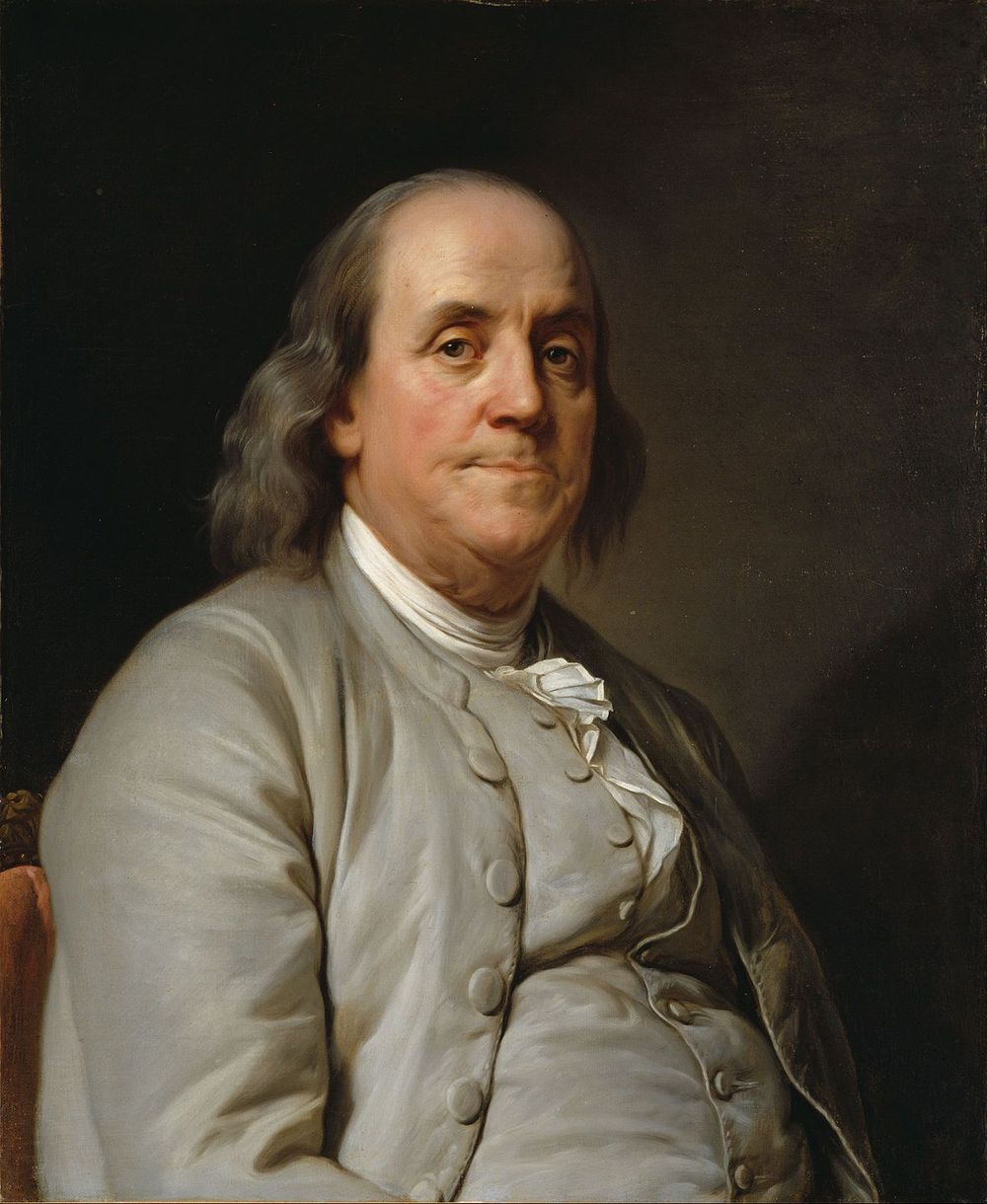
Benjamin Franklin FRS FRSA FRSE (January 17, 1706 [O.S. January 6, 1706] – April 17, 1790) was an American polymath and one of the Founding Fathers of the United States. Franklin was a leading writer, printer, political philosopher, politician, Freemason, postmaster, scientist, inventor, humorist, civic activist, statesman, and diplomat. As a scientist, he was a major figure in the American Enlightenment and the history of physics for his discoveries and theories regarding electricity. As an inventor, he is known for the lightning rod, bifocals, and the Franklin stove, among other inventions.[1] He founded many civic organizations, including the Library Company, Philadelphia’s first fire department,[2] and the University of Pennsylvania.[3]
Franklin earned the title of “The First American” for his early and indefatigable campaigning for colonial unity, initially as an author and spokesman in London for several colonies. As the first United States ambassador to France, he exemplified the emerging American nation.[4] Franklin was foundational in defining the American ethos as a marriage of the practical values of thrift, hard work, education, community spirit, self-governing institutions, and opposition to authoritarianism both political and religious, with the scientific and tolerant values of the Enlightenment. In the words of historian Henry Steele Commager, “In a Franklin could be merged the virtues of Puritanism without its defects, the illumination of the Enlightenment without its heat.”[5] To Walter Isaacson, this makes Franklin “the most accomplished American of his age and the most influential in inventing the type of society America would become.