The drone is adapted from a robot that killed off coral’s predators.
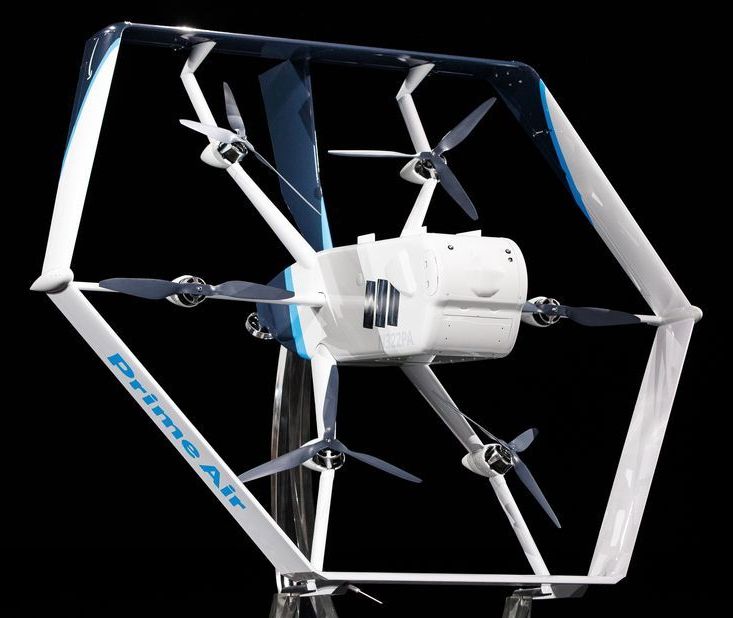
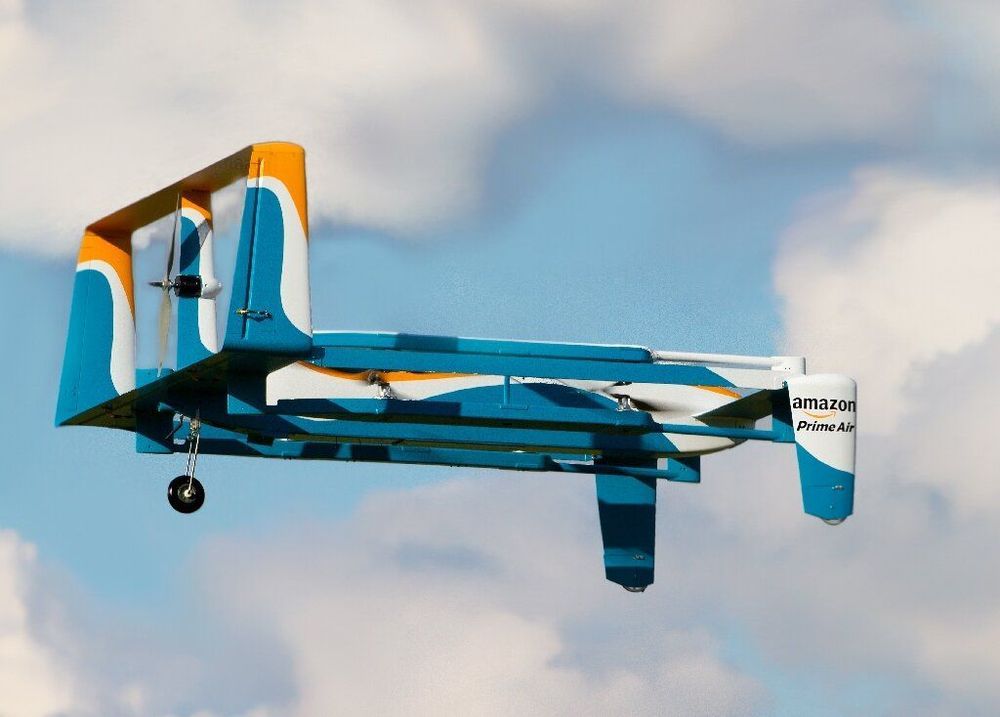




Amazon said Wednesday it expects to begin large-scale deliveries by drone in the coming months as it unveiled its newest design for its “Prime Air” fleet.
Jeff Wilke, head of Amazon’s consumer operations, told the company’s Machine Learning, Automation, Robotics and Space conference in Las Vegas that drones would play a role in ramping up efforts to shorten delivery times for many items to just one day for Amazon Prime members.
“We’ve been hard at work building fully electric drones that can fly up to 15 miles (25 kilometers) and deliver packages under five pounds (2.3 kilos) to customers in less than 30 minutes,” Wilke said in a blog post.
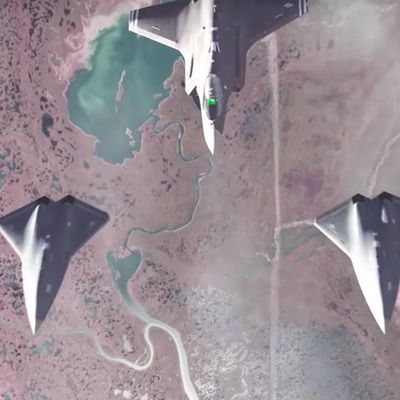

DARPA’s Air Combat Evolution program aims to find out — and so shape America’s future arsenal.
A U.S. military research program is advancing the study of humans and machines working together by testing how well pilots and artificially intelligent entities trust each other in one of the most challenging of tasks: aerial combat, or dogfighting.
The idea behind DARPAs Air Combat Evolution, or ACE, program, is that human fighter pilots will soon be flying alongside increasingly capable drones — dubbed “Loyal Wingmen” — that will help evade other fighters and air defenses. Military leaders often describe the F-35 Joint Strike Fighter as a kind of flying command center, with the human operator working less like a traditional pilot and more like a team captain. The craft is loaded with AI features that pilots say make it easier to fly than traditional fighters. That enables the pilot to digest and put to use the immense amount of data the F-35 pulls in.
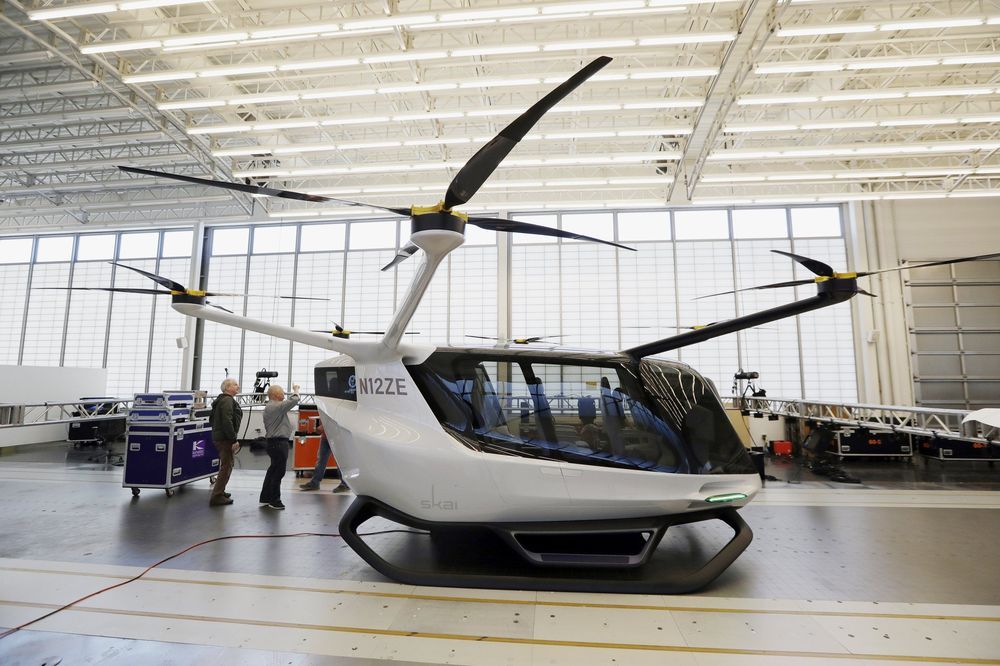

LOS ANGELES (AP) — A transportation company is betting its sleek new hydrogen-powered electric flying vehicles will someday serve as taxis, cargo carriers and ambulances of the sky, but experts say they will have to clear a number of regulatory hurdles before being approved for takeoff years in the future.
With six rotors on the roof and seats inside for five people, a passenger model of the Skai (pronounced “sky”) unveiled Wednesday near Los Angeles resembles an oversized drone crossed with a luxury SUV.
Like a drone, the vehicle from Alaka’i Technologies takes off and lands vertically. It’s one of many similar electric flying crafts in production, including prototypes from Boeing and Airbus that made successful test flights this year, according to Vertical Flight Society, an industry group.


DARPA, the Department of Defense’s research arm, is paying scientists to invent ways to instantly read soldiers’ minds using tools like genetic engineering of the human brain, nanotechnology and infrared beams. The end goal? Thought-controlled weapons, like swarms of drones that someone sends to the skies with a single thought or the ability to beam images from one brain to another.
This week, DARPA (Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency) announced that six teams will receive funding under the Next-Generation Nonsurgical Neurotechnology (N3) program. Participants are tasked with developing technology that will provide a two-way channel for rapid and seamless communication between the human brain and machines without requiring surgery.
“Imagine someone who’s operating a drone or someone who might be analyzing a lot of data,” said Jacob Robinson, an assistant professor of bioengineering at Rice University, who is leading one of the teams. [DARPA’s 10 Coolest Projects: From Humanoid Robots to Flying Cars].


What if drones and self-driving cars had the tingling “spidey senses” of Spider-Man?
They might actually detect and avoid objects better, says Andres Arrieta, an assistant professor of mechanical engineering at Purdue University, because they would process sensory information faster.
Better sensing capabilities would make it possible for drones to navigate in dangerous environments and for cars to prevent accidents caused by human error. Current state-of-the-art sensor technology doesn’t process data fast enough—but nature does.
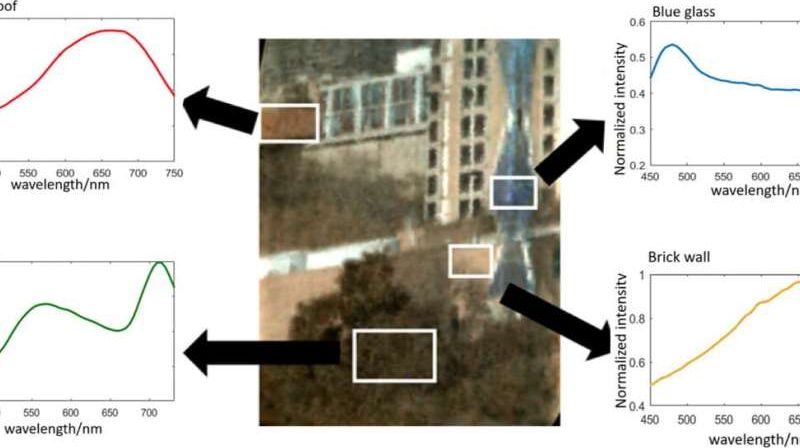
Standard snapshots from space don’t quite show Earth in all its glory. There’s so much more to see.
To reveal details impossible to observe with the naked eye, Rice University engineers are building a portable spectrometer that can be mounted on a small satellite, flown on an airplane or a drone or someday even held in the hand.
Bioengineer Tomasz Tkaczyk and his colleagues at Rice’s Brown School of Engineering and Wiess School of Natural Sciences have published the first results from a NASA-funded project to develop a small, sophisticated spectrometer with unusual versatility. Their paper appears in Optics Express.