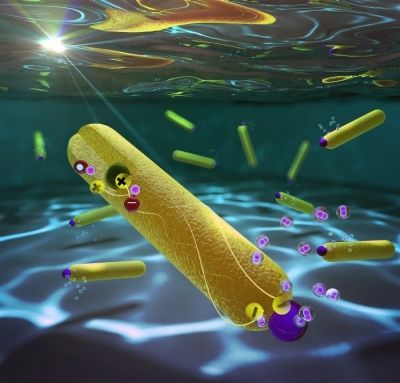
The substance that provides energy to all the cells in our bodies, Adenosine triphosphate (ATP), may also be able to power the next generation of supercomputers. The discovery opens doors to the creation of biological supercomputers that are about the size of a book. That is what an international team of researchers led by Prof. Nicolau, the Chair of the Department of Bioengineering at McGill, believe. They’ve published an article on the subject earlier this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), in which they describe a model of a biological computer that they have created that is able to process information very quickly and accurately using parallel networks in the same way that massive electronic super computers do.
Except that the model bio supercomputer they have created is a whole lot smaller than current supercomputers, uses much less energy, and uses proteins present in all living cells to function.
Doodling on the back of an envelope
“We’ve managed to create a very complex network in a very small area,” says Dan Nicolau, Sr. with a laugh. He began working on the idea with his son, Dan Jr., more than a decade ago and was then joined by colleagues from Germany, Sweden and The Netherlands, some 7 years ago. “This started as a back of an envelope idea, after too much rum I think, with drawings of what looked like small worms exploring mazes.”