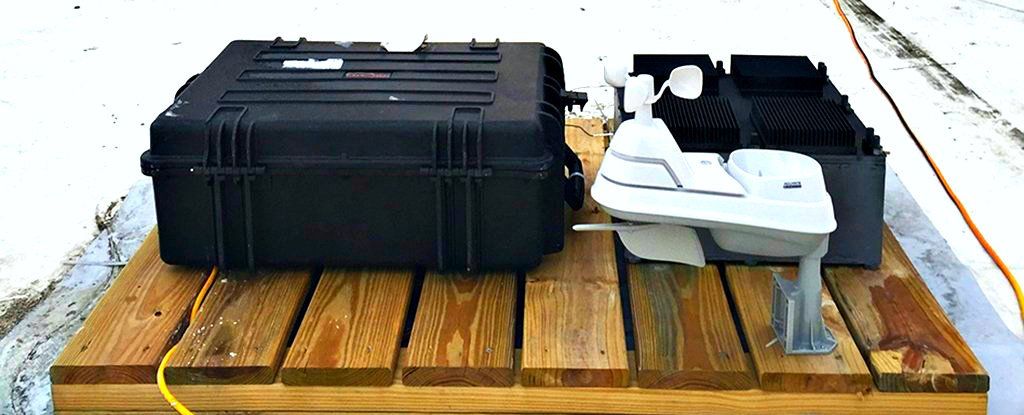
Temperature changes large and small are happening around us all the time, and scientists have come up with a machine that can convert those fluctuations into electricity, potentially powering sensors and communication devices almost out of thin air.
The energy harvesting is done through what’s called a thermal resonator: a device that captures heat on one side and radiates it over to the other. As both sides try and reach equilibrium, the energy can be caught using the process of thermoelectrics.
According to the team from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, the new thermal resonator could keep remote sensors or any off-grid devices powered up for years, just by using temperature swings – like the natural ones between night and day, for instance.