The SCiO is the world’s first spectrometer that fits in a pocket, and it can measure the molecular fingerprint of just about anything you see.
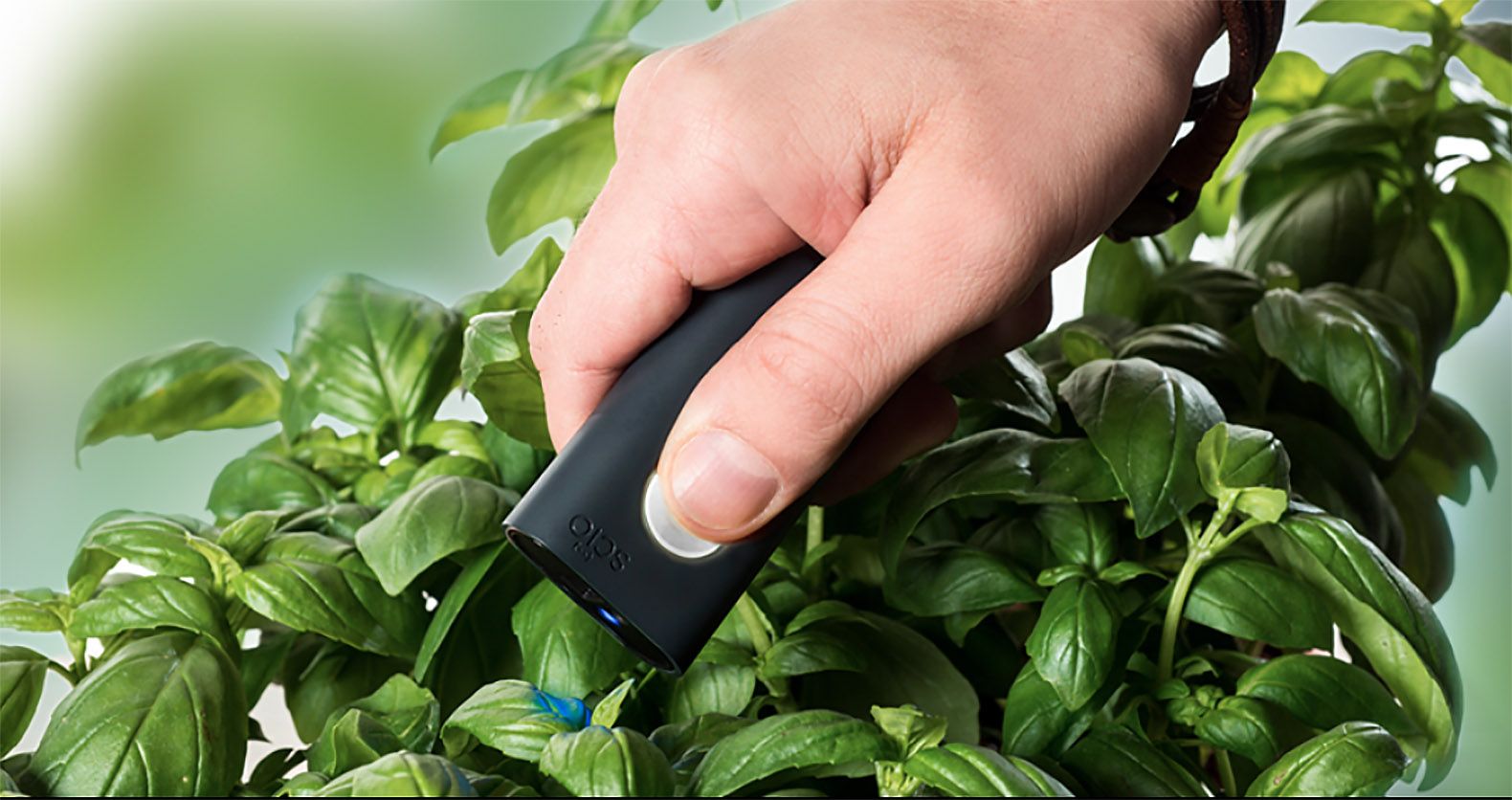


The SCiO is the world’s first spectrometer that fits in a pocket, and it can measure the molecular fingerprint of just about anything you see.

“An analysis of the history of technology shows that technological change is exponential, contrary to the common-sense “intuitive linear” view. So we won’t experience 100 years of progress in the 21st century — it will be more like 20,000 years of progress (at today’s rate). The “returns,” such as chip speed and cost-effectiveness, also increase exponentially. There’s even exponential growth in the rate of exponential growth. Within a few decades, machine intelligence will surpass human intelligence, leading to The Singularity — technological change so rapid and profound it represents a rupture in the fabric of human history. The implications include the merger of biological and nonbiological intelligence, immortal software-based humans, and ultra-high levels of intelligence that expand outward in the universe at the speed of light.” — Ray Kurzweil.
Two separate teams of researchers have found evidence for a theorized type of massless particle known as a “Weyl fermion.” The discovery was made by scientists at Princeton University in New Jersey and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, and could herald a whole new age of better electronics.
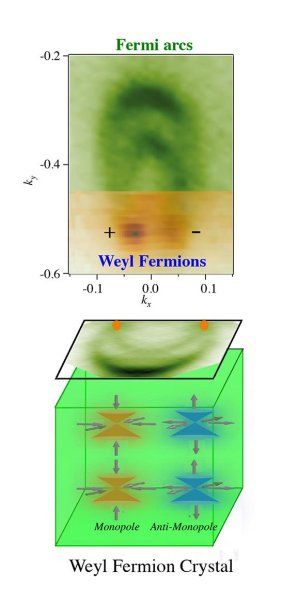
Scientists have discovered Weyl fermions, elusive massless particles theorized 85 years ago that could give rise to faster and more efficient electronics because of their unusual ability to behave as matter and antimatter inside a crystal.

#Handy New Wireless Charger Can Simultaneously Power 30 Mobile Phones at Distance.
Scientists at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) have developed an omnidirectional wireless charging technology that can charge multiple devices at once, at a distance and, crucially, at peak efficiency regardless of which way the devices are facing.
An effective wireless transmitting power of 30 watts means the device can, according to the researchers, power either 30 smartphones or five laptops simultaneously.
The results were published in last month’s issue of the journal IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, and a spinoff company is now conducting pilot studies to apply this technology in cafes and offices.
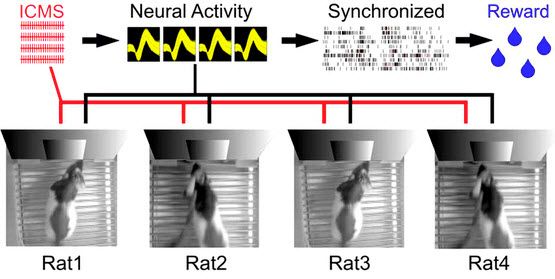
Experimental apparatus scheme for a Brainet computing device. A Brainet of four interconnected brains is shown. The arrows represent the flow of information through the Brainet. Inputs were delivered (red) as simultaneous intracortical microstimulation (ICMS) patterns (via implanted electrodes) to the somatosensory cortex of each rat. Neural activity (black) was then recorded and analyzed in real time. Rats were required to synchronize their neural activity with the other Brainet participants to receive water. (credit: Miguel Pais-Vieira et al./Scientific Reports)

In semiconductor chip research, IBM has been racking up the breakthroughs for decades. And now it says that work is paying off with the creation of the first 7-nanometer chips.
And these chips will ensure that industry progress, summarized as Moore’s Law, will continue for at least another generation. Once the chips proliferate in the market, we’ll see faster, cheaper, and better electronics products out in the marketplace, from faster computers to smarter “Internet of things” devices, or everyday objects that are smart and connected.
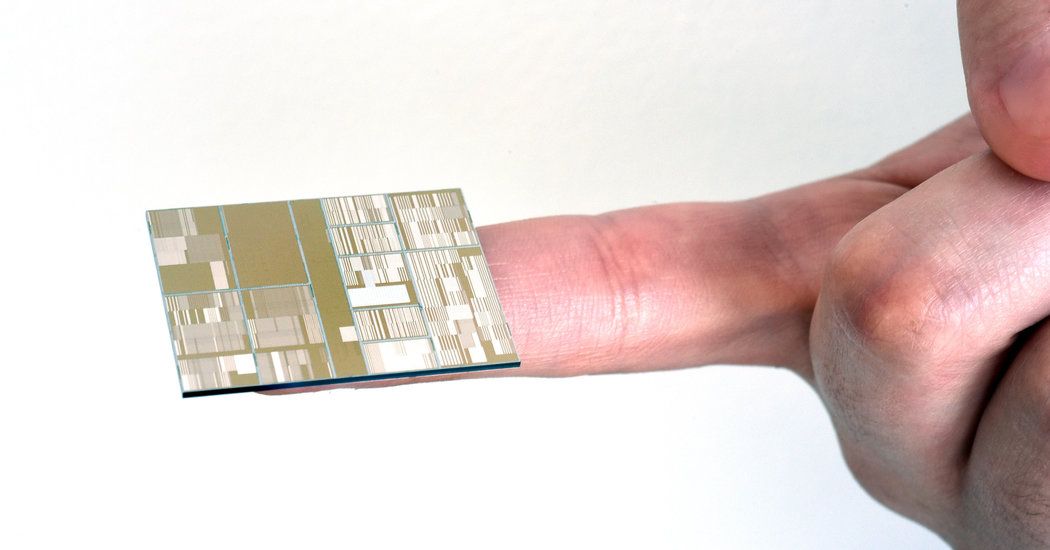
A consortium of which the company is a part has made working versions of ultradense seven-nanometer chips, capable of holding much more information than existing chips.

IBM’s newest computer chips contain seven-nanometer transistors. As points of comparison, a strand of DNA is about 2.5 nanometers in diameter and a red blood cell is roughly 7,500 nanometers in diameter.
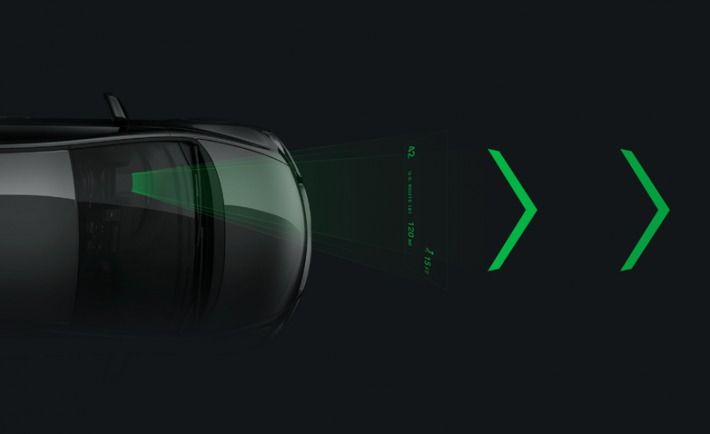

There are plenty of ways to get directions in the car, but most have one big shortcoming. Whether you’re using a standalone GPS, in-car navi system, smartphone, the Apple Watch, or even a paper map, you have to look away from the road (you know, that thing you’re supposed to be paying attention to when driving) in order to see where you’re supposed to be going.
So how to keep your eyes on the road and not get lost? One option is the heads-up display. Increasingly common on high-end cars, these devices project things like navigation directions and current speed onto the windshield, so the driver has important information right in their field of vision. Read more