century, scientists have understood that, when heated, all materials emit light in a predictable spectrum of wavelengths. Research published today in Nature Scientific Reports presents a material that emits light when heated that appears to exceed the limits set by that natural law.
In 1900, Max Planck first mathematically described a pattern of radiation and ushered in the quantum era with the assumption that energy can only exist in discrete values. Just as a fireplace poker glows red hot, increasing heat causes all materials to emit more intense radiation, with the peak of the emitted spectrum shifting to shorter wavelengths as heat rises. In keeping with Planck’s Law, nothing can emit more radiation than a hypothetical object that absorbs energy perfectly, a so-called “blackbody.”
The new material discovered by Shawn Yu Lin, lead author and a professor of physics at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, defies the limits of Planck’s law, emitting a coherent light similar to that produced by lasers or LEDs, but without the costly structure needed to produce the stimulated emission of those technologies. In addition to the spectroscopy study just published in Nature Scientific Reports, Lin previously published an imaging study in IEEE Photonics Journal. Both show a spike in radiation at about 1.7 microns, which is the near-infrared portion of the electromagnetic spectrum.

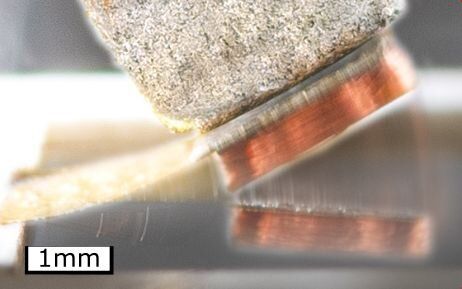
Use of waste heat contributes largely to sustainable energy supply. Scientists of Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) and Tōhoku University in Japan have now come much closer to their goal of converting waste heat into electrical power at small temperature differences. As reported in Joule, electrical power per footprint of thermomagnetic generators based on Heusler alloy films has been increased by a factor of 3.4.

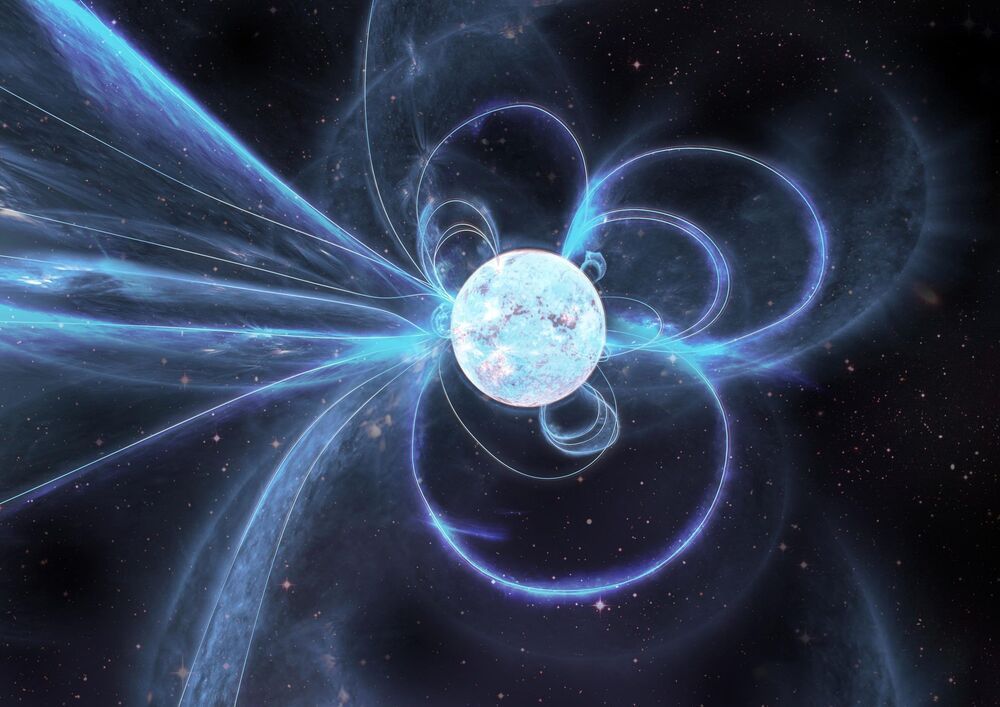
Astronomers from the ARC Centre of Excellence for Gravitational Wave Discovery (OzGrav) and CSIRO have just observed bizarre, never-seen-before behavior from a ‘radio-loud’ magnetar—a rare type of neutron star and one of the strongest magnets in the Universe.
Their new findings, published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (MNRAS), suggest magnetars have more complex magnetic fields than previously thought – which may challenge theories of how they are born and evolve over time.
Magnetars are a rare type of rotating neutron star with some of the most powerful magnetic fields in the Universe. Astronomers have detected only thirty of these objects in and around the Milky Way —most of them detected by X-ray telescopes following a high-energy outburst.


Dotty graphene and doping: Whatever it takes for Russia’s record plasmonics to shine.
Physicists from MIPT and Vladimir State University, Russia, have achieved a nearly 90% efficiency converting light energy into surface waves on graphene. They relied on a laser-like energy conversion scheme and collective resonances. The paper came out in Laser & Photonics Reviews.
Manipulating light at the nanoscale is a task crucial for being able to create ultracompact devices for optical energy conversion and storage. To localize light on such a small scale, researchers convert optical radiation into so-called surface plasmon-polaritons. These SPPs are oscillations propagating along the interface between two materials with drastically different refractive indices — specifically, a metal and a dielectric or air. Depending on the materials chosen, the degree of surface wave localization varies. It is the strongest for light localized on a material only one atomic layer thick, because such 2D materials have high refractive indices.